Formalin-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
Creative Bioarray provides a formalin-induced inflammatory pain model for our global clients, facilitating the screening and evaluation of your drug candidates. Our services are tailored to deliver dependable and precise outcomes, thereby expediting the critical phases of your drug development process.
The formalin-induced inflammatory pain model is extensively utilized to investigate both acute and persistent pain in rats or mice, deemed a more reliable representation of clinical pain for screening analgesic drugs. The formalin-induced inflammatory pain model can induce three main behavioral responses flexion, tonic flexion, and licking of the injected limb. Upon intraplantar injection of formalin into the paw of mice or rats, biphasic nocifensive behavior is observed. The initial phase of the nocifensive response manifests within 5 minutes post-injection and typically endures for up to 10 minutes. This is followed by a quiescent phase (sensitization) lasting approximately 10 minutes, during which the subject exhibits relatively reduced pain responses. Subsequently, the second phase of responses commences around the 15th minute and continues for an estimated 40 to 60 minutes. Essentially, the first phase is attributed to the direct activation of nociceptors, such as C-fibers and low-threshold mechanoreceptors, accompanied by the upregulation of substance P. In contrast, the second phase involves central sensitization in rodents, stemming from inflammatory processes within the dorsal horn neurons, including the upregulation of serotonin, histamine, prostaglandins, and bradykinin.
Our Formalin-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
The mid-plantar surface of the hind paw is carefully infused with a formalin solution via syringe.
- Endpoints
- Number of licks
- Lick duration
- qPCR or Western blot
- Histology analysis
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
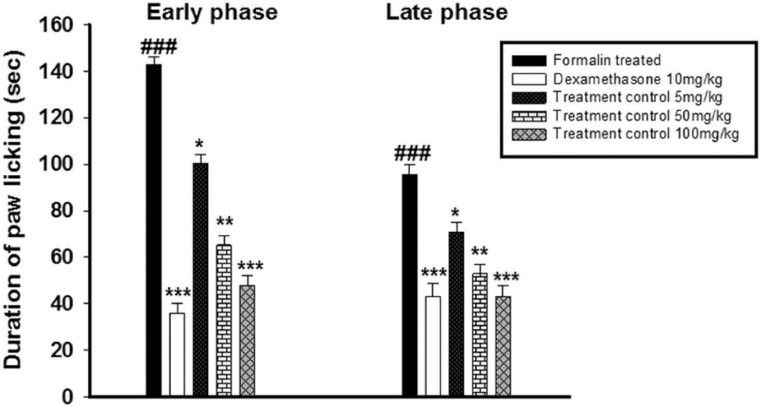 Fig.1 The anti-inflammatory activity of J. adhatoda against formalin-induced biphasic response. (Basit et al. 2022)
Fig.1 The anti-inflammatory activity of J. adhatoda against formalin-induced biphasic response. (Basit et al. 2022)
Moreover, we also provide other inflammatory pain models that maybe you are interested in:
- Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Capsaicin-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
Quotation and Ordering
At Creative Bioarray, our scientists are equipped with profound expertise in the study of disease animal models and are dedicated to providing you with tailored solutions to meet your specific needs. We are eager to collaborate with you, offering personalized pharmacological evaluation services for disease models. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Basit, A., et al. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential of leaf extract of Justicia adhatoda L. (Acanthaceae) in Carrageenan and Formalin-induced models by targeting oxidative stress. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2022, 153: 113322.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models