ONLINE INQUIRY
BEAS-2B
Cat.No.: CSC-C9087W
Species: Human
Source: Bronchus
Morphology: epithelial
Cell Type: Epithelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
BEAS-2B cells are a widely utilized immortalized, non-tumorigenic human cell line, established in 1988 from a bronchial epithelial biopsy of a healthy male, lacking cancerous pathology. This cell line was immortalised by infection and cloning with the adenovirus 12-SV40 hybrid virus while maintaining the potential to differentiate into squamous tissue when exposed to serum. BEAS-2B cells also encode many lung epithelial cell markers, including cytokeratin, E-cadherin and alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). BEAS-2B cells in serum-free medium have the typical polygonal shape of respiratory epithelial cells, while those in serum-rich media become more fibroblastic at lower cell counts.
BEAS-2B cell line has been instrumental in numerous areas of research. In addition to being used as an in vitro model of lung epithelial cells to test chemical and pharmaceutical toxicology, it is also used for the analysis of lung cancer, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For viral infection, BEAS-2B cells are routinely employed to determine the infectivity and pathogenicity of respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial virus. Furthermore, as an immortalised cell line, BEAS-2B cells are very abundant and transfectible, making them ideal targets for genetic editing. Scientists use technologies like CRISPR/Cas9 gene knockout, knock-in or point mutations on BEAS-2B cells to examine the functioning of genes and the underlying pathologies. All in all, the cellular anatomy, location and function of BEAS-2B cells make them an essential tool for studies on lung tumours, viral infections, and drug metabolism.
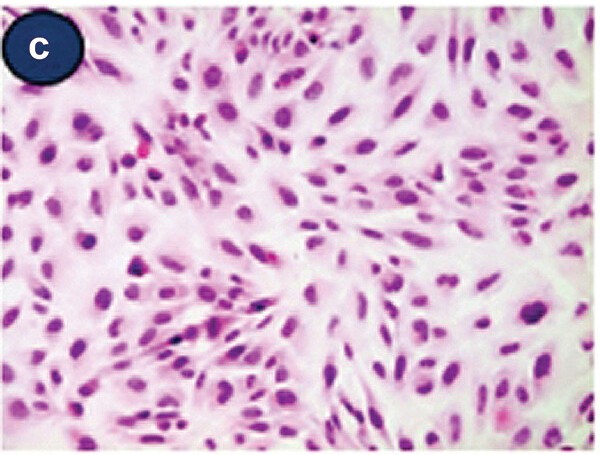 Fig. 1. Light micrographic findings of attached Beas-2B cells (H&E staining) (Lee, Y. and Ryu, Y. J., 2023).
Fig. 1. Light micrographic findings of attached Beas-2B cells (H&E staining) (Lee, Y. and Ryu, Y. J., 2023).
Cytotoxic and ROS-Inducing Effects of NH2-PS-MPs in BEAS-2B Cells
Microplastics are small, persistent particles that can enter the human body through inhalation and penetrate deep into the lungs. While a number of studies have shown their inhalation toxicity, the findings are still controversial.
Jeon's team tested the inhalation toxicity of three different-charged PS-MPs on human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) and on animals. PS-MPs were evaluated for their cytotoxic properties by WST-1 and MTT, in which BEAS-2B cells were exposed to 25–400 g/ml PS-MPs, COOH-PS-MPs, and NH2-PS-MPs for 24 hours. Only NH2-PS-MPs showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity with lower cell viability, a result consistent between the assays, especially at 200 g/ml. In addition, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was measured by oxidised DCFH-DA levels, with hydrogen peroxide as a positive control. These measurements demonstrated a dramatic rise in ROS from BEAS-2B cells exposed to NH2-PS-MPs over PS-MPs or COOH-PS-MPs, as well as an impressive surge after 24 hours under 100 and 200 g/ml NH2-PS-MPs. These findings revealed that only the positively charged PS-MPs (NH2-PS-MPs) were cytotoxic and also produced more ROS in BEAS-2B cells.
