
Creative Bioarray provides an easily accessible reference for histological techniques. Here, we detail the techniques for investigating the expression of many different types of targets in a variety of tissue and samples from sections and cells, covering a wide range of techniques from biospecimen treatment to tissue sections, tissue staining, and various types of immunostaining. We provide step-by-step guide to techniques including guidelines, methods and notes.
Classification: Biospecimen Collection, Processing and Storage.
Guidelines: A wide variety of specimen types may be collected for storage, depending on availability and study goals, such as tissues that from autopsy and transplant, cell lines, and so on.
Classification: Biospecimen Collection, Processing and Storage.
Guidelines: Specimens are processed according to the study design and the methods most appropriate for preserving the analytes of interest. For a particular specimen type and analysis, several processing methods may be appropriate.
Classification: Biospecimen Collection, Processing and Storage.
Guidelines: Depending on the intended laboratory analyses, and other considerations, specimens and their aliquots may be stored under different suitable conditions.
Classification: Biospecimen Collection, Processing and Storage.
Guidelines: Driven by advances in molecular technologies, information management is critical to the molecular epidemiology research enterprise.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Freshly harvested tissue of interest should be immediately fixed to avoid degradation.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Decalcification is required for processing bone tissue in routine diagnostic practice. Control of this step is crucial because it may have important consequences for establishing the diagnosis.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Decolorization refers to the process of removing brightly colored organic impurities from the sample mixture. The procedure is usually carried out in the solution phase after the solid product and impurities are dissolved in a suitable solvent.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: The process of replacing water contained in tissues or cells with a dehydrating agent is called tissue dehydration.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: After the tissue is completely transparent with the transparent agent, it is placed in the paraffin wax which is melted at about 65°C. The process of impregnation in the electric thermostat at 65°C is called wax immersion.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Embedding is to remove the fixed, dehydrated, transparent and wax-soaked tissue blocks from the final wax bath and place them into the embedding frame filled with molten paraffin wax. Embedding into blocks enables the tissue and embedding agent to be fused together and cooled rapidly. This procedure is called embedding.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Snap freezing refers to the ultra-low temperature freezing method used to prepare high-quality cryosections. The method below uses a super-cooled bath of 2-methylbutane (-150°C) that can freeze a standard specimen within 1 minute, thus, greatly reducing crystal formation.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: Tissue clearing is a broad term that defines techniques that have the final goal of reducing the opacity of biological tissues to see features deep within a sample while maintaining its original structure.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Paraffin sectioning is the procedure of cutting thin slices of tissue that has been dehydrated and infiltrated with wax using specialized equipment.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Certain tissues have special cutting protocols, most common for biopsies including liver, kidney, lung, striated muscle, spleen, skin, thyroid and breast carcinoma.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Since as thin as 0.5-2 μm, they are also called semi-thin sections, and are an effective positioning method in the ultrathin sectioning technique for electron microscopy.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Frozen tissue sectioning is the use of freezing to harden the tissue in a relatively short period of time, which can be cut into very thin sections and applied to various examinations.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Serial sectioning is the procedure of collecting and mounting sections on a slide in the sequential order in which they were cut on the microtome.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: The skin is the largest organ of the human body and covers the whole body. The skin tissue structure is relatively complex, which poses certain difficulties for section making.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: Histology of the brain, for obvious reasons, is a research tool rather than a clinical tool.
Classification: Tissue Sections.
Guidelines: To determine whether an organ is a tumor lesion, a pathological section is required. Only through tumor pathology section examination can the nature of the tumor, whether it is benign or malignant, be clarified.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Carmine is a commonly used stain in histology used by early botanists such as John Hill in their studies in 1770s. The stain was used to study microscopic tissue structures when in ammoniacal solution form and it is still used today in histologic studies.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: The haemitin demonstrates cell nuclei. Full cellular detail is obtained by counterstaining with the eosin mixture.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Silver Nitrate has had a long usage in historical staining techniques and is still used in modern pathology. Grocott-Gomori’s Methenamine Silver (GMS) stain is a histological silver staining. Its initial application to assess missing tissues and diseases in the liver and the rectum and then used for the identification of carbohydrates in fungal microorganisms.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Giemsa stain was a name adopted from a Germany chemist scientist, for his application of a combination of reagents in demonstrating the presence of parasites in malaria. It belongs to a group of stains known as Romanowsky stains.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: The Gram staining method was named after a Danish inventor Hans Christian Gram, who invented it as an approach to differentiating bacteria species in 1875. The method is often used in modern histology especially in paraffin fixatives for tissue sectioning.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Masson’s Trichrome Staining is a histological staining method used for selectively stain collagen, collagen fibers, fibrin, muscles, and erythrocytes. It uses three stains for staining hence the term Trichrome. These are Weigert’s Hematoxylin, Biebrich scarlet-acid fuchsin solution and Aniline blue.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Periodic-Acid Schiff (PAS) staining technique is used in histochemistry and histological studies to demonstrate the presence of carbohydrates and carbohydrate compounds such as polysaccharides, mucin, glycogen, and fungal cell wall components. It has been used to detect glycogen in tissues such as the skeletal muscles, the liver, the cardiac muscles.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: The subependymal zone is located near the striatum in the wall of the lateral ventricle and produces olfactory bulb interneurons.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: Depending on the composition and assembly structure, the cytoskeleton can be divided into microtubules (MT), microfilaments (MF), and intermediate fibers (IF). Microfilaments are prevalent in a wide range of cells and have a role in cell shape and movement.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: Transmission electron microscopy is a technique for observing the fine details of organelles in cells or tissues. This protocol is to be used to examine the membrane structure in cells with or without virus infection. Modifications should be made if users want to get images from tissues.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: This technique is used to study mice's respiratory and ocular systems. This method involves collecting tissue samples from the trachea and eyes of mice and embedding them in a microscopic medium for analysis. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) allows for high-resolution imaging of the samples, providing detailed information about the structure and function of these systems.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Live cell labeling refers to the process of labeling cells with specific biomolecules, such as fluorescent dyes, antibodies, or other probes, while the cells are still alive and active.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: In vivo imaging of living animals uses two main techniques, bioluminescence and fluorescence. Bioluminescence is the labeling of cells or DNA with the luciferase gene (Luciferase). At the same time, fluorescence techniques use fluorescent reporter genes such as green fluorescent protein, red fluorescent protein, and fluorescein such as FITC, Cy5, Cy7, and quantum dots for labeling.
