Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
In Vitro DMPK Services
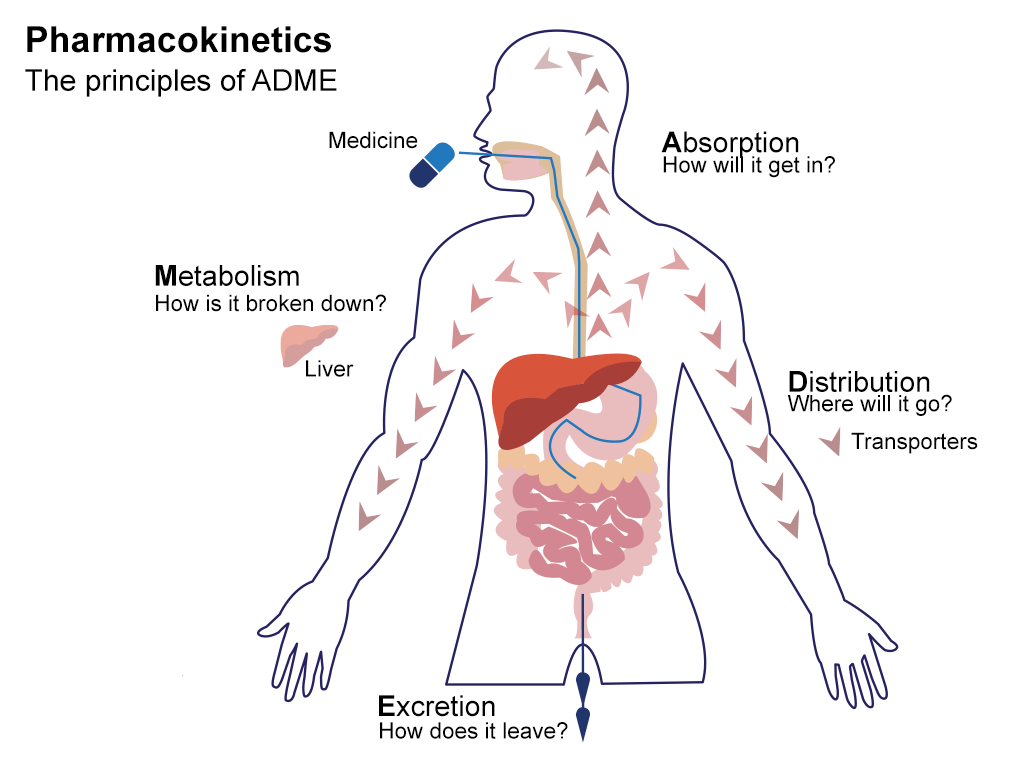
ADME is short for "absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion." The four properties determine the drug exposure to tissues, the drug level within a body. Also, a compound's metabolic process can help predict the bioactivity and bioavailability of a drug. Therefore, understanding the ADME properties of a compound is essential to drug development.
Creative Bioarray provides a variety of in vitro ADME/PK services, including high-throughput ADME screening, in vitro binding, in vitro metabolism, in vitro permeability, and transporter assays.
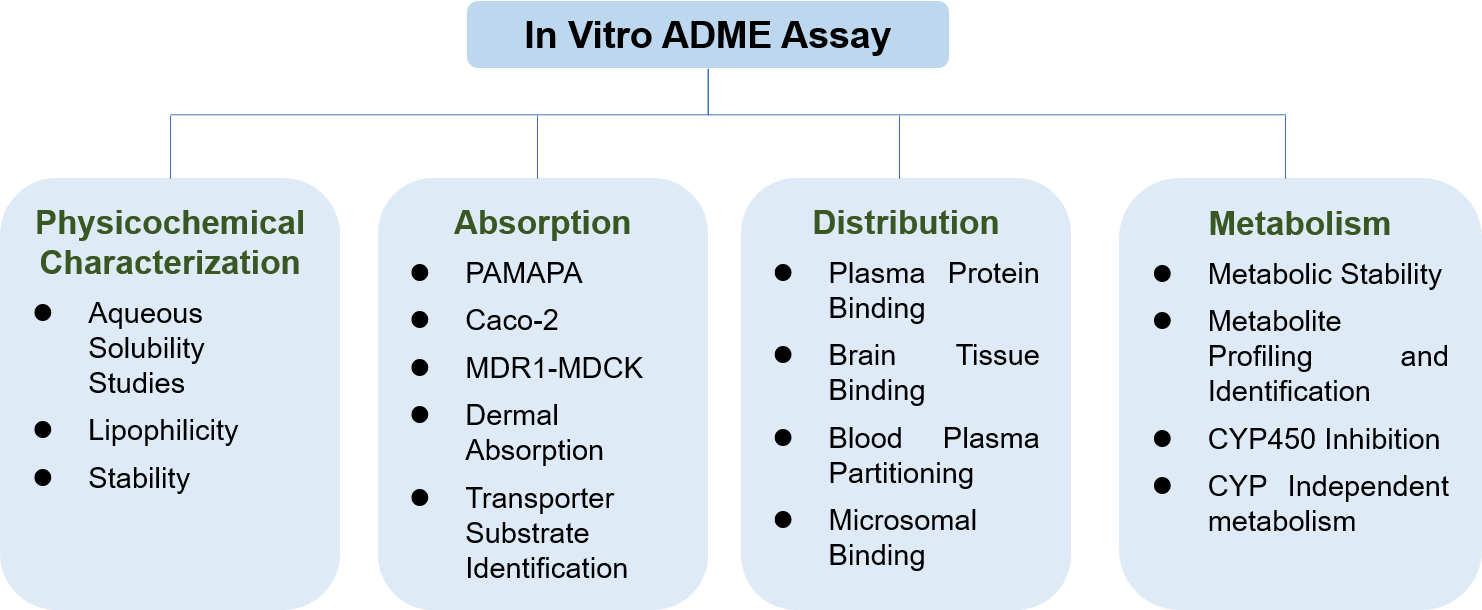
Physicochemical Characterization
Physicochemical properties of a drug include lipophilicity, stability, molecular size, ionization, hydrogen bonding, solubility, etc. Understanding the physicochemical properties of compounds are fundamental for drug formulation development and absorption, distribution studies in vivo.
Permeability and Absorption
Drug absorption is drugs' movement into the bloodstream. This process is influenced by many factors, including drugs formulation, physicochemical properties, and route of administration. Regardless of the route of administration, the drug must first be dissolved and absorbed before it can exert a therapeutic effect. By intervening in factors that affect drug absorption, its pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics can be changed.
Drugs' permeability across biological membranes is a critical factor that influences the absorption and distribution. Drugs may cross cell membranes through passive diffusion, facilitated passive diffusion, active transport, and pinocytosis. The drug's physicochemical properties (such as lipophilicity and molecular size), and membrane-based efflux, can lead to poor permeability.
- Dermal Absorption
- Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA)
- Caco-2 Permeability
- MDCK Permeability
- Transporter Substrate Identification
Drug Distribution
