- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- In Vitro Drug Distribution Services
- Brain Tissue Binding Assay
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Brain Tissue Binding Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
In the field of neurosciences, successful drug discovery relies on the drug's capacity to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and be distribute effectively throughout the brain. The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective barrier, which usually prevents many drug molecules from entering the central nervous system (CNS). Therefore, understanding and optimizing the fraction unbound (fu) of a drug in brain tissue is an integral part of the drug development process. Creative Bioarray employs equilibrium dialysis to measure the fraction of compounds unbound to brain tissue (fu,brain), which is one of the most recognized methods for assessing drug-tissue binding. By quantifying the concentration of free drug, this assay provides scientists with an in-depth comprehension of the binding properties of a drug candidate to brain tissue.
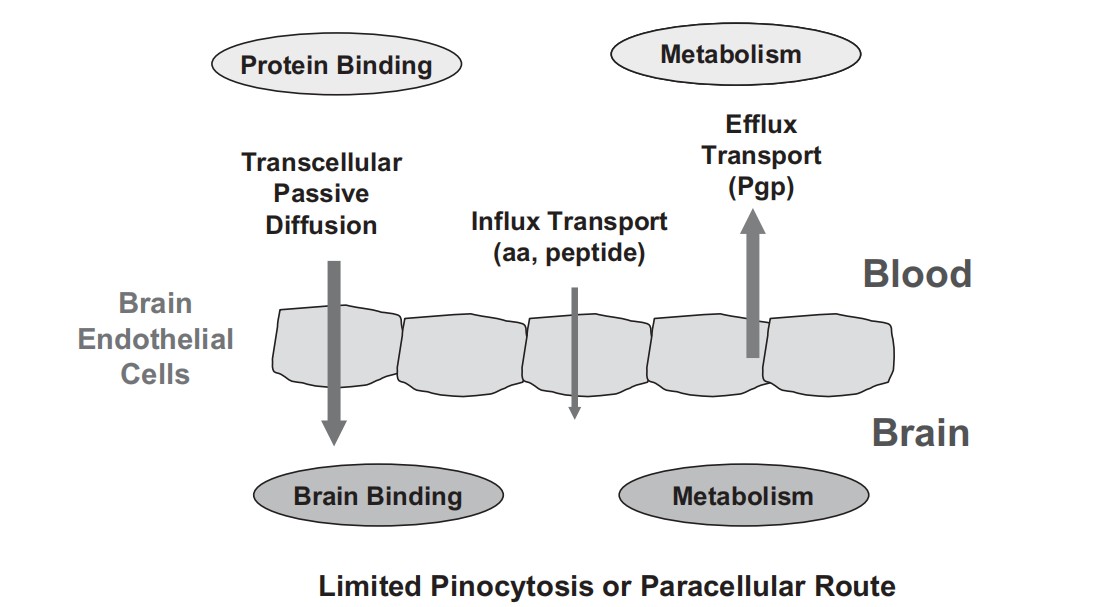 Fig.1. Mechanisms for brain penetration (Di L, Kerns E H, et al., 2012).
Fig.1. Mechanisms for brain penetration (Di L, Kerns E H, et al., 2012).
Why we need brain tissue binding assays?
Analyzing unbound drug concentrations in the brain is essential to pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) calculations of CNS drugs, because only unbound compounds pass the BBB and reach the action site.
Drug distribution in brain tissue affects CNS permeability. For CNS-targeted drugs, the drug concentration in the brain directly affects efficacy, whereas non-targeted drugs may trigger adverse effects due to excessive intracerebral distribution.
Brain tissue differs significantly from plasma in composition, with plasma being higher in protein and brain tissue being rich in lipids; therefore, the free fraction in plasma is not a substitute for the unbound brain concentration.
Creative Bioarray's Brain Tissue Binding Assay
Creative Bioarray has a well-established equilibrium dialysis assay technology that allows us to rapidly and accurately quantify the unbound portion of a drug in brain tissue using our 96-well equilibrium dialysis device. The basic principle of equilibrium dialysis involves adding a target compound into tissue homogenate and buffer chambers separated by a semipermeable membrane. Free compounds diffuse from the tissue to the buffer chamber until equilibrium is reached. Using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), we measure the compound concentrations in both the homogenate and buffer to calculate the unbound compound proportion. All assays are performed in duplicates to ensure accuracy.
| Objective | Evaluate the value of fraction of compound unbound to brain tissue (fu,brain) |
| Analysis Method | LC-MS/MS quantification |
| Typical Test Article Concentration | 2 µM (different concentrations available) |
| Sample Requirement | Minimum weight of dry compound (1~ 2mg) or 100 μL of 10 mM DMSO stock solution is required for this assay. |
| Number of Replicates | 2 |
| Data Analysis | 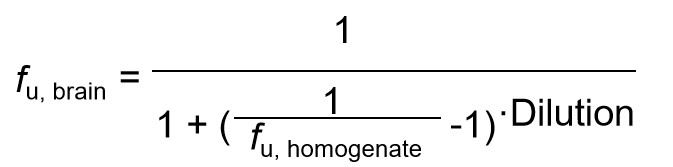 fu, brain: The unbound fraction in brain tissue fu, homogenate: The unbound fraction in brain homogenate Dilution is the dilution factor for the brain homogenate |
| Deliverables | Fraction unbound (fu), %recovery, and methods reported in Excel format |
Creative Bioarray offers routine in vitro ADME assays such as metabolic stability assays in different matrices (microsomes, S9 fraction, plasma, whole blood, hepatocyte, etc.), Metabolite identification, Caco-2 permeability, Cytochrome P450 Assay (Phenotyping, Induction, Inhibition).
We also offer CNS permeation and distribution assays, i.e., bidirectional MDR1-MDCK permeability assay, plasma protein binding, and brain homogenization assays. If the compounds prove effective in in vitro assays, we also provide corresponding in vivo BBB assays to further determine the girdle kinetics and brain plasma ratio of the compounds.
Features
- High throughput: rapid and accurate determination of unbound fraction of drugs in brain tissue using 96-well equilibrium dialysis equipment
- Accurate and reliable: ensure data accuracy and consistency through strict quality control and repetitive experiments.
- Customized service: able to use different concentrations and parameters in the assay according to customers' needs, adapting to a variety of R&D needs.
FAQ
Q1: What is the role of brain tissue binding assays in drug discovery?
Brain tissue binding assays are essential for predicting drug distribution in the brain, therapeutic efficacy, and potential central nervous system (CNS)-related side effects. It is also useful for predicting in vivo drug clearance, human dosing, cross-species comparisons, and elucidating potential pharmacologic and toxicologic effects.
Q2: How long does the assay take?
Typically, the entire assay process takes 1-2 weeks, depending on the number and complexity of samples.
Q3: How much sample and what information is required?
Typically, 1-2 mg of dry compound, or 100μL of 10 mM DMSO stock solution, is required. Compound information such as the brutto formula, molecular weight (free base form and salt form), purity, solubility, and storage condition are needed.
Quotation and Ordering
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Di L, Kerns, E. H, et al. Methods for Assessing Blood–Brain Barrier Penetration in Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2012.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

