- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Anti-CD40 Antibody Induced Colitis Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Anti-CD40 Antibody Induced Colitis Model
Creative Bioarray stands at the forefront of preclinical research, providing cutting-edge models the Anti-CD40 Antibody Induced Colitis Model to propel your drug discovery initiatives forward. Partner with us to unlock the potential of your drug candidates and advance the fight against inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Critical Role of CD40 in Intestinal Inflammation
The interaction between CD40 and its ligand CD154 (CD40L) is crucial for the initiation and maintenance of T cell-mediated intestinal inflammation, a hallmark of IBD. This interaction is evident in both human IBD patients and mouse models of IBD, where CD40+ antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are found in close association with CD40L+ T cells within the inflamed intestinal tissue. By activating CD40 with an agonist antibody, the model effectively replicates this critical interaction, providing a unique platform to study the inflammatory pathways and evaluate potential therapeutic interventions.
The result of CD40 activation in this model is a robust innate immune response characterized by the upregulation of IL-23 and IL-12 mRNA in myeloid cells, increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the serum, and the development of colonic inflammation. This response closely mirrors the inflammatory environment seen in IBD, making the Anti-CD40 Induced Colitis Model an invaluable tool for understanding the disease's pathogenesis and for testing new therapeutic strategies aimed at mitigating intestinal inflammation.
Our Anti-CD40 Antibody Induced Colitis Model
Animal Species
- Mouse
Modeling Method
- SCID mice or RAG2-/- mice are injected (i.p.) with anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies to induce ulcerative colitis.
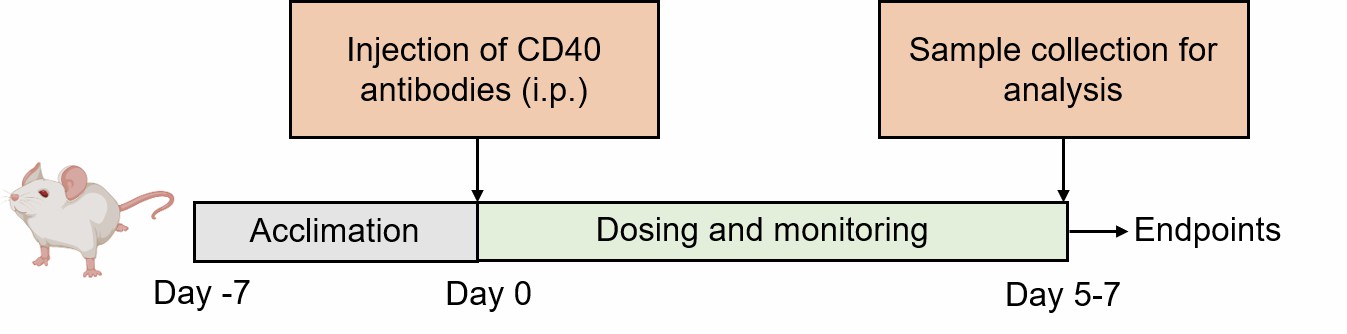 Fig. 1 Modeling method of Anti-CD40 Induced Colitis Model
Fig. 1 Modeling method of Anti-CD40 Induced Colitis Model
Endpoints
- Body weight
- DAI score
- Colon weight
- Colon length
- Cytokine analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Histology analysis
- Other customized endpoints according to your specific needs
Example Data
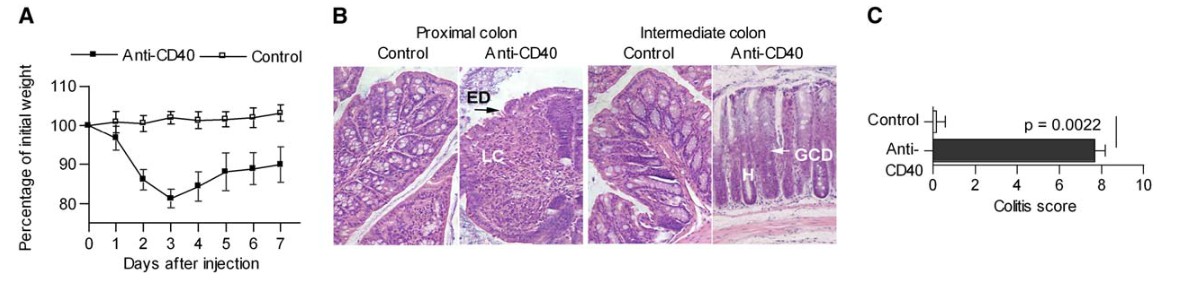 Fig. 2 Anti-CD40 Stimulation Induces Wasting Disease and Intestinal Inflammation. Rag1 KO mice received 200 mg CD40 mAb i.p. Control mice received isotype control antibodies or PBS. (A) Weight as a percentage of the initial weight at day 0. (B) H&E staining of proximal and intermediate colon. Epithelial hyperplasia (H), epithelial cell damage (ED), leucocytic cell clusters (LC) in the lamina propria, and a depletion of goblet cells (GCD) were found after CD40 stimulation. (C) Colitis score (Uhlig et al. 2006)
Fig. 2 Anti-CD40 Stimulation Induces Wasting Disease and Intestinal Inflammation. Rag1 KO mice received 200 mg CD40 mAb i.p. Control mice received isotype control antibodies or PBS. (A) Weight as a percentage of the initial weight at day 0. (B) H&E staining of proximal and intermediate colon. Epithelial hyperplasia (H), epithelial cell damage (ED), leucocytic cell clusters (LC) in the lamina propria, and a depletion of goblet cells (GCD) were found after CD40 stimulation. (C) Colitis score (Uhlig et al. 2006)
Quotation and Ordering
By leveraging our state-of-the-art facilities and deep scientific expertise, Creative Bioarray offers you a robust solution that not only accelerates your drug discovery process but also ensures the rigorous evaluation and optimization of your compounds for superior efficacy and safety. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Uhlig, H.H., et al. Differential activity of IL-12 and IL-23 in mucosal and systemic innate immune pathology. Immunity, 2006, 25(2): 309-318.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

