Semithin Sectioning Protocol
GUIDELINE
Since as thin as 0.5-2 μm, they are also called semi-thin sections, and are an effective positioning method in the ultrathin sectioning technique for electron microscopy. The preparation of semi-thin sections is a common means of sample preparation nowadays. As the clarity and resolution of semi-thin section images are much better than paraffin sections, and the field of view is larger than that of ultrathin sections, it facilitates the acquisition of high-quality light microscopy images. Semi-thin sections are used in various aspects, such as embryology, pathology, etc., and can be considered as a widely used and more common way of sectioning.
METHODS
- Double fixation. The specimen was first fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) for more than 4 hours; washed three times in the phosphate buffer; then postfixed with 1% OsO4 in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) for 1 hour and washed three times in the phosphate buffer.

- Dehydration. The specimen was first dehydrated by a graded series of ethanol (50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95% and 100%) for about 15 to 20 minutes at each step, transferred to absolute acetone for 20 minutes.
- Infiltration. The specimen was placed in 1:1 mixture of absolute acetone and the final Spurr resin mixture for 1 hour at room temperature, then transferred to 1:3 mixture of absolute acetone and the final resin mixture for 3 hours and to final Spurr resin mixture for overnight.
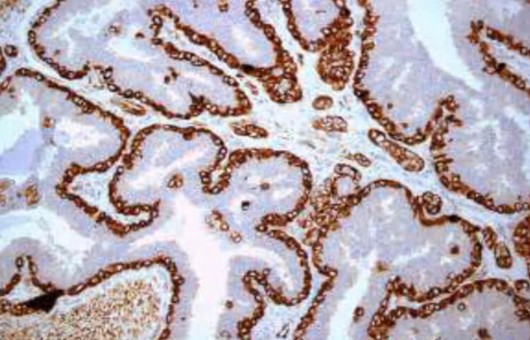
- Embedding and semi-thin sectioning. Specimen was placed in capsules contained embedding medium and heated at 70°C for about 9 hours. Semi-thin sections (1 μm) were sliced under a ultramicrotome and stained with 0.5% toluidine blue.
NOTES
- The embedding surface of the specimen should not be too large, otherwise it will easily cause wrinkles.
- Light movements during embedding to prevent the generation of air bubbles.
- Skin should not touch the reagent as much as possible to avoid discomfort.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Resources
- FAQ
- Protocol
- Cell Culture Guide
- Technical Bulletins
-
Explore & Learn
-
Cell Biology
- CHO Cell Line Development
- How to Isolate PBMCs from Whole Blood?
- How to Handle Mycoplasma in Cell Culture?
- Comparison of the MSCs from Different Sources
- T Cell Activation and Expansion
- How to Isolate and Analyze Tumor-Infiltrating Leukocytes?
- Troubleshooting Cell Culture Contamination: A Comprehensive Guide
- Contamination of Cell Cultures & Treatment
- Generation and Applications of Neural Stem Cells
- Stem Cell Markers
- What are the Differences Between M1 and M2 Macrophages?
- What Cell Lines Are Commonly Used in Biopharmaceutical Production?
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Comprehensive Exploration
- Tips For Cell Cryopreservation
- Organoid Differentiation from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Quantification of Cytokines
- How to Assess the Migratory and Invasive Capacity of Cells?
- Enrichment, Isolation and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
- Strategies for Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
- Multi-Differentiation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- How to Decide Between 2D and 3D Cell Cultures?
- Neural Differentiation from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Circulating Tumor Cells as Cancer Biomarkers in the Clinic
- CFU Assay for Hematopoietic Cell
- How to Eliminate Mycoplasma From Cell Cultures?
- What Are Myeloid Cell Markers?
- Monocytes vs. Macrophages
- How to Detect and Remove Endotoxins in Biologics?
- Comparison of Different Methods to Measure Cell Viability
- How to Start Your Culture: Thawing Frozen Cells
- Cryopreservation of Cells Step by Step
- What are PBMCs?
- Biomarkers and Signaling Pathways in Tumor Stem Cells
- Techniques for Cell Separation
- Guidelines for Cell Banking to Ensure the Safety of Biologics
- Cell Cryopreservation Techniques and Practices
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Major Problems Caused by the Use of Uncharacterized Cell Lines
- Direct vs. Indirect Cell-Based ELISA
- Cell Culture Medium
- What Is Cell Proliferation and How to Analyze It?
