Cell Cycle Assays
- Service Details
- Features
- Case Studies
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
The cell cycle encompasses the processes of cell growth, DNA replication, and cell division, which are classified into G1, S, G2, and M phases. This tightly regulated mechanism maintains normal cell growth and division, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic information. Under certain conditions, cells can exit the cell cycle into a quiescent state (G0 phase), which is particularly prevalent in some differentiated cell types and stem cells. Additionally, in response to stress or environmental factors, cells may enter senescence, leading to cell cycle arrest in the G1 or G2 phase. Cell cycle assays are essential for understanding cell proliferation dynamics, developmental programs, and responses to external stimuli.
Therefore, researchers have developed numerous experimental techniques to study the cell cycle. Flow cytometry, the first technique developed, remains widely used in this area. Additionally, microscopic imaging, with its ability to capture real-time cellular changes, serves as an important complement to cell cycle research. These methods not only reveal the phase status of cell populations in both live and fixed cells but also provide precise and detailed data support for cell biology research. They are widely applied in various fields, including cancer research, drug development, toxicity testing, and stem cell research. With the precise cell cycle analysis we offer, you can:
- Assess cell proliferation and apoptosis.
- Study the effects of drugs on the cell cycle.
- Understand cell cycle regulation mechanisms.
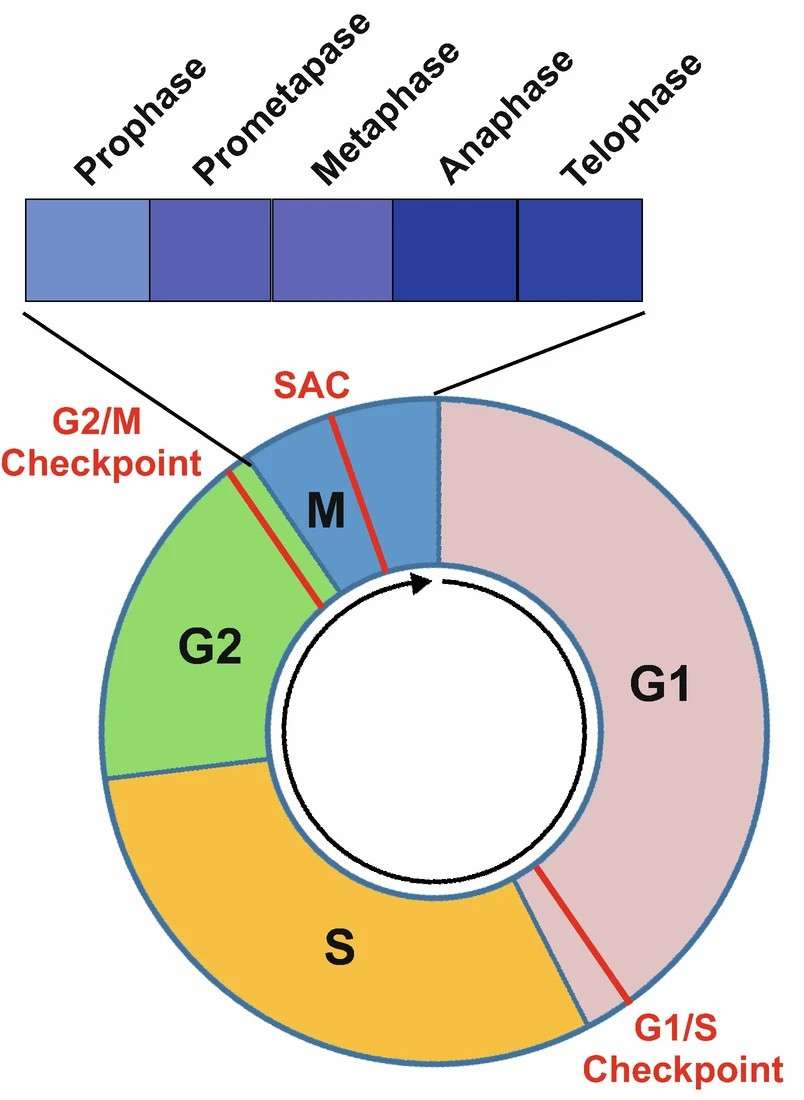 Fig. 1. Diagram to illustrate a complete cell cycle progression (Wang Z., 2022).
Fig. 1. Diagram to illustrate a complete cell cycle progression (Wang Z., 2022).
Creative Bioarray's Cell Cycle Assays:
- Flow cytometry for cell cycle detection:
Suitable dyes are selected to stain DNA and other components within the cells, with these dyes binding specifically to different DNA content during various cell cycle stages.
The stained cells are filtered through a flow cytometer. Single cells are guided through a laser beam, and the scattered light and fluorescence energy of each are taken and recorded.
Given the intensity and distribution of the fluorescent signals, we can discriminate cells between the G1/G0, S, and G2/M phases and correctly calculate the percentage of cells in each phase.
- Microscopic imaging for live cell cycle:
We offer a suitable growth environment for live cells, ensuring normal cell growth and proliferation.
Non-toxic dyes are used to stain live cells.
With high-resolution microscope systems, cutting-edge imaging instruments, and software, we can observe phenomena such as cellular morphology and chromosome activity live from start to finish.
