- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Pain Models
- Visceral Pain Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Visceral Pain Model
Are you searching for a trustworthy partner to assist you with your research on visceral pain? Look no further than Creative Bioarray. Our team has years of experience and uses the most advanced technology available to develop a pain model that closely mimics the biological and pathological features of visceral pain. This provides our clients with a reliable, predictive platform for evaluating the safety and efficacy of their drug candidates. You can trust us to deliver accurate and dependable results to help drive your research forward.
The global impact of visceral pain is profoundly significant, accounting for a substantial proportion of all chronic pain conditions. Visceral pain arises from the stimulation of nociceptors located within the thoracic, pelvic, or abdominal viscera, the body's internal organs. This type of pain is characterized by its diffuse nature, making it challenging to pinpoint its exact source, and it frequently manifests by being referred to as a remote, typically superficial, body structure. To study and understand visceral pain more deeply, our scientists have established an animal model that replicates the conditions of visceral pain in humans. The model is instrumental in investigating the mechanisms of visceral pain, testing potential therapeutic interventions, and advancing our knowledge towards more effective pain management strategies.
Our Visceral Pain Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
Rats are intraperitoneally injected of acetic acid to induce visceral pain.
- Endpoints
- Number of writhes for 30 minutes
- Cytokines analysis
- Histology analysis
- qPCR and Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
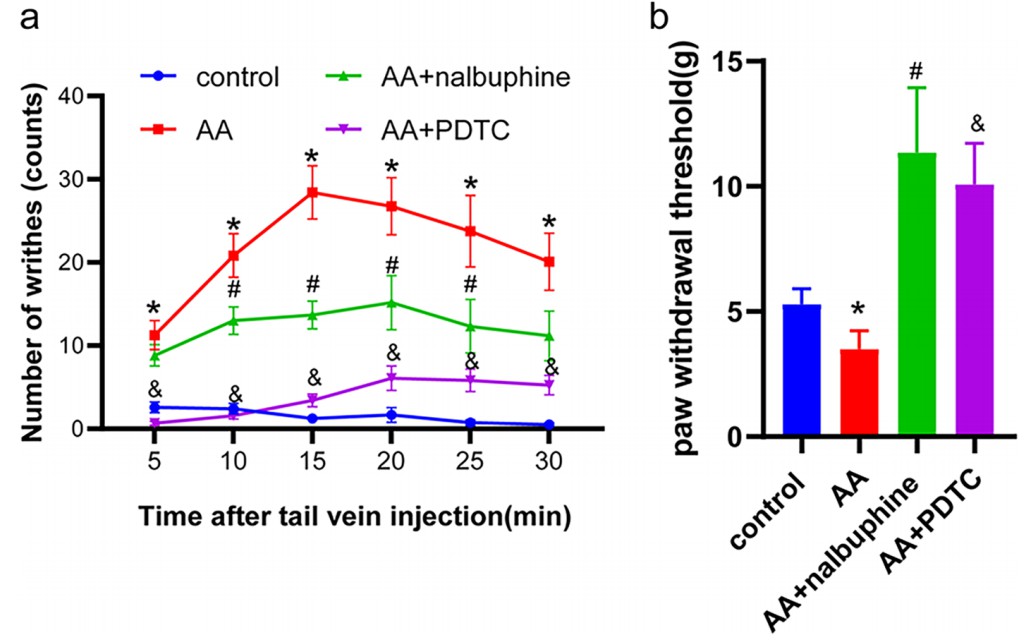 Fig. 1 The effects of acetic acid, nalbuphine, and PDTC on the writhing test and paw withdrawal threshold (PWT). a The number of writhes for 30minutes in each group. b Mechanical paw withdraw threshold in each group. (Ruan et al. 2022)
Fig. 1 The effects of acetic acid, nalbuphine, and PDTC on the writhing test and paw withdrawal threshold (PWT). a The number of writhes for 30minutes in each group. b Mechanical paw withdraw threshold in each group. (Ruan et al. 2022)
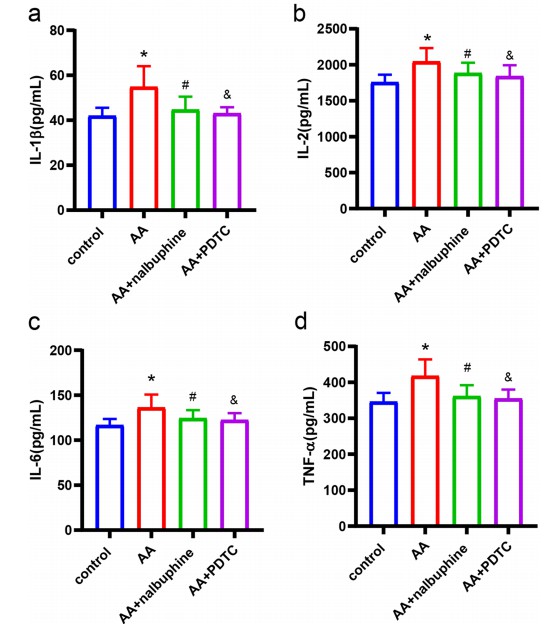 Fig. 2 Results of plasma levels of several inflammatory factors. The expressions of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α were compared between groups. (Ruan et al. 2022)
Fig. 2 Results of plasma levels of several inflammatory factors. The expressions of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α were compared between groups. (Ruan et al. 2022)
Meanwhile, we also provide other pain models that maybe you are interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is committed to offering our clients robust and reliable disease models that are designed to significantly accelerate their drug development process. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Ruan, D., et al. Nalbuphine alleviates inflammation by down-regulating NF-κB in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2022, 23(1): 34.
- Pacheco-Carroza, E.A. Visceral pain, mechanisms, and implications in musculoskeletal clinical practice. Medical Hypotheses, 2021, 153: 110624.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