- IL-12 Family Cytokines and Their Immune Functions
- Critical Quality Attributes and Assays for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Human Primary Cells: Definition, Assay, Applications
- What are Mesothelial Cells?
- How to Scale Up Single-Cell Clones?
- STR Profiling—The ID Card of Cell Line
- Comparison of Several Techniques for the Detection of Apoptotic Cells
- Unveiling the Molecular Secrets of Adipogenesis in MSCs
- Tumor Stem Cells: Identification, Isolation and Therapeutic Interventions
- Isolation, Expansion, and Analysis of Natural Killer Cells
- Spheroid vs. Organoid: Choosing the Right 3D Model for Your Research
- Adherent and Suspension Cell Culture
- Understanding Immunogenicity Assays: A Comprehensive Guide
- From Collection to Cure: How ACT Works in Cancer Immunotherapy
- How to Maximize Efficiency in Cell-Based High-Throughput Screening?
- 3D-Cell Model in Cell-Based Assay
- Role of Cell-Based Assays in Drug Discovery and Development
- Immunogenicity Testing: ELISA and MSD Assays
- What are White Blood Cells?
- Types of Cell Therapy for Cancer
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Adoptive Cell Therapy?
- Eosinophils vs. Basophils vs. Neutrophils
- 3D-Cell Model in Cell-Based Assay
- Immunogenicity Testing: ELISA and MSD Assays
- Cultivated Meat: What to Know?
- A Complete Guide to Immortalized Cancer Cell Lines in Cancer Research
- Cell Viability, Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays
- What Are CAR T Cells?
- From Blur to Clarity: Solving Resolution Limits in Live Cell Imaging
- Exploring Cell Dynamics: Migration, Invasion, Adhesion, Angiogenesis, and EMT Assays
- Live Cell Imaging: Unveiling the Dynamic World of Cellular Processes
- Optimization Strategies of Cell-Based Assays
- Overview of Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Key Techniques in Primary, Immortalized and Stable Cell Line Development
- From Primary to Immortalized: Navigating Key Cell Lines in Biomedical Research
- From Blur to Clarity: Solving Resolution Limits in Live Cell Imaging
- Cell-Based High-Throughput Screening Techniques
- Mastering Cell Culture and Cryopreservation: Key Strategies for Optimal Cell Viability and Stability
- Cell Immortalization Step by Step
- Optimization Strategies of Cell-Based Assays
- Live Cell Imaging: Unveiling the Dynamic World of Cellular Processes
-
Histology
- Troubleshooting in Fluorescent Staining
- Fluorescent Nuclear Staining Dyes
- Immunohistochemistry Controls
- Overview of the FFPE Cell Pellet Product Lines
- Guides for Live Cell Imaging Dyes
- Instructions for Tumour Tissue Collection, Storage and Dissociation
- Multiple Animal Tissue Arrays
- Tips for Choosing the Right Protease Inhibitor
- Mitochondrial Staining
- Stains Used in Histology
- Cell Lysates: Composition, Properties, and Preparation
- Immunohistochemistry Troubleshooting
- Cell and Tissue Fixation
- Comparison of Membrane Stains vs. Cell Surface Stains
- Microscope Platforms
- How to Apply NGS Technologies to FFPE Tissues?
- Overview of Common Tracking Labels for MSCs
- How to Choose the Right Antibody for Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- How to Begin with Multiplex Immunohistochemistry (mIHC)
- Common Immunohistochemistry Stains and Their Role in Cancer Diagnosis
- Serum vs. Plasma
- Comparing IHC, ICC, and IF: Which One Fits Your Research?
- Multiplexing Immunohistochemistry
- From Specimen to Slide: Core Methods in Histological Practice
- What You Must Know About Neuroscience IHC?
- Modern Histological Techniques
- How Immunohistochemistry Makes the Invisible Brain Visible?
- Histological Staining Techniques: From Traditional Chemical Staining to Immunohistochemistry
-
Exosome
- What's the Potential of PELN in Disease Treatment?
- Classification, Isolation Techniques and Characterization of Exosomes
- Emerging Technologies and Methodologies for Exosome Research
- How to Enhancement Exosome Production?
- How to characterize exosomes?
- How to Label Exosomes?
- How to Efficiently Utilize MSC Exosomes for Disease Treatment?
- Exosomes as Emerging Biomarker Tools for Diseases
- How to Apply Exosomes in Clinical?
- How to Perform Targeted Modification of Exosomes?