Sample type:
- Fixed cells
- Live cells
Dyes
Depending on the sample type, such as fixed or live cells, and the client's experimental requirements, suitable dyes are selected. We offer commonly used dyes, including:
Propidium iodide (PI),
5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU),
Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU),
7-amino actinomycin-D (7-AAD),
4'6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI),
Hoechst 33342 and Hoechst 33258,
And other optimized dyes for live cell applications.
Features
Adopting high-sensitivity and high-resolution flow cytometry tools to accurately detect weak fluorescent signals and ensure the accuracy of cell percentage calculations at all stages of the cell cycle.
Using a high-definition and high-frame-rate micro-imaging system to accurately capture the most subtle dynamic changes during cell division.

Providing customized cell cycle analysis services according to customers' specific needs.

Providing customers with detailed and comprehensive data reports, including not only the test data but also the professional interpretation and analysis of the data.
Case Studies
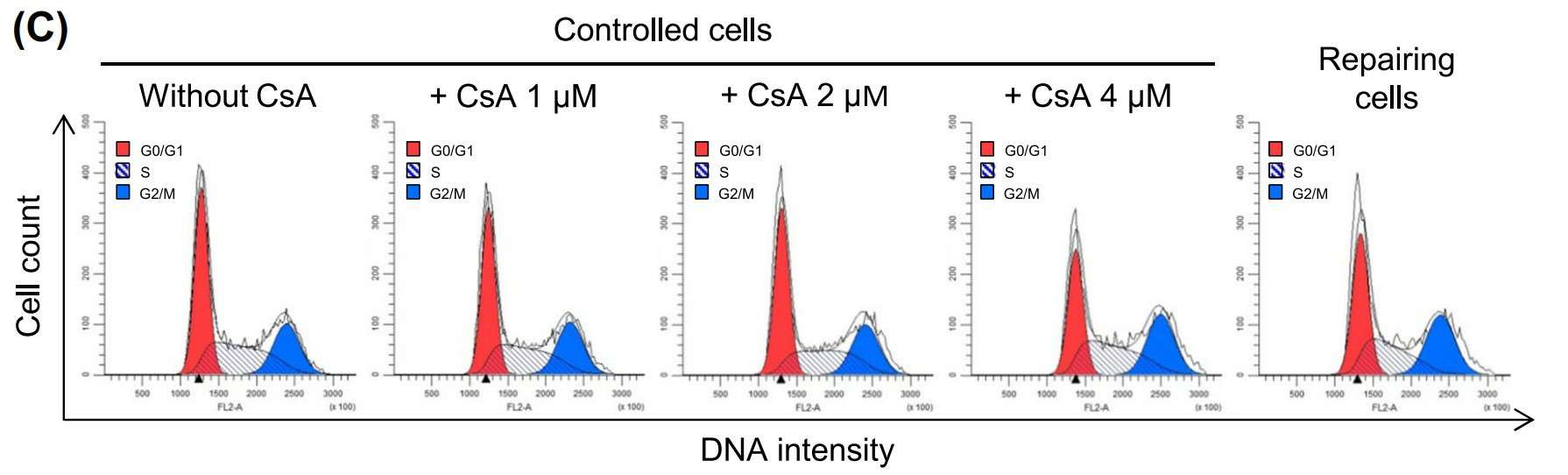 Fig. 2. Cell cycle shift by CsA at non-toxic doses. Cell cycle analysis was performed on CsA-treated cells compared to repairing and controlled cells. (Khamchun S, Thongboonkerd V., 2018).
Fig. 2. Cell cycle shift by CsA at non-toxic doses. Cell cycle analysis was performed on CsA-treated cells compared to repairing and controlled cells. (Khamchun S, Thongboonkerd V., 2018).
FAQ
1. Can cell cycle analysis be performed on different cell types?
Yes, our services are applicable to various types of cells, including adherent and suspension cells.
2. What are the requirements for samples?
For flow cytometry detection, cell samples need to maintain certain viability and concentration, with specific requirements varying by cell type. Generally, cells should be in good growth condition, avoiding excessive cell clumps and debris. For fixed cells, the quality of fixation is important to avoid over or under-fixation impacting results. For microscopic imaging of live cells, suitable medium and culture conditions information are needed to ensure normal cell growth during observation.
3. What are the pros and cons of flow cytometry versus microscopic imaging?
Flow cytometry is suitable for large-scale, rapid analysis but lacks spatial resolution; microscopic imaging provides detailed structural and dynamic information at the cellular level but takes longer to process and analyze. The method choice depends on research objectives and sample characteristics.
Quotations and Ordering
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day! We thank you for choosing Creative Bioarray services! If you want to perform the analysis in-house, Creative Bioarray also provides a Cell Cycle Analysis Kit to assist with your research.
References
- Wang Z. Cell Cycle Progression and Synchronization: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. 2579:3-23.
- Khamchun S, Thongboonkerd V. Cell cycle shift from G0/G1 to S and G2/M phases is responsible for increased adhesion of calcium oxalate crystals on repairing renal tubular cells at injured site. Cell Death Discov. 2018. 4:106.
Explore Other Options

