- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
Creative Bioarray provides a stable atopic dermatitis (AD) model induced by oxazolone for novel drug discovery and development. Our scientific team has extensive experience helping our clients with the selection of appropriate models and assays, as well as obtaining reliable and accurate results to accelerate the development process of your drugs.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that recurs frequently, resulting from intricate interactions among genetic predisposition, environmental factors, immune dysregulation, and skin barrier dysfunction. Given its complexity, researchers have sought to replicate its symptoms in animal models to gain a deeper understanding of the disease. One such well-established model is the mouse model with oxazolone-induced AD-like skin manifestations. This model is induced through repeated epicutaneous administrations of oxazolone, a powerful hapten capable of eliciting a chronic Th2 hypersensitivity response that closely mimics the initial features observed in human AD. Through this model, we can investigate the pathogenesis of AD and potentially develop more effective therapeutic strategies.
Our Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Available Animal
Mouse - Modeling Method
Step 1: In the sensitization phase, mice are sensitized with oxazolone or vehicle applied to the shaved dorsal skin and ear.
Step 2: In the challenge phase, mice are repeatedly challenged with oxazolone or vehicle applied to the shaved dorsal skin and ear. - Endpoints
- Body weight
- Ear thickness
- Serum analysis: total IgE, TNF-α, etc.
- H&E staining
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
Example Data
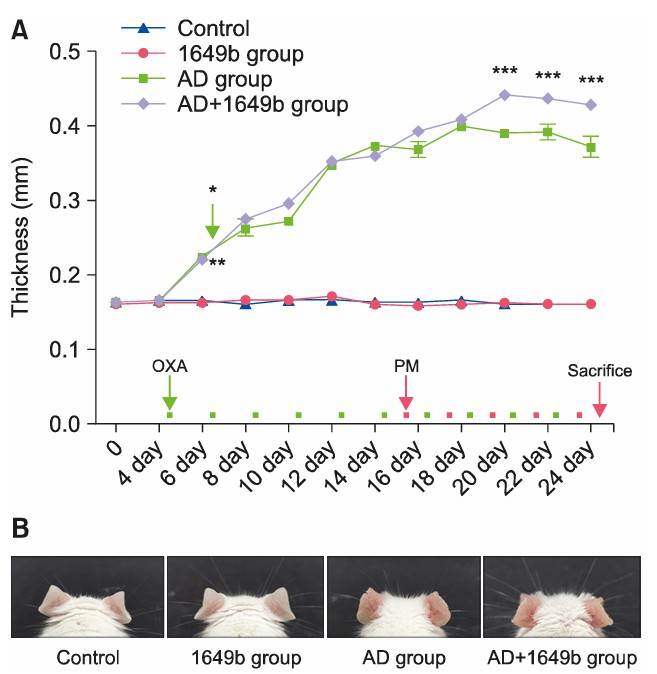 Fig. 1 (A) Ear thickness of mouse. (B) Ear morphology of mouse.
Fig. 1 (A) Ear thickness of mouse. (B) Ear morphology of mouse.
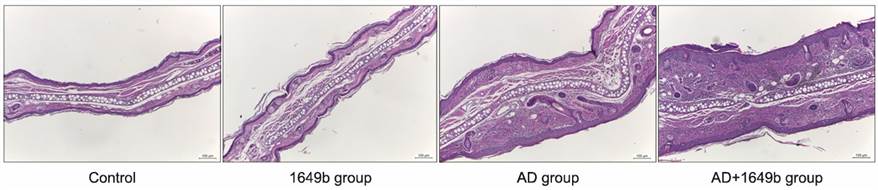 Fig. 2 Histological examination confirmed that epidermal and dermal thickness were increased with dermal inflammatory cell infiltration in the AD+1649b group compared to the AD group (H&E, Scale bar=100 μm).
Fig. 2 Histological examination confirmed that epidermal and dermal thickness were increased with dermal inflammatory cell infiltration in the AD+1649b group compared to the AD group (H&E, Scale bar=100 μm).
In addition, we also provide other AD models that maybe you are interested in:
- 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNBF)-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Calcipotriol (MC903)-Induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is happy to share our cutting-edge technology and extensive expertise in rodent disease models to facilitate our clients' research and project development. If you are interested in our service, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Bae, Y.J., et al. Effects of particulate matter in a mouse model of oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis. Annals of Dermatology, 2020, 32(6): 496.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

