- You are here: Home
- Applications
- 3D Spheroid & Organoid Culture
- Organoid Platform for Drug Development
- Organoid-based High-throughput Screening
Applications
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Organoid-based High-throughput Screening
Organoid-based High-throughput Screening is a powerful tool that bridges the gap between traditional cell culture and in vivo testing. By leveraging the physiological and genetic relevance of organoids, researchers can accelerate the drug discovery process, predict clinical outcomes more accurately, and advance personalized and precision medicine. Despite some challenges, advancements in automation, data analysis, and organoid technology continue to expand the capabilities and applications of this promising field. Creative Bioarray utilizes advanced organoid-based high-throughput screening (HTS) technology to enhance drug discovery, disease modeling, and personalized medicine research. By integrating cutting-edge organoid culture systems with automated HTS platforms, we provide robust, physiologically relevant, and high-efficiency screening solutions.
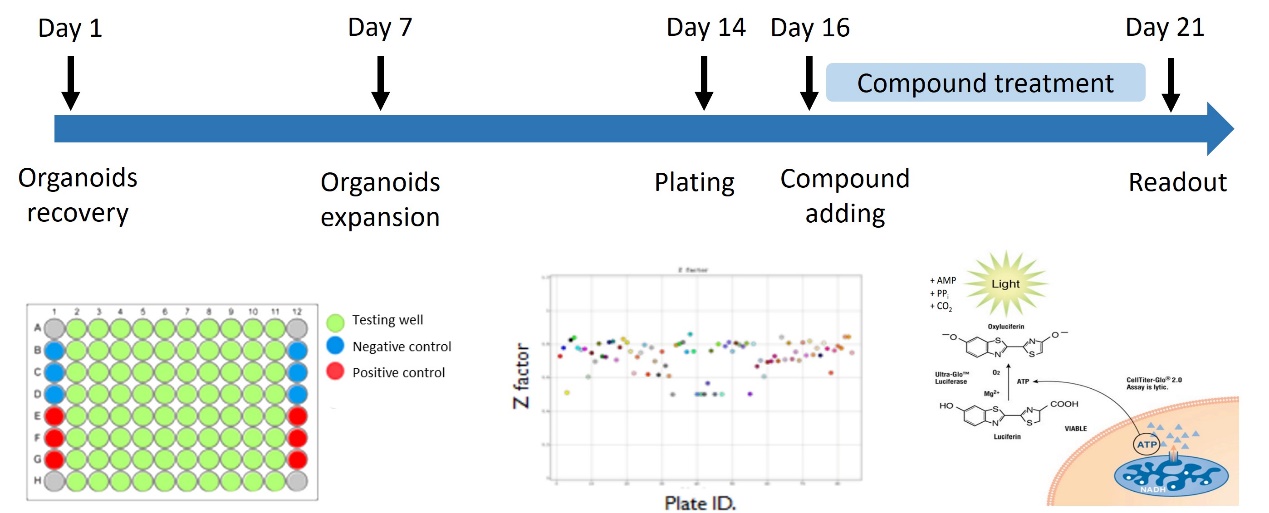 Figure 1. Organoid-based High-throughput Screening
Figure 1. Organoid-based High-throughput Screening
Leveraging the CellTiter-Glo® 3D Cell Viability Assay developed by Promega, we evaluated the viability of organoid cells with precision and reliability. This assay quantifies viable cells in patient-derived organoid (PDO) cultures by detecting intracellular ATP levels, which are a key indicator of metabolically active cells. By measuring ATP content, the assay provides an accurate assessment of cell viability, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of cellular health and functionality within the organoid models.
Creative Bioarray's organoid-based HTS platform offers exceptional opportunities for accelerating drug discovery and advancing precision medicine. Whether you are screening large compound libraries, developing patient-specific therapies, or exploring disease mechanisms, our innovative solutions and expert team can help you efficiently and accurately achieve your research objectives.
