- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Adoptive T Cell Transfer Induced Colitis Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Adoptive T Cell Transfer Induced Colitis Model
For a trusted partner in evaluating novel therapies that target the immunological mechanisms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Creative Bioarray is your go-to expert. We offer a well-established Adoptive T Cell Transfer Induced Colitis Model, designed specifically to facilitate drug development for therapies that operate through T cell-dependent mechanisms. Our model is not only stable and reliable but also backed by a team of experienced scientists dedicated to advancing the effectiveness and efficiency of your research. Partner with Creative Bioarray to ensure your drug development process is supported by cutting-edge technology and unparalleled expertise, tailored to achieve groundbreaking results in IBD therapy.
The Adoptive T Cell Transfer Induced Colitis Model is a powerful and widely used tool in IBD research. This model involves transferring naive CD4+ T cells from immunocompetent donor mice to T cell-deficient strains. It effectively replicates human colitis features like inflammatory cell infiltration, colonic gland loss, and epithelial hyperplasia. This model is particularly significant in drug development for therapies with T cell-dependent mechanisms, as it closely mirrors human IBD immunopathology.
Our Adoptive T Cell Transfer Induced Colitis Model
Animal Species
- SCID mouse
- RAG KO mouse
Modeling Method
On the initial day of the study, spleens are harvested from donor mice for the isolation of CD4+CD45RBhigh cells. Following the extraction and sorting of these cells, each recipient mouse is administered an injection of the CD4+CD45RBhigh cells to initiate the development of colitis. Over the course of 3 to 8 weeks, the injected cells become activated within the colon, leading to the onset of colitis.