- Exosome Quality Control: How to Do It?
- Exosome Transfection for Altering Biomolecular Delivery
- Summary of Approaches for Loading Cargo into Exosomes
- Collection of Exosome Samples and Precautions
- Techniques for Exosome Quantification
- How do PELN Deliver Drugs?
- Current Research Status of Milk Exosomes
- Common Techniques for Exosome Nucleic Acid Extraction
- How Important are Lipids in Exosome Composition and Biogenesis?
- What are the Functions of Exosomal Proteins?
- Exosome Size Measurement
- The Role of Exosomes in Cancer
- Applications of MSC-EVs in Immune Regulation and Regeneration
- Unraveling Biogenesis and Composition of Exosomes
- Production of Exosomes: Human Cell Lines and Cultivation Modes
- Exosome Antibodies
-
ISH/FISH
- ISH probe labeling method
- Reagents Used in FISH Experiments
- CARD-FISH: Illuminating Microbial Diversity
- Comprehensive Comparison of IHC, CISH, and FISH Techniques
- RNAscope ISH Technology
- Comparative Genomic Hybridization and Its Applications
- What are the Differences between FISH, aCGH, and NGS?
- What are Single, Dual, and Multiplex ISH?
- Overview of Oligo-FISH Technology
- Differences Between DNA and RNA Probes
- What Is the Use of FISH in Solid Tumors?
- Mapping of Transgenes by FISH
- What Types of Multicolor FISH Probe Sets Are Available?
- FISH Tips and Troubleshooting
- Multiple Options for Proving Monoclonality
- FISH Techniques for Biofilm Detection
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes for FISH
- Telomere Length Measurement Methods
- Guidelines for the Design of FISH Probes
- Overview of Common FISH Techniques
- Multiple Approaches to Karyotyping
- In Situ Hybridization Probes
- Different Types of FISH Probes for Oncology Research
- How to Use FISH in Hematologic Neoplasms?
- Small RNA Detection by ISH Methods
- ImmunoFISH: Integrates FISH and IL for Dual Detection
- 9 ISH Tips You Can't Ignore
-
Toxicokinetics & Pharmacokinetics
- Toxicokinetics vs. Pharmacokinetics
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Drugs and Calculations
- Pharmacokinetics of Therapeutic Peptides
- Organoids in Drug Discovery: Revolutionizing Therapeutic Research
- What Are Metabolism-Mediated Drug-Drug Interactions?
- How to Improve Drug Plasma Stability?
- How Is the Cytotoxicity of Drugs Determined?
- How to Improve the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Peptides?
- How to Conduct a Bioavailability Assessment?
- Experimental Methods for Identifying Drug-Drug Interactions
- Organ-on-a-Chip Systems for Drug Screening
- Key Considerations in Toxicokinetic
- Pharmacokinetics Considerations for Antibody Drug Conjugates
- Traditional vs. Novel Drug Delivery Methods
- Comparison of MDCK-MDR1 and Caco-2 Cell-Based Permeability Assays
- What factors influence drug distribution?
- How to Design and Synthesize Antibody Drug Conjugates?
- Methods of Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assays
- Key Factors Influencing Brain Distribution of Drugs
- Unraveling the Role of hERG Channels in Drug Safety
- Predictive Modeling of Metabolic Drug Toxicity
- The Rise of In Vitro Testing in Drug Development
- Overview of In Vitro Permeability Assays
- How to Improve Drug Distribution in the Brain
- Effects of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism on Drug Interactions
- What Are Compartment Models in Pharmacokinetics?
- What Is the Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Drug Delivery?
- Parameters of Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion
- What are the Pharmacokinetic Properties of the Antisense Oligonucleotides?
- From Cells to Systems: Modern Approaches to Disease Modeling
- How Genotoxicity Testing Guides Safer Drug Development
- What Is Genotoxicity in Pharmacology? Mechanisms and Sources
- What Are the Best Methods to Test Cardiotoxicity?
- Why Cardiotoxicity Matters in R&D?
-
Disease Models
- Preclinical Models of Acute Liver Failure
- What Human Disease Models Are Available for Drug Development?
- Overview of Cardiovascular Disease Models in Drug Discovery
- Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Summary of Advantages and Limitations of Different Oncology Animal Models
- Disease Models of Diabetes Mellitus
- Why Use PDX Models for Cancer Research?
-
Cell Biology
- Life Science Articles
- Download Center
- Trending Newsletter