- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
Creative Bioarray's specialized focus on pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) models positions us as a pivotal resource for the research and development of innovative therapeutic interventions aimed at combating PAH. Our PAH models are meticulously designed to simulate the complex pathophysiology of PAH, offering an invaluable platform for scientists to explore, validate, and refine potential treatments. With a commitment to excellence and innovation, we continue to advance the frontiers of PAH research, ensuring that our clients have access to the most sophisticated and reliable preclinical models to accelerate their drug development pipelines.
PAH is a chronic condition marked by a gradual increase in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP >25 mmHg), culminating in right heart failure and mortality. PAH is characterized by aberrant remodeling of the small peripheral lung vasculature, resulting in the progressive narrowing of arterial lumens. This disease is multifactorial and heterogeneous, with various pathogenetic alterations observed within similar phenotypes. Factors leading to this disease include environmental triggers, shear stress, genetic susceptibility, parasites and infections, and systemic and circulating factors.
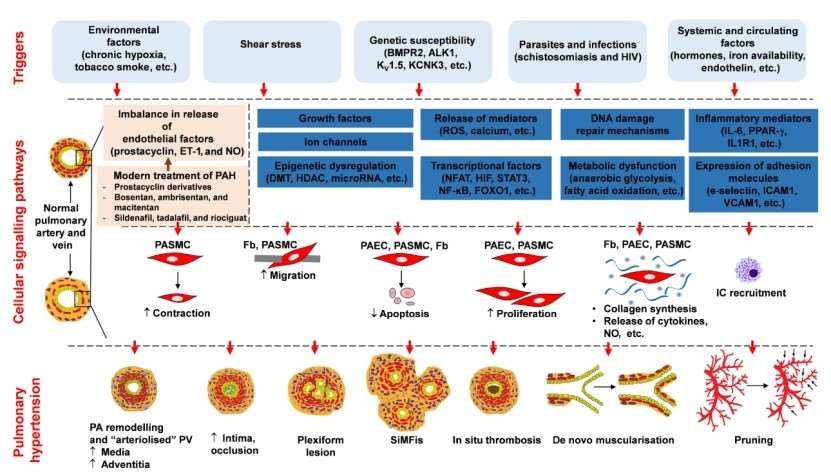 Fig. 1 Patho-mechanisms underlying PAH. (Sommer et al. 2021)
Fig. 1 Patho-mechanisms underlying PAH. (Sommer et al. 2021)
Our Animal Models of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
Creative Bioarray has meticulously developed and refined two main animal models of PAH, tailored to assist our clients in the critical process of screening and evaluating potential drug candidates.
- Monocrotaline (MCT)-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Model
- Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Model
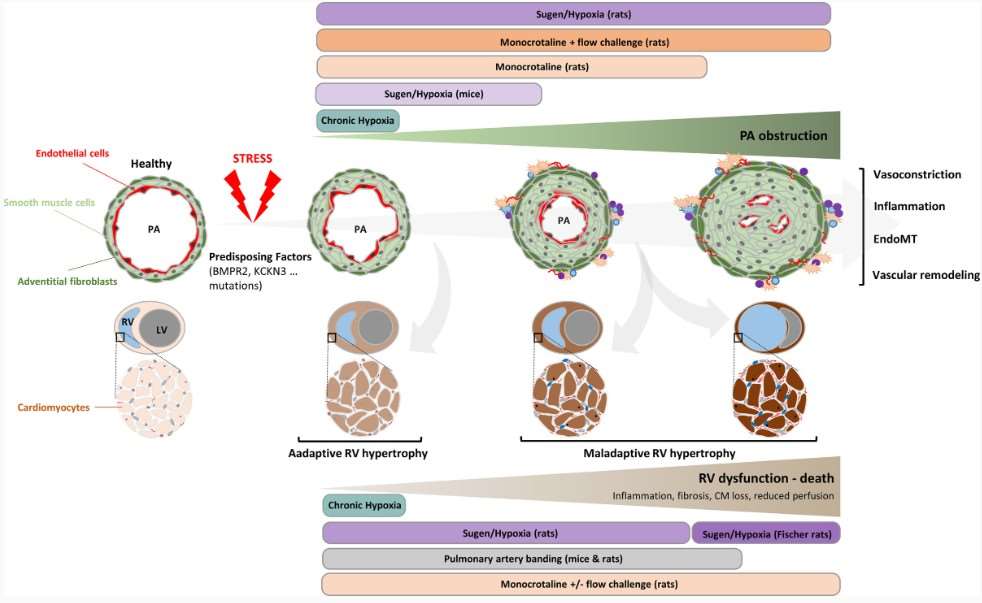 Fig. 2 Schematic progression of PAH with animal models commonly used to address different aspects of the pathophysiology and test candidate treatments or preventive interventions. (Boucherat et al. 2022)
Fig. 2 Schematic progression of PAH with animal models commonly used to address different aspects of the pathophysiology and test candidate treatments or preventive interventions. (Boucherat et al. 2022)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray boasts a wealth of experience in conducting in vivo efficacy studies, equipping us with a profound understanding of the intricacies required to meticulously design and execute these studies. Our expertise enables us to adeptly assist our clients in achieving optimal results while efficiently utilizing minimal resources. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Sommer, N., et al. Current and future treatments of pulmonary arterial hypertension. British journal of pharmacology, 2021, 178(1): 6-30.
- Boucherat, O., et al. The latest in animal models of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure. Circulation research, 2022, 130(9): 1466-1486.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