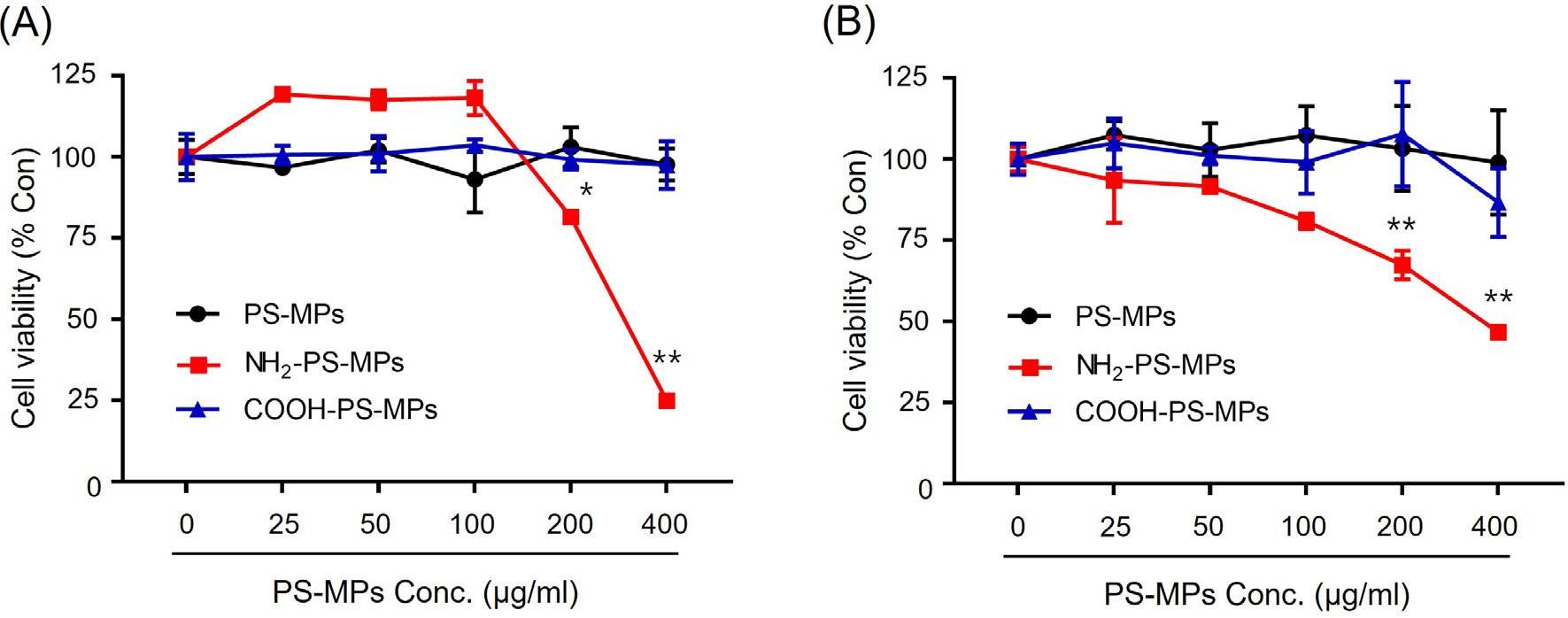 Fig. 1. Cytotoxicity of various PS-MPs were measured using (A) WST-1 assay and (B) MTT assay (Jeon, M. S., Kim, J. W., et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Cytotoxicity of various PS-MPs were measured using (A) WST-1 assay and (B) MTT assay (Jeon, M. S., Kim, J. W., et al., 2023).
