- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Drug-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
Isoproterenol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic agonist, cause cardiac injury and is commonly used in the study of heart disease. These models are classified into acute and chronic heart failure depending on the dose and duration of isoproterenol administration. Isoproterenol induced acute heart failure is a model characterized by acute apical segment ventricular dysfunction, simulating stress-induced cardiomyopathy (SIC) in human. Besides, the chronic model mimics advanced heart failure in humans. These models provides tools to study structural and functional adaptation of myocardium during the progression of heart failure.
Creative Bioarray specializes in providing customized pharmacodynamic research services to help customers assess the efficacy of drug candidates and study the associated pathological mechanisms through isoproterenol-induced heart failure model.
 Figure. 1. Acute and chronic isoproterenol models
Figure. 1. Acute and chronic isoproterenol models
Species available
- Mouse
- Rat
Our Capabilities
- We detect changes in myocardial morphology by H&E staining and so on.
- We evaluate left ventricular internal diameters in diastole (LVIDD, mm), left ventricular internal diameters in systole (LVIDS, mm) and left ventricular ejection fraction (EF, %) and left ventricular fractional shortening by Echocardiography.
Assays available
- Echocardiography
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- Histopathological evaluation
- Biochemical analysis
With extensive experience in the field of cardiovascular diseases, we are confident to help you overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
 Figure. 2. Effect of OMT on cardiac histopathological changes of ISO-induced heart failure rats (H&E staining 200×). (A) Control. (B) OMT 100 mg/kg. (C) Isoproterenol 5 mg/kg. (D) OMT 100 mg/kg + isoproterenol. (E) OMT 50 mg/kg + isoproterenol.
Figure. 2. Effect of OMT on cardiac histopathological changes of ISO-induced heart failure rats (H&E staining 200×). (A) Control. (B) OMT 100 mg/kg. (C) Isoproterenol 5 mg/kg. (D) OMT 100 mg/kg + isoproterenol. (E) OMT 50 mg/kg + isoproterenol.
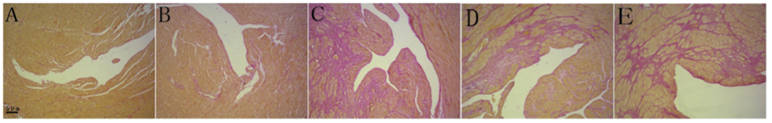 Figure. 3. Representative Van Gieson-stained sections of the cardiac apex (100×). (A) Control. (B) OMT 100 mg/kg. (C) Isoproterenol 5 mg/kg. (D) OMT 100 mg/ kg + isoproterenol. (E) OMT 50 mg/kg + isoproterenol. Red indicates fibrotic regions.(For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend,the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Figure. 3. Representative Van Gieson-stained sections of the cardiac apex (100×). (A) Control. (B) OMT 100 mg/kg. (C) Isoproterenol 5 mg/kg. (D) OMT 100 mg/ kg + isoproterenol. (E) OMT 50 mg/kg + isoproterenol. Red indicates fibrotic regions.(For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend,the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
 Figure. 4 Representative raw tracings of M-mode echocardiography
Figure. 4 Representative raw tracings of M-mode echocardiography
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
References
Zhou R, et al. Oxymatrine attenuated isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rats via regulation of COX-2/PGI2 pathway[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2016:S0753332216311386.
Rui, He, et al. MiR-1a-3p mitigates isoproterenol-induced heart failure by enhancing the expression of mitochondrial ND1 and COX1.[J]. Experimental cell research, 2019.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