Case Study
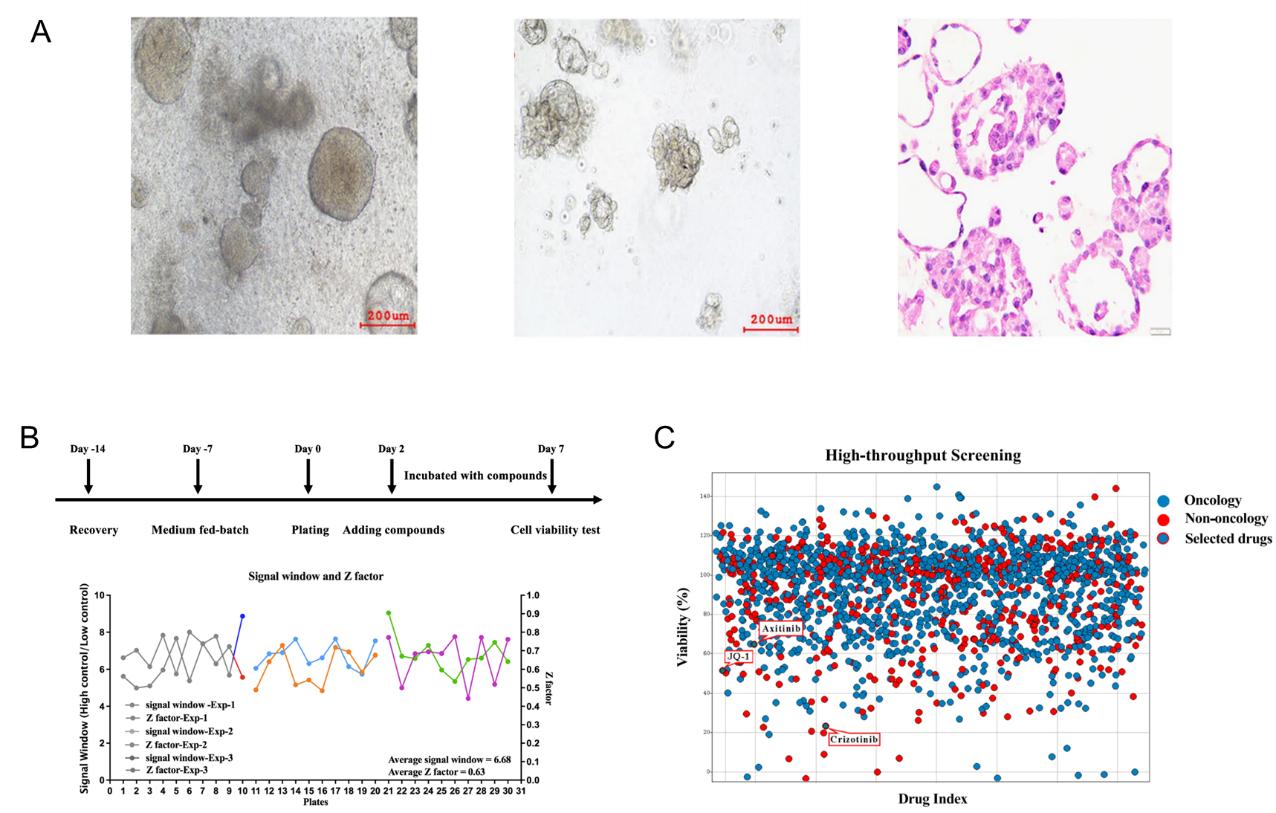 Figure 2. High-throughput drug screening in metastatic PRCC-TFE3 fusion translocation renal cell carcinoma organoids. [1] A. Representative bright-field and HE-stained images of patient-derived organoids (PDOs). B. Timeline for the preparation of PDOs and the high-throughput drug screening process. Assay quality and robustness were evaluated using the signal window (SW) and Z factor across three independent experiments, each consisting of ten plates. C. Primary screening of 1,816 compounds in the high-throughput screening (HTS) assay. Blue spots indicate compounds derived from oncology, while red spots indicate compounds derived from non-oncology. Axitinib, crizotinib, and JQ-1 were identified.
Figure 2. High-throughput drug screening in metastatic PRCC-TFE3 fusion translocation renal cell carcinoma organoids. [1] A. Representative bright-field and HE-stained images of patient-derived organoids (PDOs). B. Timeline for the preparation of PDOs and the high-throughput drug screening process. Assay quality and robustness were evaluated using the signal window (SW) and Z factor across three independent experiments, each consisting of ten plates. C. Primary screening of 1,816 compounds in the high-throughput screening (HTS) assay. Blue spots indicate compounds derived from oncology, while red spots indicate compounds derived from non-oncology. Axitinib, crizotinib, and JQ-1 were identified.
Reference
- Cao, Chuanzhen et al. "Phenotypical screening on metastatic PRCC-TFE3 fusion translocation renal cell carcinoma organoids reveal potential therapeutic agents." Clinical & translational oncology: official publication of the Federation of Spanish Oncology Societies and of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico vol. 24,7 (2022): 1333-1346. doi:10.1007/s12094-021-02774-8
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