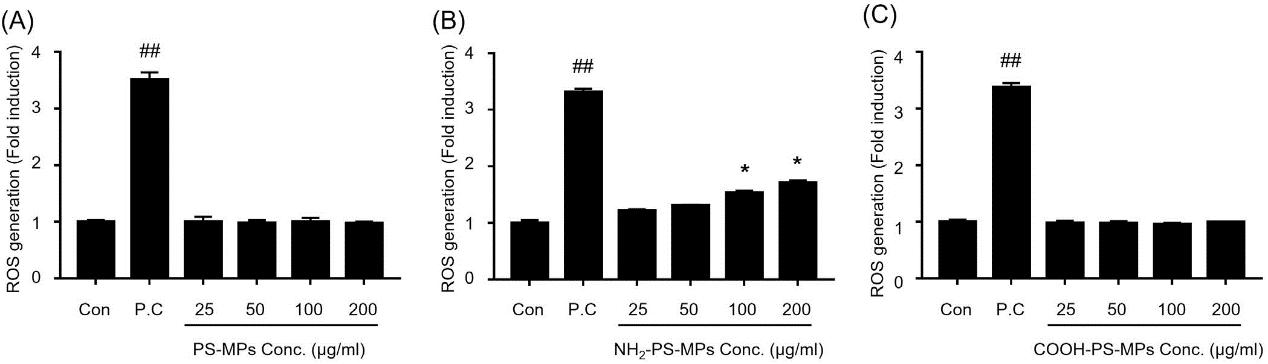 Fig. 2. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by various PS-MPs were measured using DCF-DA assay (Jeon, M. S., Kim, J. W., et al., 2023)
Fig. 2. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by various PS-MPs were measured using DCF-DA assay (Jeon, M. S., Kim, J. W., et al., 2023)
Effects Of Cadmium on Apoptosis, ROS Levels, and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in BEAS-2B
Cadmium, a harmful heavy metal pollutant from industrial activities, posing risks for diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, and emphysema. Cao's team examined cadmium's toxicity on human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Results show decreased cell viability, increased ROS, and enhanced apoptosis via mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway and MAPK signaling activation, providing insights into cadmium-induced lung disease mechanisms.
Hoechst33258 is a fluorescent marker that detects cell death. When cadmium was added to BEAS-2B cells in the following amounts (20, 40 and 60 M), hoechst33258 fluoresced brighter, and the fluorescent spots were generally more widely distributed. The fluorescence intensity of cadmium-treated samples was 4.34, 5.21 and 5.92 times that of control sample respectively. The ROS measurement showed that the fluorescence intensity of the cadmium-treated mice was 2.78, 4.20, and 4.68 times higher than that of the control; intracellular ROS increased dose-dependently as cadmium levels increased. These mitochondrial membrane potential assay results showed that cadmium treatment fluorescence was 0.83, 0.37 and 0.34 times stronger than the control (dose-dependently decreasing fluorescence intensity following cadmium treatment).
