- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- Drug-Drug Interaction
- Cytochrome P450 Inhibition Assay
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Cytochrome P450 Inhibition Assay
Human cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes play an essential role in drug metabolism. Even subtle changes in the activities of CYP enzymes may cause severe drug-drug interactions. Creative Bioarray aims to help our clients with evaluating the interaction potential of your compounds.
CYP450 Inhibition Assay Introduction
- Why CYP450 inhibition assay?
- Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) are a family of enzymes that play a significant role in drug metabolism.
- A common consequence of multiple medications is an increase in adverse drug events, mainly from drug-drug interactions. Most currently available drugs are metabolized by CYP450 enzymes. Interactions caused by CYP450-mediated metabolic pathways due to the sharing of multiple drugs are common, especially through reversible or irreversible CYP450 inhibition.
- The inhibition of CYPs is associated with an increase in the incidence of clinical drug-drug interactions (DDI). CYP450 inhibition data can be used to design strategies to study clinical DDI studies.
- CYP450 inhibition mechanisms
CYP450 enzymes are one of the main enzymes for drug clearance. Drugs can occupy many active sites of drug enzymes or weaken the activity of drug enzymes, slow down the metabolism of other drugs or themselves, increase blood drug concentration, and improve drug efficacy, but may enhance side effects.
Drug interactions due to drug metabolism inhibition are frequent since (1) CYP450-mediated metabolism is the primary route of elimination for a large number of drugs, and (2) multiple drugs can compete for the same CYP450 active site. Mechanisms of CYP450 inhibition can be categorized as:
- Reversible Inhibition
- Competitive
- Non-competitive
- Irreversible/quasi-irreversible (mechanism-based inhibition)
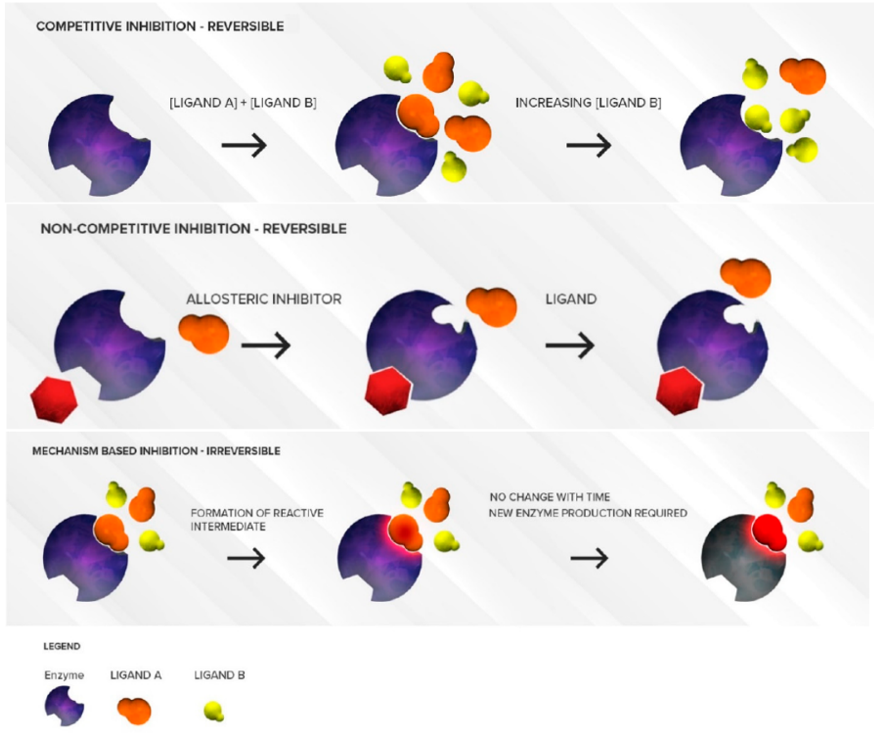 Figure 1. CYP450 inhibition mechanisms(Deodhar et al.,2020).
Figure 1. CYP450 inhibition mechanisms(Deodhar et al.,2020).
Brief Protocol
Various cytochrome P450 isoforms have been studied in the CYP450 inhibition test. The isoform-specific substrate is incubated with human liver microsomes and a series of test compound concentrations separately. At the end of the incubation, the formation of metabolites was monitored by LC-MS/MS at each test compound concentration.
The reduction in metabolite formation compared to the vehicle control is used to calculate the IC50 value (the concentration of test compound that produces 50% inhibition).
| Test Platform | Cryopreserved human hepatocytes (3 donors) |
| CYP Isoforms | CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 (other isoforms are available on request) |
| Measurement Method | LC-MS/MS |
| Data | IC50, Standard error of IC50 |
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
References
- Deodhar; et al. "Mechanisms of CYP450 Inhibition: Understanding Drug-Drug Interactions Due to Mechanism-Based Inhibition in Clinical Practice." Pharmaceutics, vol. 12, no. 9, Sept. 2020, p. 846.
- EMA. Guideline on the investigation of drug interactions (June 2012)
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

