- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Radiation-Induced Lung Injury (RILI) Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Radiation-Induced Lung Injury (RILI) Model
Creative Bioarray offers in vivo pharmacodynamics studies for radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) using a validated and well-established animal model. This service is valuable for quickly assessing the potential efficacy of a test compound. Our team of scientists will collaborate with you to meet your specific needs, guiding you through study design, data analysis, and final reporting. You can trust us to deliver reliable and reproducible results.
RILI, which is a common complication after thoracic radiotherapy, presents a major challenge when it comes to finding effective treatments. The progression of RILI involves the gradual buildup, growth, and change of fibroblasts, which eventually leads to an excessive buildup of extracellular matrix. This excess buildup then causes fibrosis, a condition that seriously impairs lung function and adds to the burden faced by cancer patients receiving treatment. Due to the complexity and seriousness of RILI, it is crucial and urgent to search for new and innovative ways to alleviate this debilitating outcome.
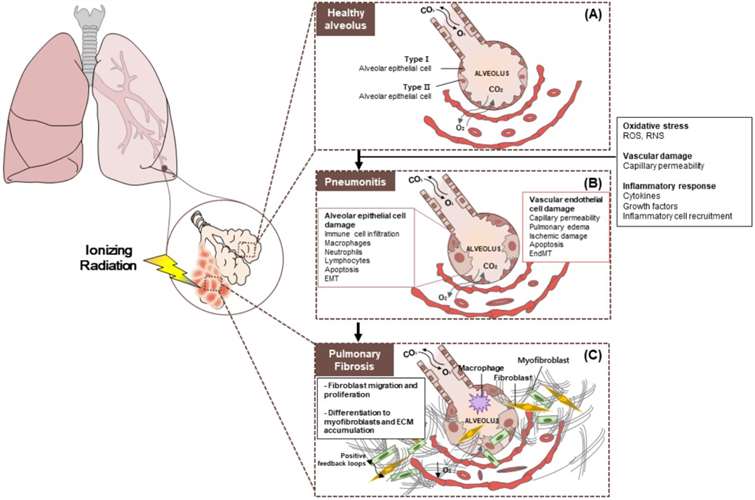 Fig.1 Pathobiology of radiation pneumonitis and radiation-induced lung injury. (A) Healthy alveolus. (B) Radiation pneumonitis is inflammation of the lungs caused by radiotherapy. (C) Pulmonary fibrosis. (Jin et al. 2020)
Fig.1 Pathobiology of radiation pneumonitis and radiation-induced lung injury. (A) Healthy alveolus. (B) Radiation pneumonitis is inflammation of the lungs caused by radiotherapy. (C) Pulmonary fibrosis. (Jin et al. 2020)
Our Radiation-Induced Lung Injury (RILI) Model
- Available Animal
C57BL/6 mouse (female)
- Modeling Method
After acclimation, mice are treated with an X-ray radiation dose of 18 Gy to induce RILI.
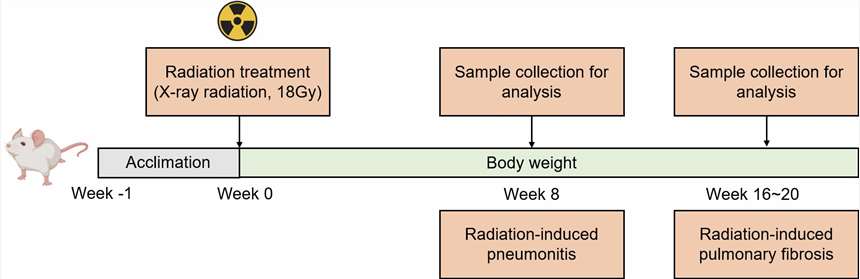 Fig. 2 Modeling method of RILI model.
Fig. 2 Modeling method of RILI model.
