- You are here: Home
- Services
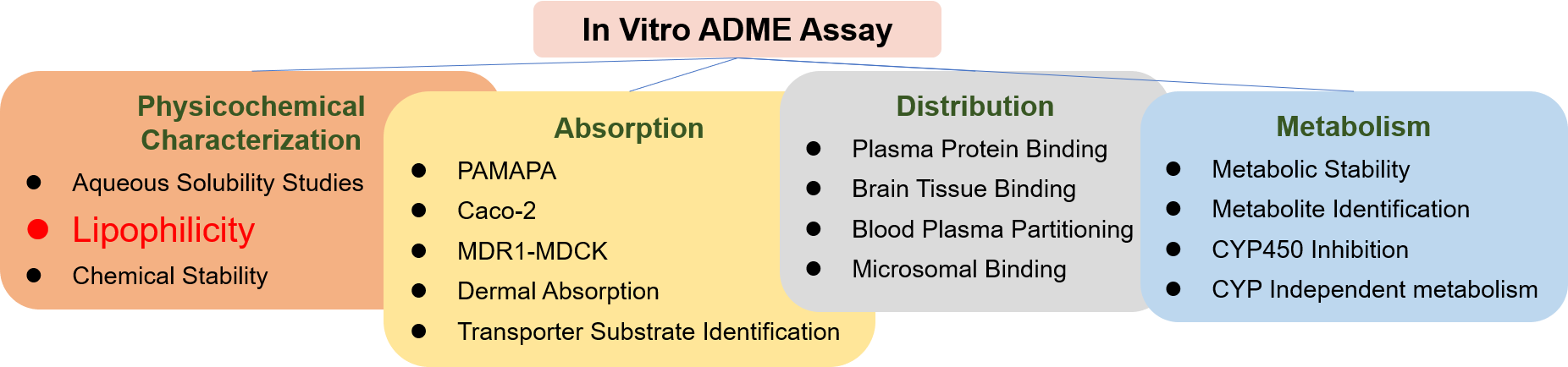
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- Physicochemical Characterization Assays
- Lipophilicity and pKa Assays
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Lipophilicity and pKa Assays
Creative Bioarray provides Lipophilicity and pKa Assays to help customers accurately evaluate the drug lipophilicity and pKa, allowing customers to gain more insight into the solubility and permeability of drugs.
Why is it necessary to determine drug lipophilicity and pKa?
- Lipophilicity and pKa are essential factors in permeability and solubility, and they are frequently tested during drug development.
- The assessment of lipophilicity is fundamental to the understanding of molecular properties. In a drug development context, it is also vital to consider about ionization of molecules in the aqueous phase, especially at pH 7.4. Therefore, the distribution coefficient (Log D) is the preferred descriptor of lipophilicity.
- The distribution of a molecule between a lipid or nonpolar environment and an aqueous or polar environment is affected by lipophilicity. The equilibrium distribution of a chemical between water and octanol is commonly quantified as Log P. Lower aqueous solubility and higher membrane permeability is associated with compounds with a higher Log P.
- pKa influences the ionization of molecules in an aqueous solution; it is measured by the change of ionization with pH. Basic compounds with pKa of 9 have an even distribution of protonated and neutral molecules at pH9. The lower the pH, the higher the protonation and the more neutral species. Acidic compounds with pKa of 4 have an equal distribution of deprotonated and neutral molecules at pH 4, with more neutral species at low pH and more deprotonated species at high pH.
Brief Protocol
Thermodynamic and kinetic solubility assays are two commonly used laboratory methods to determine drug solubility.
- Log D7.4, Log P (Shake-flask Method)
- The test substance is sonicated with octanol (pre-saturated with buffer). After that, a pH 7.4 buffer (pre-saturated with octanol) is added to the octanol.
- A buffer mixed with octanol is prepared. The system is mixed to ensure that the chemical is distributed evenly throughout the two phases.
- After separation, the chemical is measured in the aqueous and octanol phases using LC-MS/MS, and the Log D7.4/Log P is calculated using the equation below.
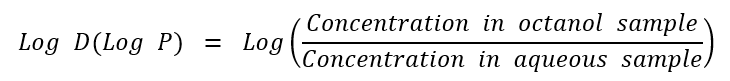
- pKa
pH-Metric Titration: The pH-metric method is a critical reference method because it can be used to measure all pKas between 2 and 12, with or without a UV chromophore, provided that the sample can be dissolved in water or water/co-solvent over the pH range of interest. While the pH-metric method is not fast enough for rapid screening, it provides a valuable backup for measuring samples without UV absorbance.
Hybrid pH-Metric/UV Method: Multi-wavelength UV absorbance of the sample solution is monitored throughout the titration. Samples must have a chromophore, and the absorbance must change as a function of ionization. During measurement, samples are acid-base titrated across a pH range that includes the pKa(s), and multi-wavelength UV spectra are measured at each pH. The pKas are calculated using a technique based on target factor analysis (TFA)
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
References
- Van de Waterbeemd, Han, H. Lennernäs, and P. Artursson. "Drug bioavailability." Methods and principles in medicinal chemistry 18 (2004).
- Meanwell, Nicholas A., ed. Tactics in contemporary drug design. Berlin: Springer, 2015.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

