- You are here: Home
- Services
- Cell Services
- Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Cell Angiogenesis Assays
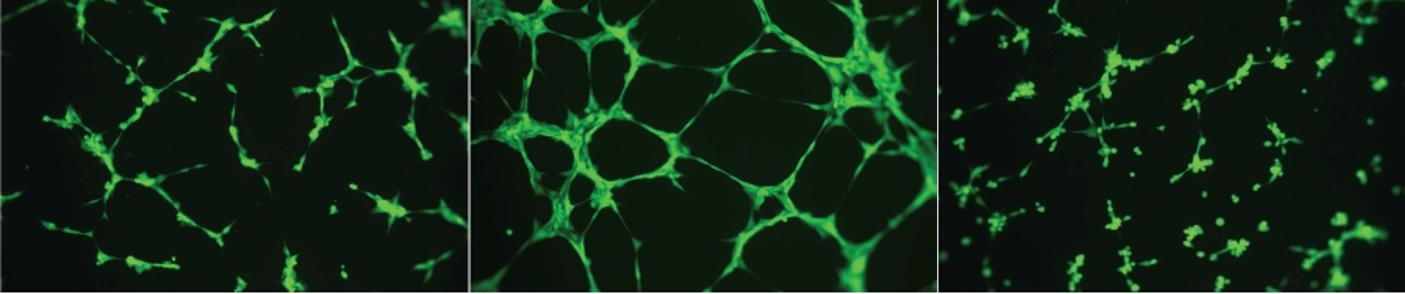
Blood vessel growth, a process known as angiogenesis, is essential for normal tissue growth, development and repair. The formation of new blood vessels is a complex process that requires a strict balance between stimulatory and inhibitory signals. Dysregulation of angiogenesis causes many pathologies such as immune, inflammatory, ischemic, and malignant disease states. Common examples of diseases caused by excessive angiogenesis include cancer, psoriasis, arthritis and even obesity. While, insufficient blood vessel growth may result in neurodegeneration, ischemia, hypertension or osteoporosis.
Angiogenesis assays are used to test efficacy of both pro- and anti-angiogenic agents. Most studies of angiogenesis inducers and inhibitors rely on various models, both in vitro and in vivo.
Creative Bioarray provides a series of in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis assays to support companies and academic laboratories in the development of angiogenic or inhibitory compounds.
HUVECs Tube Formation Assay
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) tube formation assay is one of the simple, but well-established in vitro angiogenesis assays based on the ability of ECs to form three-dimensional capillary-like tubular structure, which represents the later stage of the angiogenic process. During the assay, HUVEC cells differentiate, directionally migrate to align, branch, and form the polygonal networks of blood vessels.
Rat Aortic Ring Assay
The three-dimensional in vitro aortic ring model recapitulates the complexities of angiogenesis combining the advantages of in vitro and in vivo models. The aortic rings are cultivated in a chemically defined culture environment. Microvessels grown in this system are lumenized vessels with surrounding supporting cells, which are almost indistinguishable from the microvessels formed during angiogenesis in vivo.
Corneal Angiogenesis Assay
Continuous monitoring of angiogenesis in vivo is required for the development and evaluation of drugs acting as suppressors or stimulators of angiogenesis. The corneal angiogenesis assay is carried out by placing an angiogenesis inducer into a microcapsule molded in the cornea stroma to induce blood vessel growth from the peripheral vasculature, which is a quantitative, reproducible, flexible assessment of angiogenesis in vivo. The major advantage of this assay is that the measurement of background vessels is unnecessary because the vessels grow on a physiologically avascular tissue.
Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Angiogenesis Assay
The CAM angiogenesis assay is performed by implanting a membrane or coverslip containing the compound of interest on the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane through a hole cut in the egg shell. Subsequently, the CAM is fixed and the blood vessels are quantified by counting the number of blood vessel branch points.
Matrigel Plug Angiogenesis Assay
In the matrigel plug assay, an angiogenic stimulus (usually represented by recombinant growth factors or tumor cells) is introduced into cold liquid matrigel, following subcutaneous injection in mice, gelifies and allows the recruitment of a new microvascular network. The later immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining with the endothelial marker indicates the presence of the newly formed capillaries in the sectioned gel plugs.
Quotations and Ordering
Our customer service representatives are available 24hr a day! Thank you for choosing Creative Bioarray services!
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

