- You are here: Home
- Services
- Drug Toxicity Services
- In Vitro Cardiotoxicity
- QT Prolongation Assay
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
QT Prolongation Assay
Creative Bioarray provides QT prolongation assay using human embryonic stem cell derived cardiomyocyte to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of compounds with QT interval as the indicator. As the most common reason for cardiotoxicity, QT interval prolongation can serve as a direct indicator for drug cardiotoxicity.
The QT interval, a measure of time from the start of the Q wave to the end of the T wave, represents the electrical depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles. QT prolongation implies a delayed ventricular repolarization which may cause ventricular tachyarrhythmias and possibly sudden cardiac death. Among all drug safety issues, QT prolongation is one of the leading causes of therapeutic drug failures during preclinical development.

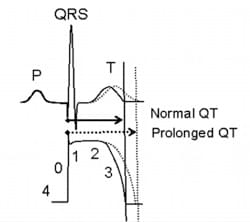
While most of the drugs that leads to prolonged QT interval by inhibiting hERG channel can be ruled out by hERG safety assay, not all hERG inhibitors cause QT prolongation, and not all QT prolongation are caused by hERG inhibition. Therefore, it’s necessary to assess the effects of a drug candidate on QT interval directly using cardiomyocytes which express all kinds of ion channels, especially for promising drug candidates that exhibits hERG channel inhibiting activity. In 2005, an in vivo QT prolongation assay is regulated in ICH S7B. However, the activity of animal cardiac cells and that of human cardiomyocytes are rather different. Results obtained in animal assays cannot be simply applied to human.
Here Creative Bioarray is offering an in vitro QT prolongation assay using human cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic, adult and iPS cells. We use an approach of single cell electrophysiology and microelectrode array (MEA) in a multi-well plate as a model for electrophysiological drug screening.
Highlights:
- Better predictivity: Uses human cardiomyocytes
- High sensitivity: Use select rophysiology method
- Multiple channels: Evaluates the combined effect of test drug on all ion channels
Creative Bioarray is dedicated to providing fast and integrated services of the highest quality to accelerate the drug discovery and development process. We are able to provide a wide range of toxicity assays and customized assays to meet the need of our clients. If you have any special requirements or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us to get support from our experienced experts. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References:
- Kannankeril P, Roden D M, Darbar D. Drug-induced long QT syndrome[J]. Pharmacological reviews, 2010, 62(4): 760-781.
- Food, U. S. "Drug Administration (2005). Guidance for industry: ICH S7B nonclinical evaluation of the potential for delayed ventricular repolarization (QT interval prolongation) by human pharmaceuticals." Federal Register 70: 61133-61134.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

