- You are here: Home
- Applications
- Hepatology
- 2D Based In Vitro Hepatotoxicity Testing Services
Applications
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
2D Based In Vitro Hepatotoxicity Testing Services
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important issues in drug development as a leading cause of discontinuation of clinical trials and withdrawal or black box warnings of approved drugs. Toxic injury to hepatocytes is produced through multiple mechanisms involving damage to biomolecules, alteration of cell homeostasis/function and cell death.
To predict DILI and reduce potential risk of toxicity to humans, early safety assays during drug development are carried out in laboratory animals. However, it often fails with poor predictivity. Over the years, various liver-derived in vitro model systems have been developed to enable investigation of the potential adverse effects of chemicals and drugs, especially the 2D-cultures of hepatocytes, which could offer the advantages of being relatively inexpensive, reproducible, robust and convenient. Human hepatocytes have been considered the gold standard in vitro model for the prediction of drug metabolism and the assessment of hepatotoxicity.
With decades of operational experience and technology platform of hepatology research, in addition to the primary cell isolation and culture technique, Creative Bioarray has established various hepatotoxicity assays using 2D-cultures of hepatocytes, which will be evaluated by several items such as cell viability, apoptosis, cellular stress, cytoplasmic membrane disruption and mitochondrial membrane potential.
Advantages
- Providing useful information to clarify toxicity generation and its mechanism
- Multi-parametric analysis of the cytotoxic effect of test articles
- Each test compound is evaluated in full dose response tested in triplicate at half log dilutions
- High throughput allows for direct comparison of multiple compounds tested under the same conditions