Classification: Imaging Observations.
Guidelines: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a technique for observing the fine details of organelles in cells or tissues. This protocol is to be used to examine the membrane structure in cells with or without virus infection.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: Staining FFPE (formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded) tissue with streptavidin-HRP (horseradish peroxidase) and biotin involves utilizing the strong affinity of biotin for streptavidin and the enzymatic activity of HRP for visualizing specific targets within the tissue.
Classification: Staining and Labeling.
Guidelines: DAPI is a popular nuclear counterstain for use in multicolor fluorescent techniques. Its blue fluorescence stands out in vivid contrast to green, yellow, or red fluorescent probes of other structures. When used according to our protocols, DAPI stains nuclei specifically, with little or no cytoplasmic labeling.
Classification: Tissue Handling and Fixation.
Guidelines: GMA embedding involves infiltrating and embedding biological tissue specimens in a polymerized GMA resin, allowing for the production of thin sections for histological examination under a microscope.
Classification: Biospecimen Collection, Processing and Storage.
Guidelines: The buffy coat is a fraction of whole blood that is rich in white blood cells (WBCs) and is named after its "buff-like" color. Preparation of a buffy coat from whole blood samples precludes many downstream applications. During processing, whole blood is centrifuged to form distinct blood fractions.
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Cells share many common features, yet they can look wildly different. In fact, cells have adapted over billions of years to a wide array of environments and functional roles. Creative Bioarray provides an easily accessible reference for cellular techniques from cell isolation to cell culture. Here, we provide step-by-step guide to techniques including guidelines, methods and notes.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Natural killer cells are an interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent natural killer (NK) cell line derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a 50-year-old white male with acute non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The cells are rounded or elliptic, transparent and grow in clumps.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Because neural stem cells (NSCs) have the potential of self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, the method of suspended neural bulb culture can be used to obtain and study.
Classification: Cell Resuscitation, Passage and Cryopreservation.
Guidelines: Cell subculture is one of the conventional methods of cell culture. once the cells are overgrown in the flask, they need to be diluted and seeded into multiple vials before the cells can continue to grow. This process is called passage.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Neural stem cells (NSCS) are special cells with self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation potential. It not only can be used to explore the molecular mechanism of nervous system development, but also can be used as an alternative means for the treatment of central nervous system injury.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: Cultured cells or tissue samples are made into single-cell suspension, and then cells are incubated in a flow tube or EP tube with fluorescence-labeled or unlabeled antibodies (It depends on the antibody). There are several ways of incubation, such as ice incubation, normal temperature incubation, and 37°C incubation.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: In a flow cytometry separation device, different cell subpopulations are labeled with different fluorescent antibodies and carry different physical (particle size, density, fluorescence intensity) information to separate target cells from the mixed cell population.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Mouse embryonic fibroblasts are suitable feeder cells for mouse or human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. They can produce factors that inhibit the autonomous differentiation of embryonic stem cells and promote the proliferation of embryonic stem cells, which can effectively promote the proliferation of cells and maintain their undifferentiated characteristics and pluripotency.
Classification: Cell Resuscitation, Passage and Cryopreservation.
Guidelines: The process of ESCs’ culture includes three parts of work, the culture of feeder cells, the preparation of feeder monolayers, and the culture of ESCs.
Classification: Cell Resuscitation, Passage and Cryopreservation.
