Caco-2 Permeability Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
At Creative Bioarray, our Caco-2 Permeability Assay is an important tool in drug discovery as it provides a powerful in vitro model to assess oral drug absorption across the human gut barrier. The transport rates of compounds in the monolayer can be precisely measured with our Caco-2 test and this gives a picture of their potential to be absorbed in vivo. By also incorporating transporter inhibitors, we provide a deeper understanding of drug permeability and efflux.
Creative Bioarray's Caco-2 Permeability Assay delivers high-quality, reproducible data and is designed for high-throughput screening using multi-well culture plates. We also provide IND-enabling Caco-2 permeability assay that complies with FDA guidelines, ensuring the delivery of reliable, consistent results. This service streamlines the drug development process and facilitates efficient and informed decision-making.
Advantages of Caco-2 Permeability Assay:
- Predictive Capability: Highly correlated with human intestinal uptake to predict in vitro drug behavior in vivo.
- Versatility: Great for studying passive diffusion as well as active transportation, drug efflux etc.
- Structured Monolayer Formation: Realistic mimic of intestinal epithelial cells with tight junctions and a brush border.
- Regulatory Compliance: The gold standard in oral drug absorption studies by many regulatory authorities, such as FDA and EMA.
- Comprehensive Transport Analysis: Allows for bidirectional transport measurement for efflux ratios and active transport.
- Integration with Inhibitors: Integrates with inhibitors of interest to investigate transport proteins such as P-glycoprotein and BCRP.
Basic Procedure
1
Cell Culture
2
Monolayer Integrity Assessment
3
Compound Application
4
Data Analysis
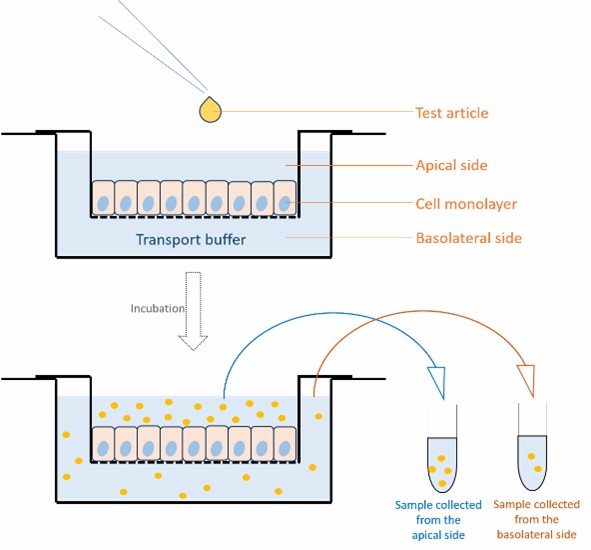
Cells culture stage
Caco-2 cells are cultured on semi-permeable inserts to create apical and basolateral compartments that mimic the intestinal barrier. Over approximately 21 days, these cells differentiate to form a monolayer with enterocyte-like characteristics, including transporter proteins and tight junctions. The process involves initial expansion in flasks, followed by seeding on Transwell supports to ensure a robust cell layer for accurate permeability testing.
Assessment of Caco2 cell monolayer integrity
Before incubation, it is necessary to check the barrier integrity of Caco-2 cells, which is typically assessed using Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) or Lucifer Yellow Rejection Assay (%LY Leakage).
Test compound permeability assay protocol
| Test Article Concentration | 2 μM |
| Number of Replicates | 2 |
| Incubation Time | 120 min |
| Buffer Type | HBSS (Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution) |
| Temperature | 37° C |
| Permeability options | Uni-directional: A->B or B->A, Bi-directional: A->B and B->A, + / – inhibitor |
| Integrity Marker | Lucifer Yellow |
| Control Compounds | With and without Pgp inhibitor; Atenolol, Propanolol, Digoxin |
| Analysis Method | LC-MS/MS |
| Readout | Papp (apparent permeability coefficient), Efflux ratio (for bi-directional assay only) % Recovery |
| Test Article Requirements | Dry compound (~2 mg or 2 μmol) or 100 µL of 10 mM DMSO solution. Brutto formulas are required. |
Data analysis:
Papp = (dQ/dt) × (1/C0) × (1/A)
Efflux ratio = Papp [B → A] / Papp [A → B]
% Recovery = 100 x [(Vr x Cr) + (Vd x Cd)] / (Vd x C0).
where:
dQ/dt: the permeability rate.
