- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- In Vitro Permeability and Transporters
- MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
The Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) permeability assay plays an important role in drug discovery and development, especially in assessing compound permeation through biological walls. Originating from canine kidney epithelial cells, MDCK cells are rapidly proliferating and differentiation, have little expression of transporter proteins, and a limited metabolic function. That is why they are the preferred choice to cell lines such as Caco-2 for measuring human intestinal barrier permeability.
By inserting the MDR1 gene into MDCK cells, it forms the MDCK-MDR1 cell line that overly expresses an efflux transporter called P-gp. Leveraging this cell line allows for the assessment of P-gp mediated drug efflux, offering insights into the potential of compounds to traverse critical barriers, such as the blood-brain barrier.
Advantages of MDCK cells
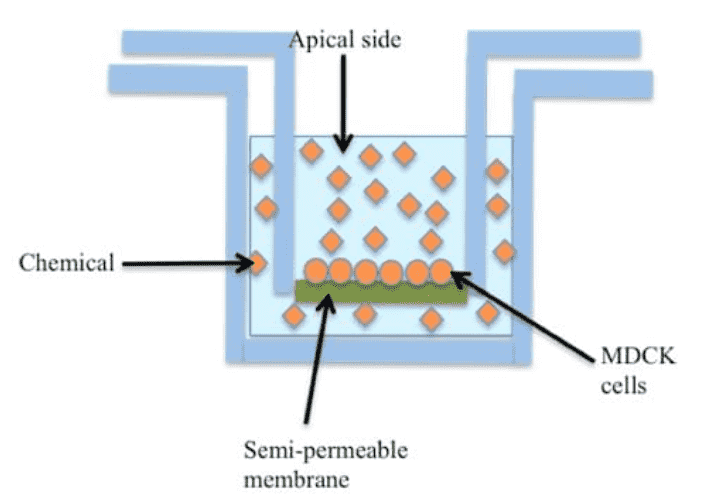
- Quick proliferation and differentiation.
- Simple to culture and manipulate.
- Low metabolic activity for passive permeability studies.
- Minimal transporter expression pre-transfection.
- Good model for biological barriers like the blood-brain barrier.
- High reproducibility for reliable data.
- Adapts to various experimental setups and techniques.
Creative Bioarray's MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay is designed to provide insights into the potential oral absorption and blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration of your compounds, guiding your drug discovery efforts with reliable data.
Our Microsomal Stability Assay Service
Workflow
1
Cell Culture
MDCK cells are grown under optimal conditions and seeded to form polarized monolayers on permeable supports.
2
Monolayer Validation
TEER measurements and fluorescent tracer assays ensure tight junction formation.
3
Compound Administration
Test compounds are added to the apical (luminal) or basolateral chamber, depending on the desired permeation direction.
4
Sample Collection
Samples are collected at specific times and analyzed for compound concentration using LC-MS/MS.
5
Data Analysis
Papp coefficients are calculated, and detailed reports are provided.
| MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay | Details |
| Test Article Concentration | 10 μM |
| The integrity of the monolayer | 3 days |
| Number of Replicates | 2 |
| Incubation Condition | Incubation in CO2 incubator at 37ºC for 90 min |
| Assay Buffer | HBSS, pH 7.4 |
| Compound required | 2mg or 100µL 10mM DMSO solution |
| Integrity Marker | Lucifer Yellow |
| Analysis Method | LC-MS/MS quantification |
| Data Delivery | Papp (apparent permeability coefficient) Efflux Ratio % Recovery |
Features

Accuracy and Reliability
By focusing on P-gp, our service minimizes the complexities linked to multiple transporters, ensuring precise identification of efflux behaviors.
Speed and Efficiency
Our MDCK cells enable swift differentiation, significantly reducing assay duration compared to other methods.

Versatility
Suitable for both passive and active transport assessments, enhancing understanding of drug absorption and brain penetration.
Cost-effectiveness
With a streamlined, automated approach, we deliver high-quality data under competitive pricing.

Regulatory Compliance
Our assays adhere to international guidelines and standards, facilitating seamless integration into regulatory submissions.
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray offers a consistent and cost-effective MDR1-MDCK permeability assay service. With a team of specialists and extensive experience in this field, we deliver high-quality data and tailored results to suit your project's specific needs. We also provide Caco-2 permeability assay and Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA). If you have additional requirements or questions, do not hesitate to contact us.
FAQ
1. Can I request specific conditions for my assay, such as using temperature-controlled chambers?
Absolutely. We offer customizable assay conditions to meet your specific research needs. Please inquire during the project setup to discuss your requirements.
2. How to choose the right cell line for permeability experiments?
Choosing the appropriate cell line depends on the specific needs of the study. The MDCK cell line is often used as an alternative to Caco-2 cells due to its shorter culture time, better prediction of BBB permeability, and closer approximation of passive permeability. If evaluating P-gp substrates is required, the MDCK-MDR1 cell line is an ideal choice.
3. Which types of drug research is this service suitable for?
This service is suitable for researching membrane transport characteristics of various small molecule drugs, biologics, etc.It is particularly prevalent in new drug screening, studies on drug absorption mechanisms, and more.
4. How to interpret MDCK-MDR1 permeability test data?
Interpreting the MDCK-MDR1 permeability test data mainly focuses on indicators like Papp (apparent permeability coefficient), Efflux Ratio, and % Recovery. By measuring the transport of compounds across the MDCK-MDR1 cell monolayer, these indicators can be calculated to determine whether the compound undergoes P-gp mediated active efflux as well as its permeability in the intestine, blood-brain barrier, and other sites.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