Guidelines: If mESCs need to be frozen, it is best to do so at an early stage of culture. Select cells with normal cell morphology and karyotype, and store them in liquid nitrogen for a long time. The method is the same as that for freezing and resuscitation of general cell lines, while the freezing solution is based on the culture medium with 10%-15% DMSO.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are abbreviated as ES, EK, or ESC cells. They are a class of cells isolated from early embryos (before the proto-intestinal stage) or primitive gonads, which have the properties of unlimited proliferation, self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation in vitro in culture. ES cells can be induced to differentiate into almost all cell types of the organism, both in vitro and in vivo environments.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: When ESCs are injected into the host blastocyst cavity, they can integrate with the cells of the host inner cell mass and develop together into individuals, i.e., a chimera. ESCs originating from different animal strains have different genetic characteristics, and observation of these genetic characteristics can determine whether ESCs integrate, differentiate, and develop.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: In vitro, differentiation of ESCs usually requires the formation of embryoid bodies (EBs), which are three-dimensional aggregates of cells containing all cell types in three germ layers.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Karyotype analysis is the study of mid-chromosome divisions. With the help of banding techniques, chromosomes are analyzed, compared, classified, and numbered according to their length, the location of mitotic sites, the ratio of long and short arms, the presence or absence of follower and other characteristics, and diagnosed according to changes in chromosome structure and number.
Classification: Cell Resuscitation, Passage and Cryopreservation.
Guidelines: In 1996, Thomson et al. established eight ES cell lines from urban monkeys, two of which were cultured in vitro for more than 1 year and maintained a normal karyotype and undifferentiated state, and could differentiate into various cell types including trophectoderm and endoderm when the feeder layer was removed.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are totipotent embryonic cells isolated from the inner cell mass (ICM) or primordial germ cells (PGCs) of animal or human blastocysts and screened by in vitro differentiation inhibition culture. ESCs can differentiate into one or more cell types with appropriate factor induction.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: A certain dose of mitomycin can stop the cells from dividing, but it does not cause immediate death and can sustain life for a period of time in vitro. Therefore, mitomycin can be used to treat feeder cells so that the feeder cells do not divide, but can survive and secrete factors that inhibit the differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and promote the value-added of embryonic stem cells to ensure the growth of ES cells.
Classification: Cell Staining.
Guidelines: Mammalian mulberry embryos, blastocyst cells, and ESCs express alkaline phosphatase (AKP). AKP hydrolyzes sodium α-phosphogalactone in the incubation solution under alkaline (pH 9.0-9.6) conditions to produce α-offering phenol, which is then coupled with azo salts to produce an insoluble sunlight-resistant dye for color development.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: To grasp the proliferation rate of cells, the common methods include cell count at different time points, the MTT method, and the CCK8 method to draw proliferation curves. The following is a brief description of the method for plotting proliferation curves using the CCK8 method as an example.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: Flow cytometric analysis is a technique for rapid quantitative analysis and sorting of cells or other biological particles (such as microspheres, bacteria, small model organisms, etc.) arranged in a single column in a liquid stream, one by one, and is widely used in all aspects from basic research to clinical practice.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Embryonic fibroblasts, the major cellular component of sparse connective tissue, are differentiated from mesenchymal cells during the embryonic period.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: The generation of human iPS cells has had a tremendous impact on the treatment of degenerative diseases. Because iPS cells have similar functions to ES cells, but bypass many of the ethical and legal bottlenecks that embryonic stem cell research has been facing. So, they have a very promising application in the medical field and have become a hot spot for stem cell research.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: Apoptosis or programmed cell death (PCD) is one of the cellular life phenomena, which was proposed by Kerr in 1972. It plays a very important role in embryonic development, tissue repair, and clearance of self-reactive T lymphocytes in the body. The deregulation of apoptosis can lead to the development of various clinical diseases.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Cell subpopulation analysis analyzes a population of cells based on whether they express a specific protein and is a common experiment used in cell identification. Cells are generally labeled by specific antibodies and isolated by methods such as flow cytometry or magnetic beads. Two methods of cell sorting are commonly used - flow cytometric sorting and immunomagnetic cell sorting.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: iPSCs are similar to embryonic stem cells (ESCs) in many characteristics, but they are more readily available than ESCs and are ideal for studying the mechanisms of targeted cell differentiation and differentiation.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: Cell quantification refers to the process of determining the number or concentration of cells in a given sample. The protocol describes a method of cell quantification.
Classification: Organoid Construction.