- Endpoints
- Body weight
- Cytokine analysis
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
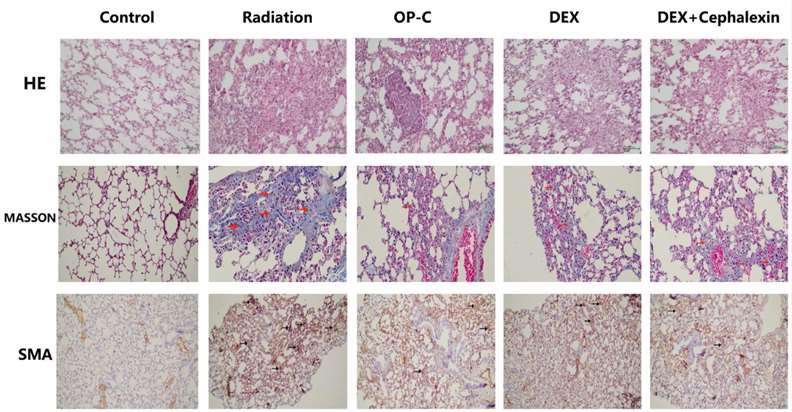 Fig. 3 Effects of Ophiopogonin C (OP-C) on the histological changes, including pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, in the lung tissue at 28 weeks after whole thoracic irradiation. Photomicrographs show staining of mouse lung tissue sections with hematoxylin and eosin staining, Masson staining, and SMA detected by immunohistochemical staining in mice from the blank control, radiation-only, OP-C, dexamethasone (DEX), and DEX + cephalexin groups. (Fu et al. 2022)
Fig. 3 Effects of Ophiopogonin C (OP-C) on the histological changes, including pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, in the lung tissue at 28 weeks after whole thoracic irradiation. Photomicrographs show staining of mouse lung tissue sections with hematoxylin and eosin staining, Masson staining, and SMA detected by immunohistochemical staining in mice from the blank control, radiation-only, OP-C, dexamethasone (DEX), and DEX + cephalexin groups. (Fu et al. 2022)
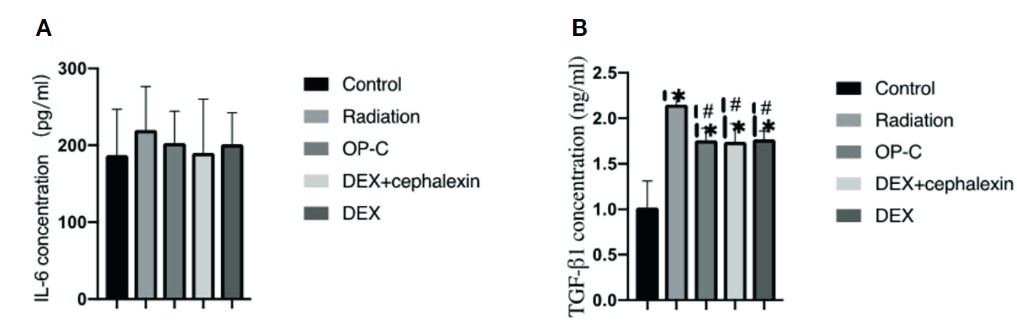 Fig. 4 Effects of OP-C on cytokine expression in serum. Expression of IL-6 (A) and TGF-β1 (B) in the serum were measured in mice from the blank control, radiation only, OP-C, DEX, and DEX + cephalexin groups. (Fu et al. 2022)
Fig. 4 Effects of OP-C on cytokine expression in serum. Expression of IL-6 (A) and TGF-β1 (B) in the serum were measured in mice from the blank control, radiation only, OP-C, DEX, and DEX + cephalexin groups. (Fu et al. 2022)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is delighted to offer our cutting-edge technology and profound expertise in rodent disease modeling to bolster our clients' research endeavors and project advancements. With a commitment to innovation and excellence, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive solutions that cater to the diverse needs of our clients. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Jin, H., et al. Radiation-Induced Lung Fibrosis: Preclinical Animal Models and Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12(6):1561.
- Fu, X., et al. The effect of ophiopogonin c in ameliorating radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice: an update study. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12: 811183.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