A: the surface area of the cell monolayer.
C0: the initial concentration in the donor compartment.
Vr: the solution volume in the receiver chamber.
Vd: the volume in the donor chambers.
Cd and Cr: the final concentrations of transport compound in donor and receiver chambers, respectively
By examining the efflux ratios with and without a Pgp inhibitor, it can determine if a test compound acts as a Pgp substrate. A compound is identified as a Pgp substrate if its efflux ratio exceeds 2.0 without the inhibitor and decreases significantly to ≤ 1.0 when the inhibitor is present.
In vivo Absorption extrapolation
| Papp values of in vitro | Predicted range of in vivo absorption |
| Papp ≤ 0.60 x 10-6 cm/s | Low (0-20%) |
| 0.60 x 10-6 cm/s < Papp < 6.0 x 10-6 cm/s | Medium (20-70%) |
| Papp ≥ 6.0 x 10-6 cm/s | High (70-100%) |
Key Features and Advantages of Our Caco-2 Permeability Assay
Standardization and Reliability
We employ a well-validated Caco-2 cell model, ensuring consistent and dependable results across various studies.

Cost-Efficiency
The Caco-2 model is both time-efficient and economical, requiring smaller quantities of compounds for effective permeability analysis.
Precision Testing Platform
Our use of cutting-edge cell culture techniques and high-throughput detection systems guarantees precise and reproducible outcomes.
Rapid Response and Effective Communication
Enjoy personalized customer service with regular updates on your project’s progress, ensuring clarity and confidence in our collaboration.

High-Throughput Screening Capability
Our service supports high-throughput screening, allowing simultaneous assessment of permeability characteristics for multiple compounds, streamlining your research pipeline.
Quotation and Ordering
Additionally, we also offer provide MDCK-MDR1 permeability and Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA) to meet your comprehensive needs. If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
FAQ
1. How to ensure the integrity of the Caco-2 cell monolayer?
Maintaining the integrity of the monolayer of Caco-2 cells is essential to the success of the experiment. This is typically checked before the experiment by measuring the Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER). The TEER values should be typically between 300-500 cm2 to ensure monolayer integrity. Less than this range can lead to pores or damage in the monolayer which will yield unreliable data. Passive diffusion of Lucifer Yellow is usually performed to validate monolayer integrity.
2. What are the common challenges in interpreting the assay data?
The most common challenge is low recovery, which can be tackled by addressing compound stability, sample handling, and assay conditions. Ensure the compound is stable in assay conditions and use proper storage to prevent degradation. Optimize sample handling by using low-binding materials to reduce non-specific adsorption. Verify the integrity of the Caco-2 cell monolayer and consider using more sensitive detection methods if needed. Additionally, evaluate potential efflux transporter activity and enzymatic metabolism, which could affect compound recovery. By focusing on these areas, we can enhance the reliability of your assay results.
3. How to assess if a compound is effluxed by active transporters?
Caco-2 cells express various transporters, such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP), which can affect compound permeability. To evaluate if a compound is actively effluxed by these transporters, inhibitors such as Verapamil for P-gp or Fumitremorgin for BCRP can be added to the assay. If permeability increases significantly with inhibitors, the compound is likely being effluxed. Additionally, by measuring transport from apical (AP) to basolateral (BL) and vice versa, the efflux ratio (ER = Papp_BL-AP / Papp_AP-BL) can be calculated. An ER greater than 2 usually indicates active efflux.
4. What is the difference between PAMPA and Caco-2 permeability assays?
PAMPA (Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay) employs synthetic membranes (usually lecithin) to mimic passive diffusion. It is simple and inexpensive, useful for high-throughput screening, but it cannot mimic active transport or efflux.
The Caco-2 cell model is made from human colon cancer cells arranged monolayer-like in vitro, mimicking the physiological features of intestinal epithelial cells. This model can simulate passive diffusion, active transport, and efflux to better capture human absorption and excretion.
Explore Other Options