Guidelines: Organoids are a complex collection of cells grown in a three-dimensional (3D) medium, which are derived from embryonic stem cells (ESC), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), or adult stem cells (ASC). Organoids are passaged with a combination of mechanical and enzymatic dissociation.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC), is a cell with a single nucleus in peripheral blood, including lymphocytes, Monocyte, Dendritic Cell (DC), and a small number of other cells. PBMC can be obtained from healthy human or animal donors’ Peripheral blood, obtained by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation (IPHASE/Huiji and source), magnetic bead sorting, and other steps.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The neuro-electrophysiological examination is an extension of neurological examination, which includes the examination of peripheral and central nerves, and its methods include electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction measurement, special examination, evoked potential (EP) examination, and also low-frequency electrodiagnosis.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: The process of fusion of two or more cells of the same or different species into one cell under natural conditions or by artificial means (physical, chemical, or biological) is called cell fusion.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The Colony-Forming Cell (CFC) assay, also known as the Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) assay, is the current gold standard for in vitro testing of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell function.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The Mouse Hematopoietic Stem Cell Long Cycle Culture System (LTC) can be used to detect and count primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells. The LTC culture system has also been used for the generation and quantification of lymphocytes.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: Cell viability is defined as the number of healthy cells in a sample. The measurement of cell viability plays an important role in all forms of cell culture. Sometimes it is the main purpose of the experiment as in toxicity assays, or it can be used to correlate cell behavior to the number of cells.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The soft agar colony formation assay is a well-established method for characterizing this capability in vitro and is considered to be one of the most stringent tests for malignant transformation in cells.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: When performing certain immunological experiments, pure T and B lymphocytes need to be isolated first. This experiment describes the procedure of the T and B lymphocyte separation test.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: Through the ectopic expression of four transcription factors, Oct4, Klf4, Sox2 and cMyc, human somatic cells can be converted to a pluripotent state, generating so-called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Thus, iPSCs have attracted considerable attention for disease modeling studies, the screening of pharmacological compounds, and regenerative therapies.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: Derivation and maintenance conditions have a critical role in determining the iPSC quality, mainly due to the involvement of animal products and feeder cells. We developed a simple procedure to derive and maintain hiPSCs in chemically defined media.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: The induced pluripotent stem (iPS) reprogramming system uses vectors based on replication in competent Sendai virus (SeV) to safely and effectively deliver and express key genetic factors necessary for reprogramming somatic cells into iPSCs.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Phagocytes have the function of phagocytosis and digestion of foreign substances (bacteria, sheep erythrocytes, chicken erythrocytes, etc.), and play an important role in nonspecific immunity of the organism.
Classification: Organelle Separation.
Guidelines: Mitochondria are prepared by tissue homogenization by differential centrifugation in a suspension medium. In a given centrifugal field, the settling velocity of a spherical pellet depends on the density, radius, and viscosity of the suspension medium.
Classification: Cell Lines Construction and Culture.
Guidelines: The Mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC) or mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) is a mixture of two unrelated individual lymphocytes cultured together, due to the different histocompatibility antigens on the lymphocyte membranes of the two, they can stimulate each other, resulting in the division of each other's lymphocytes to proliferate and transform.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: The derivation of specific neuronal or glial cell types from ESCs invariably includes the production of neural stem cells (NSCs), the self-renewing, pluripotential stem cells of the nervous system, capable of differentiating into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
Classification: Cell Differentiation.
Guidelines: The generation of the different neural lines originates in adult neural stem cells that can self-renew or differentiate into astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, or neurons in response to specific stimuli.
Classification: Cell Differentiation.
Guidelines: Astrocytes are a type of glial cell found in the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord. They constitute the largest population of glial cells and play essential roles in the development, maintenance, and functioning of the CNS. It is important to establish effective methods to differentiate reliable stem cells, such as neural stem cells, into mature astrocytes.
Classification: Cell Differentiation.
Guidelines: Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) to a functional cell type, including neurons, is the foundation for the application of hESCs. We describe here a reproducible, chemically-defined protocol that allows directed differentiation of hESCs to nearly pure neuroectodermal cells and neurons.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: Neural stem cells (NSCs) play a unique role in basic research and clinical application. Here, we provide a protocol for differentiating mouse fibroblasts into neural stem cells.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The lymphocyte conversion rate can reflect the level of cellular immunity. Therefore, the lymphocyte conversion test can be used as one of the indicators to determine the body's immune function.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: The cytoplasm of living cells contains LDH. Under normal conditions, LDH does not pass through the cell membrane and is released outside the cell when the cell is killed by NK cells.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Basophils are involved not only in tachyphylactic hypersensitivity reactions but also in the body's anti-tumor immune response. Detecting the function of basophils helps in the diagnosis of allergic diseases and the prognosis of tumors.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: In response to biological, chemical, or physical factors, human leukocytes produce a series of biologically active (functional) substances, one of which is called interleukins. Many types of interleukins have been identified, interleukin 8 (IL-8) being one of them, and it has recently been discovered that some cells other than leukocytes also can produce interleukins.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: The stimulation of B lymphocytes by suboptimal doses of anti-IgM antibodies is weak. When interleukin 4 (IL-4) is added, B lymphocytes show a significant increase in DNA synthesis in response to stimulation with sub-adapted doses of anti-IgM antibody, and the amount of 3H-TdR doping correlates with the amount of IL-4.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of live cells separates a population of cells into subpopulations based on fluorescent labeling. Sorting involves more complex mechanisms in the flow cytometer than a non-sorting analysis. Cells stained using fluorophore-conjugated antibodies can be separated from one another depending on which fluorophore they have been stained with.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Recent studies have shown that erythrocytes are also a class of immune cells. This experiment introduces the erythrocyte C3b receptor wreath and immune complex wreath test.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: This experiment describes a method to detect cell survival and growth-MTT analysis assay. The principle of the assay is that the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase in the mitochondria of living cells reduces exogenous MTT to water-insoluble blue-violet crystals of Formazan and deposits them in the cells, whereas dead cells do not have this function.
