- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Asthma Model
- Ovalbumin (OVA)-Induced Asthma Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Ovalbumin (OVA)-Induced Asthma Model
Creative Bioarray offers stable ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma model to help our clients evaluate the efficacy of their test compounds. Our model is designed to provide accurate and consistent results that can help you accelerate the development process of your compounds. With our services, you can gain valuable insights into the potential efficacy of your compound on asthma symptoms, allowing you to make informed decisions about how to proceed with your research.
OVA is the main protein found in egg white, which is not intrinsically immunogenic and therefore needs to be injected systemically in the presence of adjuvants, typically aluminum hydroxide (alum), to induce Th2 sensitization in mice. This animal model features many similarities to human allergic asthma, including the presence of eosinophilic lung inflammation, the release of inflammatory mediators and cytokines, and the presence of airway hyperresponsiveness after the antigen challenge. Researchers have extensively studied this model to understand the underlying mechanisms of allergic asthma and develop effective treatments.
Our Ovalbumin (OVA)-Induced Asthma Model
- Animal Available
Mouse - Modeling Method
In the sensitization phase: mice are intraperitoneally injected with OVA complexed with aluminum.
In the challenge phase: mice are challenged with OVA, resulting in many features of asthma. - Endpoints
- BALF analysis
- Serum IgE level analysis: total IgE, OVA specific IgE
- Cytokine analysis
- Histology analysis: H&E staining (lung)
- qPCR or Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
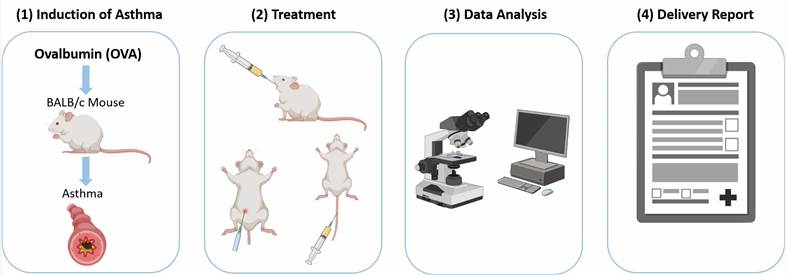 Fig. 1 Workflow of our OVA-induced asthma model
Fig. 1 Workflow of our OVA-induced asthma model
Example Data
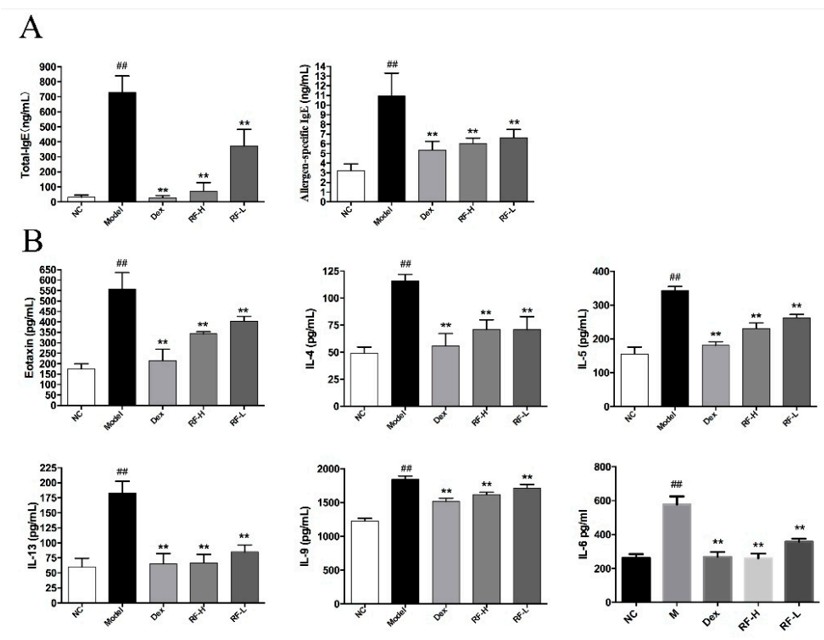 Fig. 2 The effects of Renifolin F on cytokine production in serum and BALF. (A) The levels of total IgE and allergen-specific IgE in serum. (B) The levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-9 and IL-6 in BALF. Normal control, saline-induced mice only. Model, OVA-induced mice. Dex, OVA-induced mice treated with Dex (1.0 mg/kg). RF-H, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (3.0 mg/kg). RF-L, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (1.5 mg/kg).
Fig. 2 The effects of Renifolin F on cytokine production in serum and BALF. (A) The levels of total IgE and allergen-specific IgE in serum. (B) The levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-9 and IL-6 in BALF. Normal control, saline-induced mice only. Model, OVA-induced mice. Dex, OVA-induced mice treated with Dex (1.0 mg/kg). RF-H, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (3.0 mg/kg). RF-L, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (1.5 mg/kg).
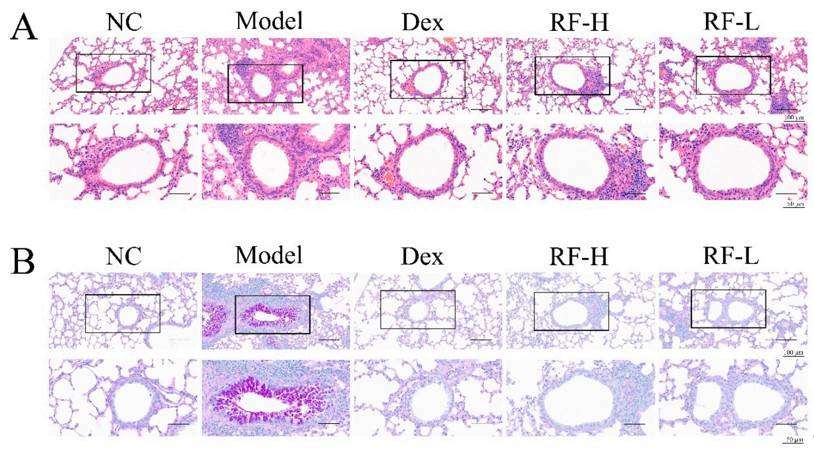 Fig. 3 The effects of Renifolin F on histopathologic changes in the lung tissues of OVA-induced allergic mice in vivo. (A) Lung tissue sections were stained with H&E. (B) Lung tissue sections were stained with PAS. Normal control, saline-induced mice only. Model, OVA-induced mice. Dex, OVA-induced mice treated with Dex (1.0 mg/kg). RF-H, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (3.0 mg/kg). RF-L, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (1.5 mg/kg).
Fig. 3 The effects of Renifolin F on histopathologic changes in the lung tissues of OVA-induced allergic mice in vivo. (A) Lung tissue sections were stained with H&E. (B) Lung tissue sections were stained with PAS. Normal control, saline-induced mice only. Model, OVA-induced mice. Dex, OVA-induced mice treated with Dex (1.0 mg/kg). RF-H, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (3.0 mg/kg). RF-L, OVA-induced mice treated with Renifolin F (1.5 mg/kg).
Additionally, we also provide another asthma model that maybe you are interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray stands as a preeminent research partner, specializing in a diverse array of rodent disease models and offering an unparalleled breadth of related services. With our skilled scientists, we are committed to assisting you in selecting the most suitable model and crafting a meticulous study plan tailored to your specific needs. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Yang, Z., et al. Therapeutic effect of Renifolin F on airway allergy in an ovalbumin-induced asthma mouse model in vivo. Molecules, 2022, 27(12): 3789.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