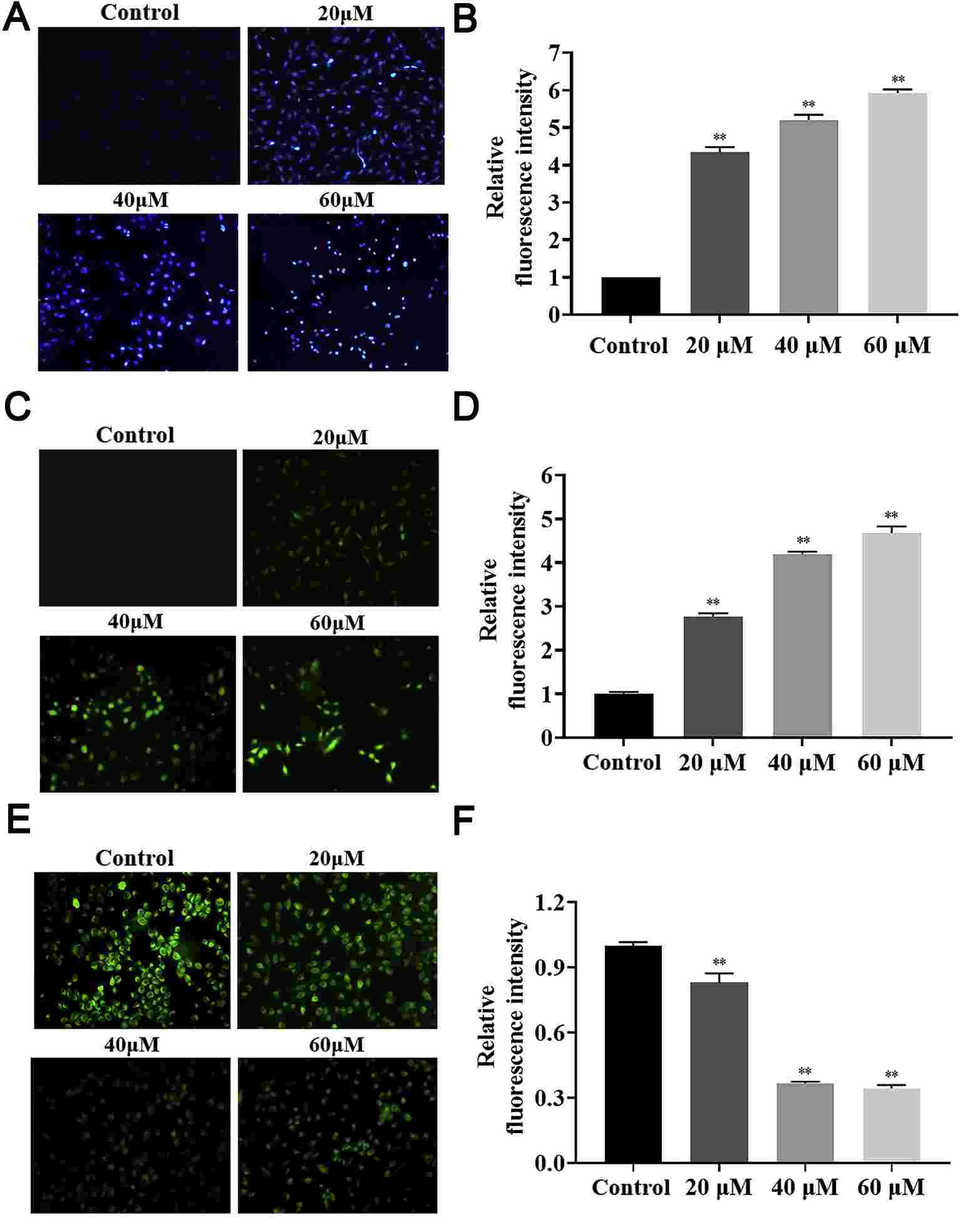 Fig. 3. The effects of cadmium on cell apoptosis (A-B) ROS levels (C-D), and mitochondrial membrane potential (E-F) of BEAS-2B cells (Cao, X., Fu, M., et al., 2021).
Fig. 3. The effects of cadmium on cell apoptosis (A-B) ROS levels (C-D), and mitochondrial membrane potential (E-F) of BEAS-2B cells (Cao, X., Fu, M., et al., 2021).
BEAS-2B is an immortalized but non-tumorigenic epithelial cell line from human bronchial epithelium. BEAS-2B cell line has been widely used as an in vitro cell model in a large variety of studies associated with respiratory diseases including lung carcinogenesis.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 5 Scientist has reviewed this product
Preferred supplier
Creative Bioarray’s professionalism and product quality make it my preferred supplier.
20 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Preferred supplier
Creative Bioarray’s professionalism and product quality make it my preferred supplier.
20 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Preferred supplier
Creative Bioarray’s professionalism and product quality make it my preferred supplier.
20 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Preferred supplier
Creative Bioarray’s professionalism and product quality make it my preferred supplier.
20 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Preferred supplier
Creative Bioarray’s professionalism and product quality make it my preferred supplier.
20 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review