Classification: Cell Quantification and Sorting.
Guidelines: Cell counting using a hemocytometer is a commonly used technique to determine the concentration of cells in a given sample. The detailed procedure explains how to obtain a viable cell count from a haemocytometer.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Identification of the labeled cells can be applied both in vitro and in vivo to produce a nuclear staining pattern. We provide a method of the 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) protocol.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: If the ambient osmotic pressure continues to fall, the erythrocytes will rupture as they continue to swell, releasing hemoglobin, which is called hemolysis. The erythrocyte membrane is resistant to hypotonic solutions, a characteristic known as the osmotic fragility of erythrocytes.
Classification: Cell Staining.
Guidelines: In this protocol, cells are first activated in vitro, stained for surface antigens, as in the regular staining protocol, and then fixed and permeabilized to allow for anti-cytokine antibodies to stain intracellularly.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: The cell proliferation reagent WST-1 is designed to be used for the non-radioactive, spectrophotometric quantification of cell proliferation, growth, viability, and chemosensitivity in cell populations using the 96-well-plate format.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: Resazurin is a cell-permeable redox indicator that can be used to monitor viable cell numbers with protocols similar to those utilizing the tetrazolium compounds.
Classification: Cell Characterization.
Guidelines: More recently developed tetrazolium reagents can be reduced by viable cells to generate formazan products that are directly soluble in cell culture medium. Tetrazolium compounds fitting this category include MTS, XTT, and the WST series.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: The SRB assay is a colorimetric method used to assess cell viability and measure cellular biomass in biological research and drug discovery.
Classification: Single Cell Isolation and Cloning.
Guidelines: This technique is widely used for the clonal isolation of hybridomas and other cell lines that are not attachment-dependent.
Classification: Single Cell Isolation and Cloning.
Guidelines: This protocol describes how to isolate single cells from a CRISPR-edited pool, and expand and genotype the subsequent clonal populations.
Classification: Single Cell Isolation and Cloning.
Guidelines: The growth of cells in a semisolid medium, whether agar, agarose, or methylcellulose, offers some advantages. The spherical bacteria-like colonies that form from monodispersed cell suspensions offer a means of isolating clones with a minimal amount of effort.
Classification: Single Cell Isolation and Cloning.
Guidelines: Glass chips have two advantages over other clonal isolation techniques. First, visual observation is generally easier; the presence of a single cell can be easily verified. Second, if you have a steady hand, a fairly large number of chips can be picked in a short period.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: This protocol allows the efficient generation of integration-free iPS cells from a small amount of peripheral blood (<1 ml). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are cultured to expand the erythroblast (EB) population.
Classification: iPSC Generation.
Guidelines: This protocol was developed as an efficient and consistent method to produce functional retroviral reprogramming factors. It avoids the need for concentrating virus via ultracentrifugation.
Classification: Cell Nuclear Transplantation.
Guidelines: Nucleus transplantation, where the nucleus of one cell is put into another cell by microinjection. The former is the donor, which can be the stem cell nucleus of an embryo or the nucleus of a somatic cell.
Classification: Cell Viability or Proliferation.
Guidelines: Primary cultures for IHC-Viability assays refer to the use of primary cells derived directly from animal or human tissue samples for IHC analysis aimed at assessing cell viability.
Immunology is the study of the immune system and is a very important branch of the medical and biological sciences. The immune system protects us from infection through various lines of defense. Creative Bioarray provides an easily accessible reference for immunology techniques, including immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), immunoprecipitation, etc. We provide step-by-step guides to techniques including guidelines, methods, and notes.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: Immunohistochemistry (or IHC) is a method for demonstrating the presence and location of proteins in tissue sections. Though less sensitive quantitatively than immunoassays such as Western blotting or ELISA, it enables the observation of processes in the context of intact tissue. This is especially useful for assessing the progression and treatment of diseases such as cancer.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: Identifying multiple proteins within the same tissue allows for assessing protein colocalization, is cost effective, and maximizes efficiency. Here, we describe a protocol for multiplex immunolabeling of proteins in free-floating brain sections.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: Immunohistochemistry is the study of localization, characterization and quantification of antigens (peptides and proteins) in tissue cells by applying the basic principle of immunology antigen-antibody reaction, through chemical reactions to develop color of chromogenic agents that label antibodies.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: The Strept Avidin-Biotin Complex (SABC) method is a simple and sensitive immunohistochemical method for displaying antigen distribution in tissues and cells. The SV (Super Vision) two-step method uses a polymerization labeling method to link peroxidase with secondary antibodies to form a super-sized antibody-enzyme polymer, replacing secondary and tertiary antibodies in the traditional method.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on biological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Immunofluorescence (IF) staining labels a specific target antigen with a fluorescent dye such as fluorescein isothiocyanate or cyanine. The fluorescent stain visualized under a fluorescent microscope allows for an assessment of the target molecule/protein distribution in the sample. The following protocol provides a method of immunofluorescence of general cells.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Immunofluorescent labeling is a straight-forward technique for assessing the presence and the subcellular localization of antigens and/or proteins. The following protocol provides a method describing a suggested protocol for sarcomeric actinin, ANP, ER and ERb fluorescent staining of cardiomyocytes.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Immunofluorescence technique, also known as fluorescent antibody technique, is one of the earliest developments in labeled immunology techniques. Some scholars have tried to combine antibody molecules with some tracer substances to localize antigenic substances in tissues or cells using antigen-antibody reactions since a long time.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: In order to be able to examine the co-distribution of two (or more) different antigens in the same sample, a double immunofluorescence procedure can be carried out. Primary antibodies raised in different species can be used either in parallel (in a mixture) or in a sequential way. We provide a protocol for immunofluorescent double staining incubating the antibodies together.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Double immunofluorescence is used to detect the presence and localization of two different proteins or antigens in a biological sample. This technique is commonly used in research areas such as immunology, cell biology, and pathology. We provide a protocol for immunofluorescent double staining incubating the antibodies separately.