Drug distribution describes the reversible movement of a drug from one location to another within the body. Usually, it refers to a drug transfer from the blood to various tissues. Theoretically, different body parts can receive different doses and remain for a different amount of time.
A drug's distribution in the body depends on many aspects. For example, drugs' physicochemical characters, like lipophilicity and aqueous solubility, decide whether a drug tends to stay in fluid tissue or lipid tissue. Permeability is another factor that affects distribution. A drug has different penetration abilities to cross different tissue membranes, leading to a different volume of distribution. Tissue and plasma protein binding is the third factor. If a drug binds to proteins circulating in the blood, It is difficult to penetrate from blood vessels to tissues efficiently. Because the drug binds tightly to the protein in specific tissues, it will also prolong the action time and accumulation of the drug.
After entering the body for a particular time, drugs will be eliminated by excretion or metabolizing to one or more metabolites. The safety and efficacy of a drug can be significantly affected by metabolism routes. Individual differences may affect the metabolic rate of drugs eliminated only through a single metabolic pathway, resulting in significant differences in the concentration of drugs and drug metabolites in blood and tissues. Achieve the safe and effective use of drugs may require dose adjustments for different individuals.
Metabolism usually occurs in the liver, and in vitro drug metabolism is measured by the activity of enzymes contained in the cytochrome CYP450 superfamily. Drug concomitants may cause interactions of inhibiting or inducing the CYP450 enzymes.
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- Metabolic Stability Assays
- Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Assays
Quotation and ordering
Creative Bioarray, staffed with well-experienced experts in the field, is dedicated to providing its clients with the most reliable and producible results at a competitive price. We are capable of accommodating the needs of our clients and achieving the goals of the study. Please contact us to find out more about our services.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

