- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Urology Disease Models
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
With extensive expertise in urology disease model establishment, Creative Bioarray offers a doxorubicin-induced nephropathy model to clients worldwide. This model is designed to facilitate the evaluation of potential novel therapeutics and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of nephropathy. By utilizing doxorubicin to induce nephropathy, researchers can closely mimic the human condition, providing valuable insights into disease pathophysiology and enabling the development of more effective treatments.
Doxorubicin (DOX), also known as Adriamycin, is a widely used chemotherapeutic drug. However, its clinical utility is limited due to its harmful effects on various organs, particularly the kidneys. Adriamycin nephropathy, a rodent model of chronic kidney disease (CKD), closely mirrors human primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). This model is characterized by podocyte injury, followed by glomerulosclerosis, tubulointerstitial inflammation, and fibrosis. These features make it an attractive system for in vivo drug screening, allowing researchers to study the mechanisms of kidney damage and evaluate the efficacy of potential therapeutic agents in a setting that closely resembles human disease.
Our Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
Creative Bioarray has developed a nephropathy model induced by tail vein injection of doxorubicin. This model is designed to closely mimic the human condition, providing researchers with a reliable platform to study the mechanisms of nephropathy and evaluate potential therapeutic agents.
- Endpoints
- Biochemical parameters analysis: blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, urine protein
- Body weight
- Kidney weight
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
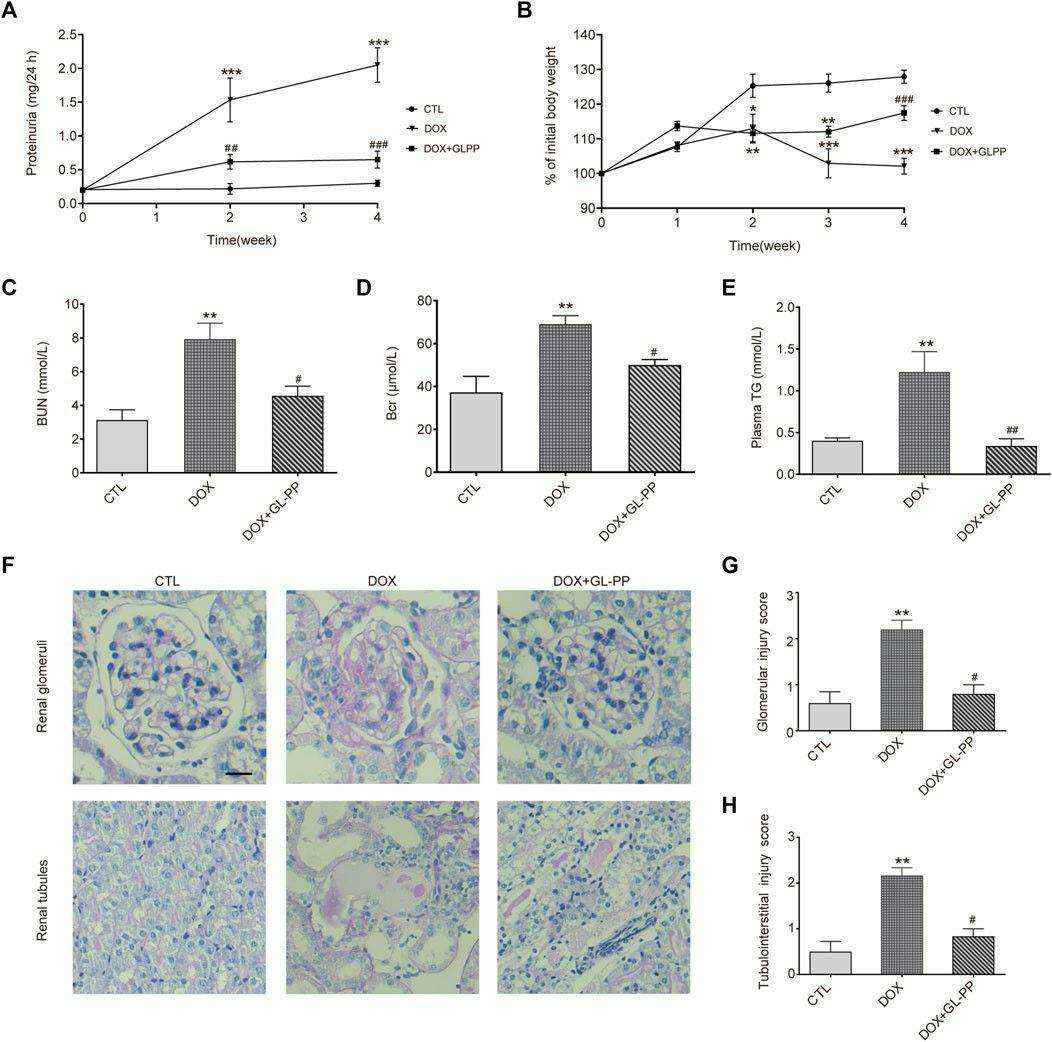 Fig. 1 GL-PP alleviates DOX-induced proteinuria and renal dysfunction in mice. (A) Temporal progression of proteinuria. (B) Change in body weight over the course of the experiment. (C) Blood urea nitrogen. (D) Blood creatinine. (E) Plasma triglycerides. (F) Representative image of renal PAS staining. (G) Semi-quantitative scoring of glomerular injury. (H) Semi-quantitative scoring of tubulointerstitial injury. (Fang et al. 2023)
Fig. 1 GL-PP alleviates DOX-induced proteinuria and renal dysfunction in mice. (A) Temporal progression of proteinuria. (B) Change in body weight over the course of the experiment. (C) Blood urea nitrogen. (D) Blood creatinine. (E) Plasma triglycerides. (F) Representative image of renal PAS staining. (G) Semi-quantitative scoring of glomerular injury. (H) Semi-quantitative scoring of tubulointerstitial injury. (Fang et al. 2023)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is committed to delivering fast and comprehensive services of the highest quality to expedite drug discovery. If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry directly to us.
Reference
- Fang, H., et al. Therapeutic potential of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide peptide in Doxorubicin-induced nephropathy: modulation of renin-angiotensin system and proteinuria Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2023, 14: 1287908.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