Classification: IF.
Guidelines: Cell staining is a very versatile technique and, if the antigen is highly localized, can detect as few as a thousand antigen molecules in a cell. In some circumstances, cell staining may also be used to determine the approximate concentration of an antigen, especially by an image analyzer. We provide the process of cells staining.
Classification: ICC.
Guidelines: Immunocytochemistry is a new technique for the qualitative, localized and quantitative determination of the corresponding antigens through antigen-antibody reactions and histochemical colorimetric reactions in tissue cells in situ with specific antibodies labeled with chromogenic agents.
Classification: WB.
Guidelines: The detection of proteins is the main marker of gene expression, and there are many methods to detect proteins, except for ELISA, but also blotting methods similar to the detection of DNA and RNA. The first two methods have the meaning of "south" and "north", so the method was extended to Western (western) blotting, which can be distinguished by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with specific proteins bound to a specific antiserum.
Classification: Antibody Preparation.
Guidelines: The traditional method of preparing immune serum is to inject the antigen into the animal body, and the B cells in the animal body will proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies.
Classification: Antibody Preparation.
Guidelines: Antisera prepared by immunizing an animal with an antigen is a very complex mixture that includes all of the components of the serum. To concentrate and increase the potency of the antibody, it is usually necessary to isolate and purify the immunoglobulins.
Classification: Antibody Preparation.
Guidelines: In immunological practice, to prepare antibodies, antigenic substances (bacteria, viruses, toxoids, serum, and other proteins) are often injected into animals. After a certain period, a large number of specific antibodies can be produced in the animal's serum. This serum containing specific antibodies is called immune serum.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has become a cutting-edge topic in the field of analytical chemistry. It is a special reagent analytical method, which is a new type of immunoassay technique based on immuno-enzymatic techniques.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: The steps for an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are the same as for a direct ELISA, except for the additional washing step and the type of antibody added after removing the buffer.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: PCR-ELISA is an immunological method to detect PCR products, which is easier and less time-consuming than the routine use of electrophoresis and Southern blot. A large number of specimens can be processed at the same time, which facilitates automation.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: This experiment describes the procedure for the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay C1q assay. The binding of solid-phase condensed IgG encapsulated on a plastic plate to enzyme-linked C1q is inhibited by immune complexes in the specimen, making it a competitive inhibition test.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for binding peptides of screened target molecules involves a technique to investigate the interaction between peptides and specific target molecules.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: Enzyme-linked immunoSpot assay (ELISpot) is an immunoassay established by replacing the polystyrene micro-reaction plate commonly used in the immune-enzymatic solid-phase carrier method with a cellulose membrane. It not only retains the advantages of conventional ELISA but also makes up for the shortcomings of antigens or antibodies not firmly encapsulated in the carrier.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: We provide a protocol using a FITC-conjugated primary antibody and a biotinylated primary antibody. Those are in turn recognized by anti-FITC HRP and streptavidin-AP conjugates.
Classification: ELISA.
Guidelines: The ELISpot (enzyme-linked immuno-spot) assay provides an effective method of measuring the antibody or cytokine production of immune cells on the single-cell level. The following protocol is an example of a typical ELISpot assay for quantifying the number of cells producing interferon-. (IFN-y) in response to antigen or non-specific activation using phytohemagglutinin (PHA).
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: Immunoglobulin (SmIg) is an antigen recognition receptor for B cells and a specific surface marker for B cells, which can be detected by direct immunofluorescence.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: The subject of this protocol is the simultaneous immunohistochemical detection of protein antigens and proliferation marker BrdU in the developing tooth.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: IHC for mouse anti-human RANTES is a technique used to detect and visualize the presence of RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted) in tissue samples. RANTES is a chemokine that plays a role in inflammation and immune response.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: All six anti-GFP antibodies are suited for the detection of native GFP, GFP variants, and most GFP fusion proteins by western blot analysis while the rabbit and mouse antibodies are also useful for immunoprecipitation.
Classification: IHC.
Guidelines: The advantage of using fluorescence to stain whole mount sections is that confocal microscopy can be used to section through the larger embryo or tissue sample without having to manually section onto slides. This gives a clearer idea of where the target protein of interest is expressed within the tissues.
