Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Protein phosphorylation is an important post-translational modification (PTM) that controls numerous cellular functions, including the cell cycle, differentiation, and metabolism. Phosphate molecules are transferred from molecules like ATP to amino acids on proteins, such as serine, threonine, or tyrosine. This modification is widespread-about 30% of all proteins in eukaryotic cells. These dynamic changes can modify protein activity, interactions, and stability, ultimately affecting signaling networks and cellular responses. Failures in phosphorylation are linked to a diverse array of diseases, highlighting the importance of phosphorylation in health and disease. Therefore, identifying the specific phosphorylation states or phosphoforms of proteins is crucial for elucidating their cellular functions. Understanding these phosphorylation mechanisms can illuminate cellular operations and reveal potential therapeutic targets for disease.
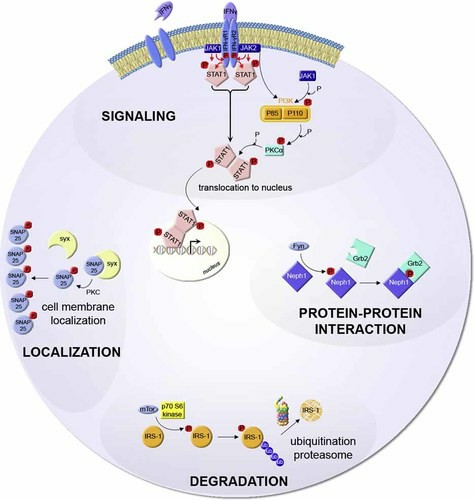 Fig. 1. Examples for important biological functions regulated by protein phosphorylation (Trost M, Bridon G, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Examples for important biological functions regulated by protein phosphorylation (Trost M, Bridon G, et al., 2023).
Creative Bioarray specializes in cell-based kinase assays and phosphorylation assays. We are particularly confident in the field of drug development for small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Creative Bioarray can help you determine the ranking of compounds based on cell-based phosphorylation data, which is critical for decisions regarding preclinical testing. After conducting in vitro cell-based kinase profiling of your compounds, a similar experimental design based on cellular phosphorylation assays will significantly enhance your understanding of your kinase inhibitors.
Detection range
Our service is capable of detecting a variety of protein phosphorylation events in various cell types, including:
- Key protein phosphorylation states in cell signaling.
- Phosphorylation changes in cell cycle-related proteins.
- Phosphorylation biomarkers in specific disease conditions.
- Changes in phosphorylation levels post-drug intervention.
Our Technologies
Western blot
Western blotting is the gold standard for testing protein phosphorylation. This technique involves purifying proteins by SDS-PAGE, transferring them to a membrane, and detecting them with phospho-specific antibodies. It offers sensitivity without the use of radioactivity and allows detection through chemiluminescence or colorimetry.
Advantages:
- Gold standard
- The ability to identify specific phosphorylation sites
- The purified phosphorylated protein can be quantified when available
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA detects protein phosphorylation quantitatively by capturing the protein with a capture antibody and capturing the phosphorylation site with a detection antibody. This test uses colorimetric or fluorometric detection, and signal strength represents phosphorylated protein levels.
Advantages:
- Offers high specificity and sensitivity
- Requiring less sample volume
- Can be quantified
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a powerful, laser-based technology for analyzing cell characteristics. Cells are labeled with fluorescently-conjugated phospho-specific antibodies for targeting specific proteins. When excited by a laser, the fluorochromes emit light, allowing quantitation of proteins in individual cells within a mixed population.
Advantages:
- Enables rapid and precise single-cell analysis
- Multiplex protein detection
- High throughput if using a 96-well plate sampler
Mass spectrometry (MS)
From the "bottom up" method, proteins are digested by enzymes into peptides, ionized, and then subjected to MS analysis. The approach simultaneously sequences and identifies phosphorylated residues with a wide dynamic range and hypothesis-free analysis, separating protein isoforms without antibodies.
Advantages:
- Multiplex protein detection
- High sensitivity
- Quantitative data possible
Our testing includes but not limited to:
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- ATP Content assay
- Drug Penetration and Distribution Studies…
Service Features and Advantages

High accuracy and reliability
Utilizes highly specific antibodies and advanced detection instruments for precise identification and quantification of phosphorylated proteins.

Customization
Offers diverse detection options and solutions tailored to the specific research needs of the client.
Comprehensiveness
Integrates multiple detection techniques to analyze cell phosphorylation from different perspectives, providing more comprehensive phosphorylation insights.
Rapid delivery
Optimized processes ensure timely submission of data, facilitating the swift advancement of research projects.
FAQ
1. How to determine the appropriate detection technique?
Our experts will choose the most suitable detection technology based on your study goals, sample size, and target protein properties. For example, if you are looking for single-cell phosphorylation changes, and your cells are suspended, you should probably consider flow cytometry. If you are wanting to screen large numbers of samples quantitatively, ELISA would be best used; mass spectrometry is best for large-scale detection of new phosphorylation sites.
2. What does the data report include?
The data report will include a summary of the experiments, raw data charts, quantitative data analysis findings, statistical results, and an informative discussion and interpretation of the findings.
3. How sensitive is phosphorylation detection?
Our service employs highly sensitive detection methods that can identify low-abundance phosphorylated proteins.
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Trost M, Bridon G, et al. Subcellular phosphoproteomics. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2010. 29(6):962-90.
Explore Other Options

