- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vivo DMPK Services
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
Bioavailability (BA) is the extent and rate to which the active drug ingredient or active moiety from the drug product is absorbed and becomes available at the site of drug action. Assessing BA early in the drug discovery process reduces attrition rates and guides subsequent drug development processes. As a critical indicator of drug absorption, BA is determined by comparing the pharmacokinetic (PK) measurements of the drug target in the systemic system following extravascular dosing or intravenous dosing.
Bioequivalence (BE) studies are often carried out between two drugs or drug formulations to compare their bioavailability (BA). BE is achieved when similar BAs are attained after administering the test and reference drugs/formulations at the same molar dose under similar conditions in an appropriately designed study. Therefore, BE is an essential component in demonstrating therapeutic equivalence and is a prerequisite to the approval of generic drug products or new drug formulations.
Creative Bioarray provides professional pharmacokinetic testing services to help customers determine the bioavailability and bioequivalence of drugs.
Animal species
- Rodents
- Non-rodents
Mice, Rats, Guinea pigs
Dogs, Minipigs, Non-human primates
Study Design
Bioavailability
The study is typically divided into different groups based on the selected dosing methods, with the most widely used intravenous (iv) injection and oral administration (po). A standard study investigating the oral BA of a drug compound in rats is as follows.
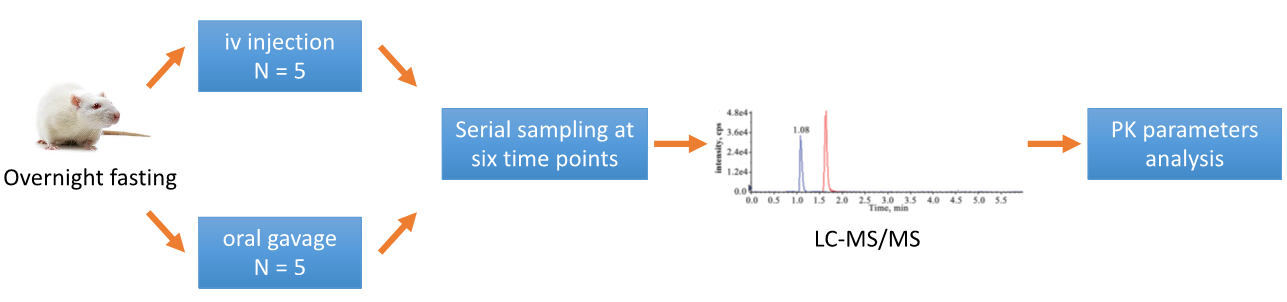 Figure 1. Standard study investigation of oral BA of a drug.
Figure 1. Standard study investigation of oral BA of a drug.
Bioequivalence
A conventional BE study design is a single-dose, two-treatment, crossover, in vivo experiment with pharmacokinetic (PK) endpoints. A typical BE study investigating the oral BE of two drug formulations in rats is as follows.
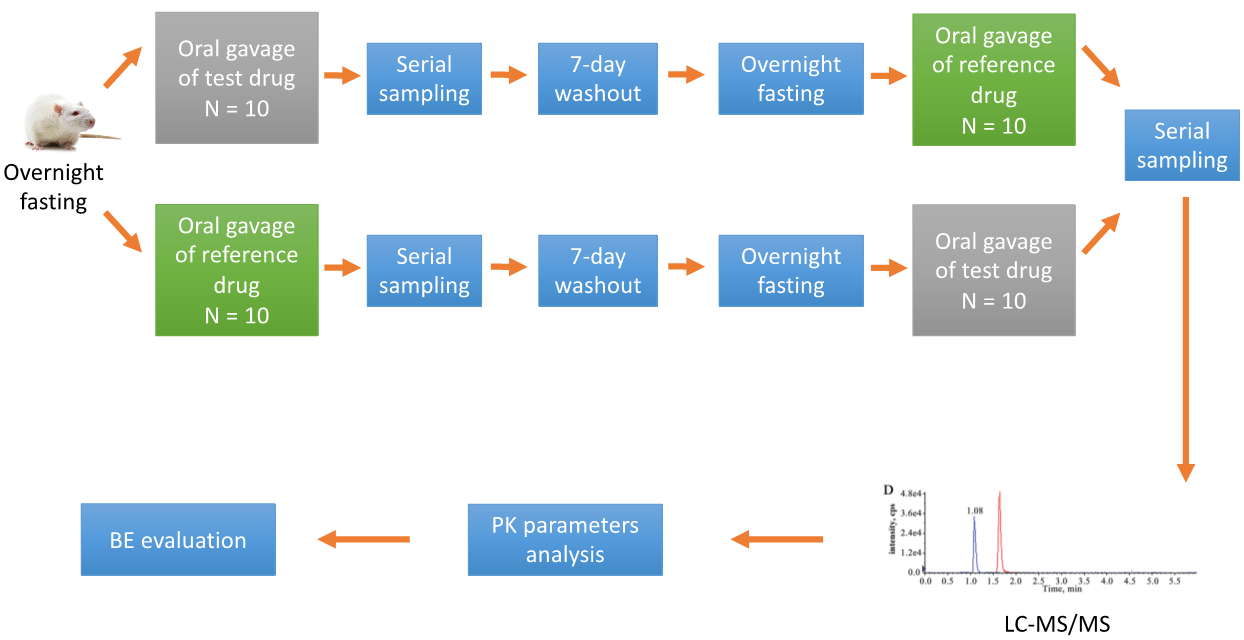 Figure 2. Standard study investigation of the oral BE of two drug formulations.
Figure 2. Standard study investigation of the oral BE of two drug formulations.
According to different research purposes, our experimental design can be adjusted in the following aspects, such as
- Additional animals
- Custom timepoints
- Parallel non-crossover designs
- Higher-order crossover designs
- Fed/food effects
- Sample size calculation
Drug dosing routes
- Default: oral administration (po)
- Others: intravenous (iv), intraperitoneal (ip), intramuscular (im), and subcutaneous (sc) injections, iv cannulation
Drug dosage
While a single dose for each drug/formulation is usually given to each animal, other drug dosing methods can be included to accommodate your specific needs.
- Additional dosage groups
- Vehicle dosing
- Repeated dosage after washout in the same animal
- Multiple-dose studies for studying steady-state exposure
- Sample collection
- Serial sampling
- Terminal blood sampling
- Additional or custom time points to cover the exposure period of test compound
- Tissues or biological fluids collection for tissue distribution analysis
Endpoints
LC-MS/MS measures the concentrations of test compounds in plasma to generate a concentration-time profile for each dosing group, based on PK parameters—including Cmax, Tmax, AUC0-t, AUC∞, BA, Ke, t1/2, C0, Vd, and CL—are calculated using non-compartmental analysis.
BE evaluation is then performed after logarithmic transformations of the PK parameters (Cmax, AUC0-t, AUC∞). For each PK parameter, BE is assessed by calculating standard 90% confidence intervals (CIs) of the geometric mean ratios between the test and reference drugs/formulations. Average BE is claimed if 90% CIs for these parameters fall within 80 ± 125% (log 0.8–1.25).
Quotation and Ordering
As with all of our in vivo services, we ensure to keep in contact during studies. If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us to support our experienced experts. We look forward to working with you in the future.
Reference
- FDA Guidance for Industry. Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites. (March 2020)
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