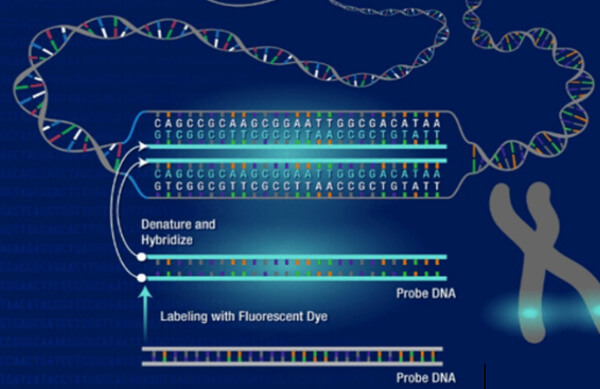
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that studies the molecular basis of biological activity. Molecular biologists conduct experiments to investigate the structure, function, processing, regulation, and evolution of biological molecules and their interactions with one another, providing micro-level insights into how life works. Creative Bioarray provides an easily accessible reference for molecular biology techniques. We provide a step-by-step guide to techniques including guidelines, methods, and notes.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: In situ hybridization (ISH) is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA or RNA strand (i.e., probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (In Situ) or in the entire tissue (whole mount ISH). Localization of endogenous transcripts is a desirable approach for confirming expression patterns.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) induces apoptosis in a variety of cancer cells playing a role in cancer growth and metastasis. In situ hybridization (ISH) is a technique that uses colorimetric or fluorescent probes to target and visualize specific DNA or RNA sequences within tissues. Here, we present the mRNA of TNF determined by in situ hybridization.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: The ability to visualize the expression of a gene in both time and space is an essential tool of developmental biology. Here, we detail a robust method for in situ hybridization of RNA probes to whole pieces of fixed tissue. This method has been optimized for reliable and sensitive visualization of the spatial patterns of gene expression in mouse embryo tissue.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Photosensitive biotin has a linker arm with biotin attached at one end and an aryl azide compound at the other. Under visible light irradiation, the aryl azide compound may become activated aryl nitrobenzene, which readily binds specifically to the adenine N-7 position of DNA or RNA, binding approximately one biotin per 50 bases.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: We describe a nonradioactive method for the detection of mRNAs. The biotinylated complementary oligonucleotide or cRNA probes hybridize with the cytoplasmic mRNAs and are detected by antibiotics. The reaction is amplified by a sandwich technique that provides layers of biotin and streptavidin-peroxidase.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Although largely replaced by the use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in animal and human molecular cytogenetics, the technique of radioactive in situ hybridization (RISH) still has some uses. The sensitivity of RISH can be increased with longer exposures, in a roughly linear fashion until the silver bromide grains in the emulsion approach saturation over the target.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Knowing the timing, level, cellular localization, and cell type that a gene is expressed in contributes to our understanding of the function of the gene. Each of these features can be accomplished with in situ hybridization to mRNAs within cells.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Nonradioactive in situ hybridization offers a unique opportunity to study gene expression on samples with preserved histological information. This method makes it possible to locate not only wherein a tissue a particular gene is expressed, but in many cases also in which specific cell type it is active.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: In the great majority of cases in situ hybridization is used to localize mRNA species at the tissue level, or DNA at the chromosome level. These approaches are generally best done by light microscopy. There are instances, however, when it becomes important to localize nucleic acids at the subcellular level, this brings us into the domain of the electron microscope.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: The utilization of in situ hybridization technology is of particular interest to those engaged in chromosome walking or genome mapping projects, in which it is essential to check all clones along a chromosome walk by in situ hybridization to identify clones containing repetitive DNA and to avoid the isolation of clones derived from regions outside that of interest.
Classification: ISH.
Guidelines: Sensitive techniques developed to detect biologically relevant proteins at the mRNA and protein levels have been major research tools in basic and applied biomedical research. The combination of these two techniques has been particularly valuable when the biological protein being studied is a secreted cell product that can bind to components of the extracellular matrix or receptors on target cells within the same tissue.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is an emerging molecular cytogenetics technique, which is a non-radioactive in situ hybridization technique developed in the late 1980s based on the original radioactive in situ hybridization technique.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) began with the combination of traditional cytogenetic and DNA techniques. It is based on the Southern blot principle, where a known nucleic acid molecule indirectly labeled with a semi-antigen such as a biotin, or digoxin or directly labeled with fluorescein is used as a probe.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (I-FISH) is a useful technique for detecting chromosomal numerical abnormalities in tumors and is gaining acceptance as a tool in cytogenetics and clinical diagnoses.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has become a powerful, practical tool for detecting genetic abnormalities such as chromosome translocations, pericentric inversions, and insertions. Most frequently, chromosomes are studied as mitotic metaphases fixed on slides. Here, we describe a basic methodology for the accomplishment of metaphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Telomere length influences numerous cellular processes such as senescence, carcinogenesis, and aging. Quantitative FISH (Q-FISH) is a comprehensive method that allows the measuring of individual chromosome telomere length in a single cell with a resolution of 200 base pairs.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Flow cytometry is a well-established method for rapid detection of fluorescence signals in individual cells in suspension which has been applied to FISH studies using chromosome-specific probes. Recently, flow cytometry using a fluorescently labeled peptide nucleic acid (PNA) probe was used to estimate the telomere length in individual cells.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: The techniques for producing transgenic mice are now being used extensively, and it is often desirable to determine the site of transgene insertion. Although fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) permits the rapid and efficient localization of DNA probes on human chromosomes, it has not been effectively applied to the mapping of sequences on mouse chromosomes.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Multicolor FISH (mFISH) is a method to facilitate the analysis of every single chromosome or chromosome part of a metaphase. Thus, marker chromosomes, complex chromosomal rearrangements, and all numerical aberrations can be visualized simultaneously in a single hybridization experiment.