- Allowing for potential optimization of the concentration ranges in regard to the toxic doses
- Time-saving
- Low compound require
Endpoints (including but not limited to):
Applications
➢ Meet the increasing demand for more predictive models for liver toxicity
➢ Determine your drug’s hepatotoxicity potential early in discovery
➢ Screen chemicals for induction and activity of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes
Study Examples
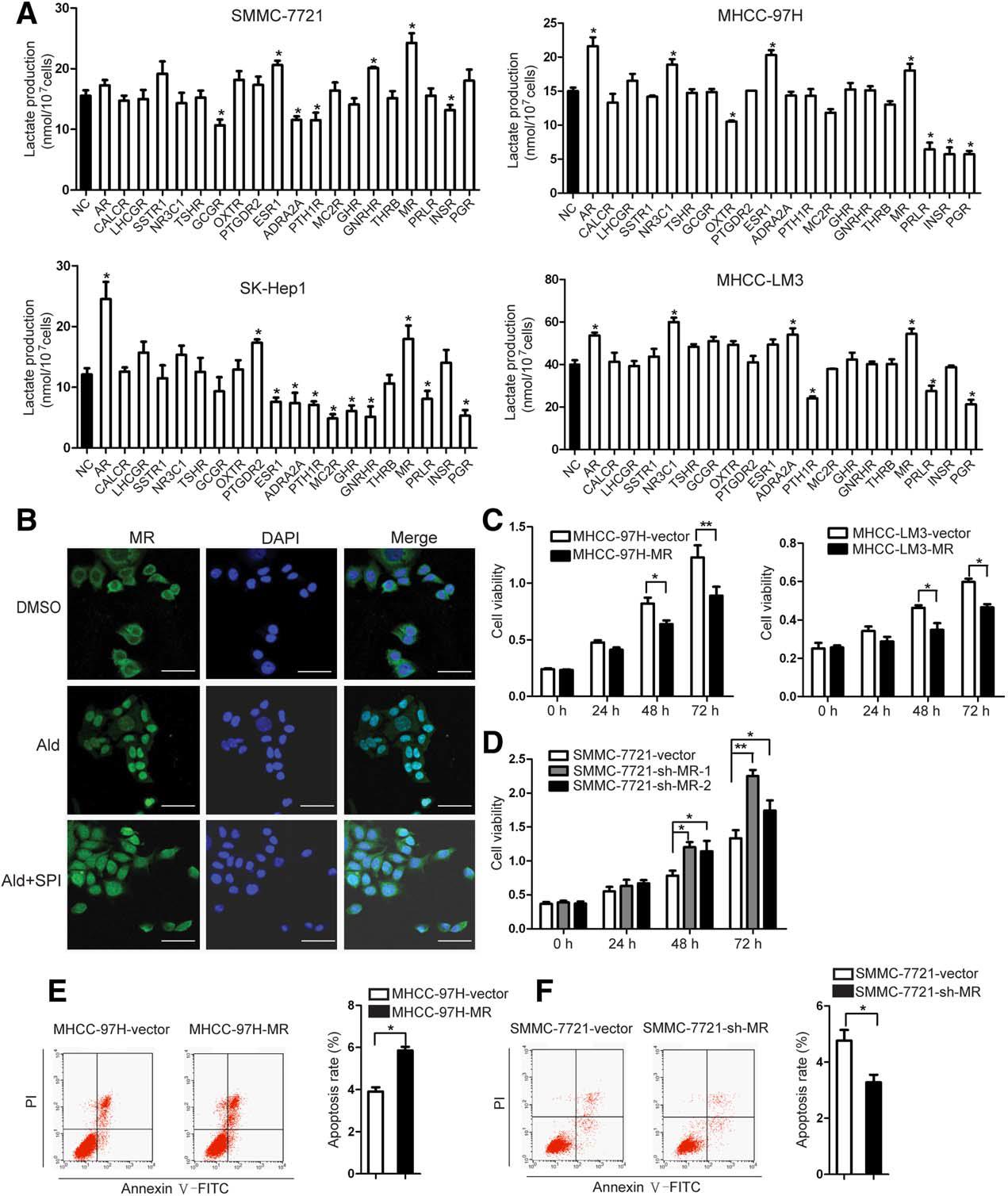 Fig.1 The mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) affects HCC cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis
Fig.1 The mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) affects HCC cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis
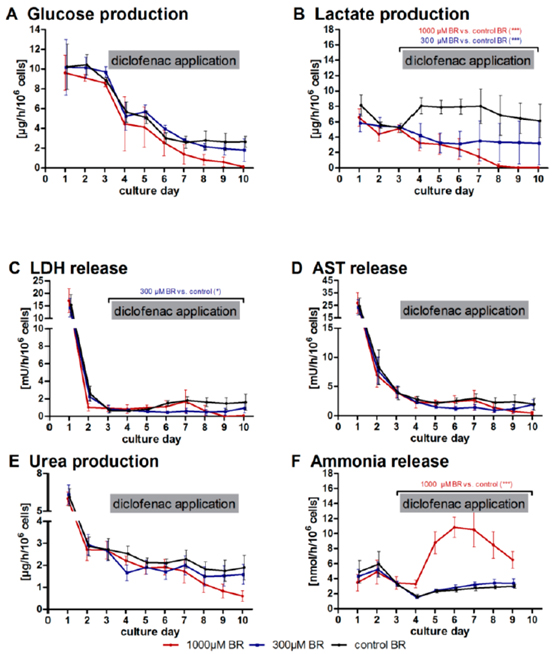 Fig.2 Time-course of clinical parameters in bioreactors with primary human liver cells treated or non-treated with diclofenac
Fig.2 Time-course of clinical parameters in bioreactors with primary human liver cells treated or non-treated with diclofenac
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs in our 2D Based In Vitro Hepatotoxicity Testing Services, please contact us. Let us know what you need and we will accommodate you. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References
- Gómez-Lechón MJ; et al. Cell-based models to predict human hepatotoxicity of drugs. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 31: 149-156.
- Nie, H; et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor suppresses cancer progression and the warburg effect by modulating the miR-338-3p-PKLR axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. HEPATOLOGY. 2015, 62(4): 1145-1159.
- Knöspel, F; et al. In vitro model for hepatotoxicity studies based on primary human hepatocyte cultivation in a perfused 3D bioreactor system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17: 584.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