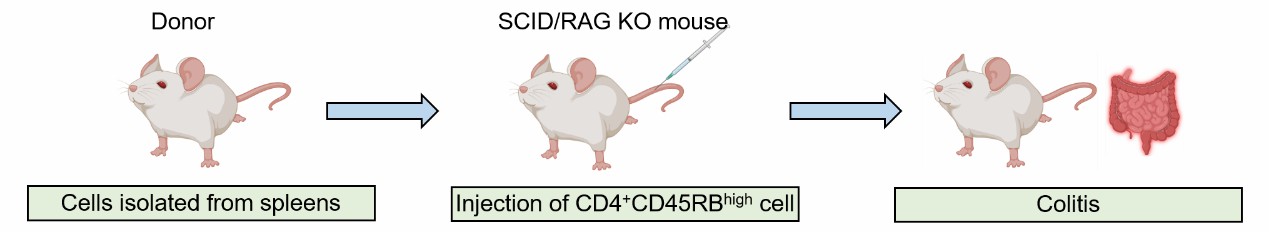 Fig. 1 Modeling method of adoptive T cell transfer induced colitis
Fig. 1 Modeling method of adoptive T cell transfer induced colitis
Endpoints
- Body weight
- DAI score
- Colon weight
- Colon length
- MPO activity
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints according to your specific needs
Example Data
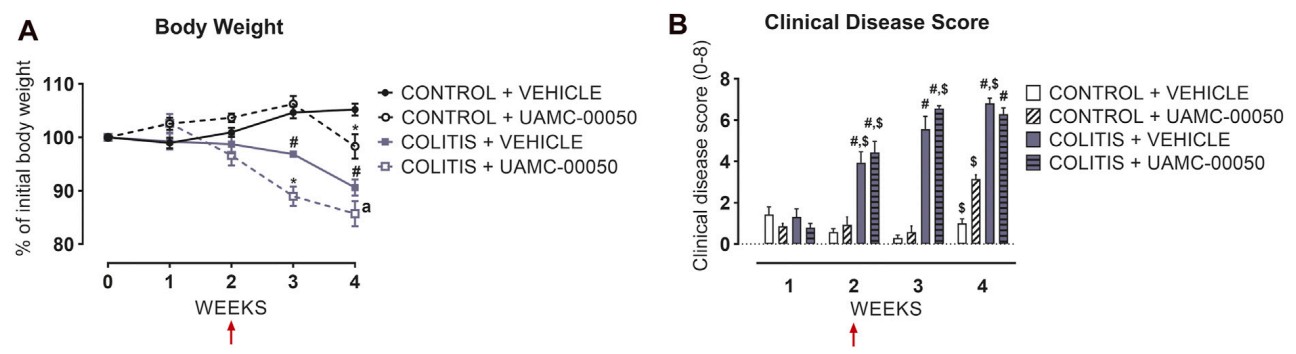 Fig. 2 Effect of curative treatment with UAMC-00050 on inflammatory parameters in experimental colitis. Effect on body weight (A), clinical disease score (B). (Van et al. 2021)
Fig. 2 Effect of curative treatment with UAMC-00050 on inflammatory parameters in experimental colitis. Effect on body weight (A), clinical disease score (B). (Van et al. 2021)
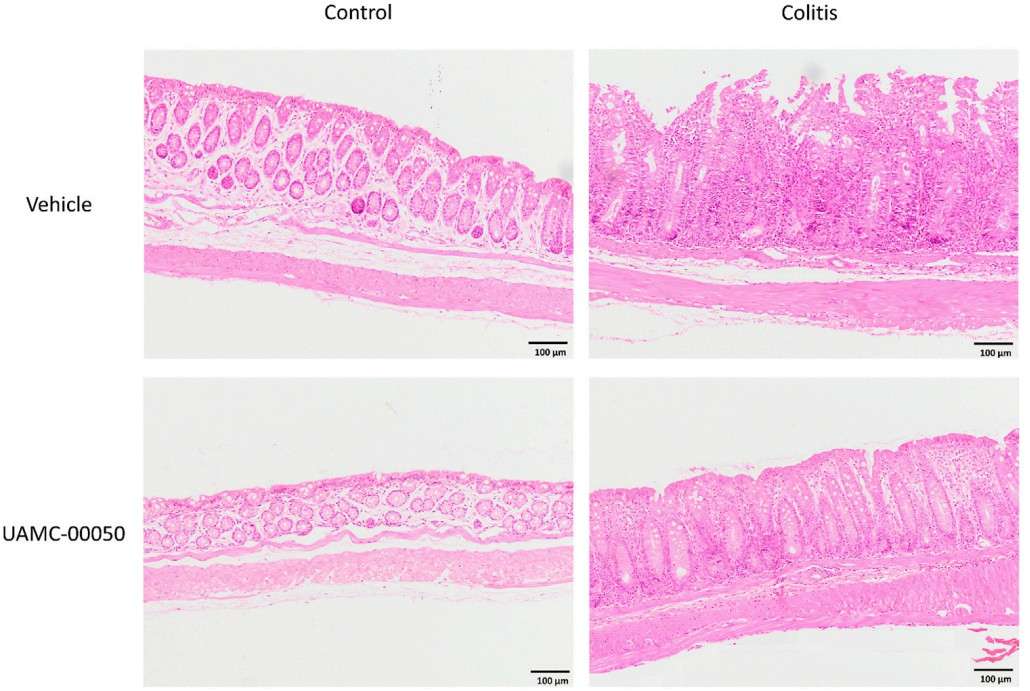 Fig. 3 Effect of curative treatment with UAVC-00050 on H&E stained colon sections in experimental colitis, Reoresentaive images of H&E stained colon sections (objective x 10, scale bar = 100 um from the four difierent exprimental groups (contrdl+ vehicle, control+ UAMC-0050, coits + vehice, cotis + UAMC00050). (Van et al. 2021)
Fig. 3 Effect of curative treatment with UAVC-00050 on H&E stained colon sections in experimental colitis, Reoresentaive images of H&E stained colon sections (objective x 10, scale bar = 100 um from the four difierent exprimental groups (contrdl+ vehicle, control+ UAMC-0050, coits + vehice, cotis + UAMC00050). (Van et al. 2021)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray provides a wide range of well-characterized IBD models to meet the needs of your drug discovery projects. Our aim is to support the success of your projects by offering relevant and reliable preclinical data. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Van, Spaendonk.H., et al. The effect of a novel serine protease inhibitor on inflammation and intestinal permeability in a murine colitis transfer model. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021, 12: 682065.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