Classification: CGH.
Guidelines: Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) allows genome-wide assessment of changes in relative copy number of DNA sequences, using tumor-cell DNA extracted from clinical samples or cell lines as a probe. In CGH, amplifications, gains, and deletions of genes are detected using a modified fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) reaction.
Classification: RNA and DNA Extraction.
Guidelines: Peripheral blood is often used for in vitro studies of the human immune system or immune responses, such as inflammation. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) are mature lymphocytes that circulate in the blood, rather than localizing to organs (such as the spleen or lymph nodes). They comprise T cells, NK cells, and B cells.
Classification: qRT-PCR.
Guidelines: The real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) technique refers to the addition of fluorescent groups to the PCR reaction system. The whole PCR process is monitored in real-time using fluorescence signal accumulation, and finally, the unknown template is quantified by a standard curve.
Classification: Gene Expression.
Guidelines: Luciferase genes encode enzymes that produce bioluminescence, allowing researchers to study gene expression, protein interactions, and cellular processes.
Classification: RNA and DNA Extraction.
Guidelines: DNA is an important component of all living cells and mainly exists in the nucleus. DNA extraction from animal tissue blocks is a fundamental process in molecular biology and genetics research.
Classification: RNA and DNA Extraction.
Guidelines: The preparation of DNA from human peripheral blood leukocytes, also known as white blood cells, is a common procedure in molecular biology and genetic research.
Classification: RNA and DNA Extraction.
Guidelines: Use specimen paper for spotting blood, as this unique filter paper disintegrates when incubated in aqueous collected using other specimen collection papers.
Classification: DNA Transformation.
Guidelines: The host cell's DNA is often protected by methylation of one of its specific recognition sites, rendering it no longer a substrate for restriction enzymes. A restriction recognition sequence is a DNA sequence that a restriction endonuclease can specifically bind to. These sequences are generally 4-6 nucleotides in length and are double symmetric, also known as palindromic sequences.
Classification: DNA Transformation.
Guidelines: The process of combining foreign DNA with carrier molecules is known as DNA recombination, resulting in the formation of recombinant or recombinant DNA.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: Chromosome painting is a powerful cytogenetic technique that allows for the visualization and identification of specific chromosomes or chromosomal regions within a cell.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: Hematology FISH is a powerful cytogenetic technique that is widely used in the diagnosis, management, and monitoring of hematological malignancies, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: FISH in FFPE tissue samples is a widely used technique that allows for the detection and visualization of specific DNA or RNA sequences within the context of the tissue architecture.
Classification: FISH.
Guidelines: RNA FISH is a powerful technique that allows for the visualization and localization of specific RNA molecules within individual cells.
Classification: DNA Transformation.
Guidelines: The liposome transfection method refers to the positively charged surface of cationic liposomes, which can be with the phosphate of nucleic acids through electrostatic interaction of DNA molecules wrapped into the formation of DNA a lipid complex.
Classification: DNA Transformation.
Guidelines: SLIC cloning is a cloning method based on recombinant DNA technology, in which gene fragments are spliced by using linearized segments of exogenous and target DNA to interface with each other and join them using sequence-independent ligases.
Classification: DNA Transformation.
Guidelines: TOPO cloning technology is based on the interaction of a special transposon sequence, the pUC18/19 vector, transposase, and DNA polymerase. The principle of the technique is that a fragment of target DNA is ligated to the transposon-bearing insertion site pUC18/19 in the TOPO vector to form the original clone.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: Corresponding cell lines have now been established for most cancers. Cancer cells cultured in vitro mostly belong to the continuous cycle cells, which can be used to prepare chromosomes.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: Human peripheral blood small lymphocytes, which are usually in the G1 (or G0) phase, do not normally divide. If phytohemagglutinin (PHA) is added to the culture medium, such small lymphocytes can be stimulated to transform into lymphoblasts and enter mitosis.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: Chromosome painting enables the visualization of chromosomes and has been used extensively in cytogenetics. Chromosome paint probes, which consist of a pooled composite of DNA-FISH probes, bind to nonrepetitive sequences for individual chromosomes.
Classification: Chromosome preparation and analysis.
Guidelines: After treatment with physical and chemical factors, the chromosomes are then differentiated and stained with dyes, so that each chromosome appears on the light and dark, or different shades of banding technique is called banding technique.




