- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- In Vitro Drug Distribution Services
- Plasma Protein Binding Assay
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Plasma Protein Binding Assay
Creative Bioarray provides Plasma Protein Binding Assay to help customers accurately detect the binding of compounds to plasma proteins and predict the distribution of compounds in blood and tissues.
Why do we need Plasma Protein Binding Assay?
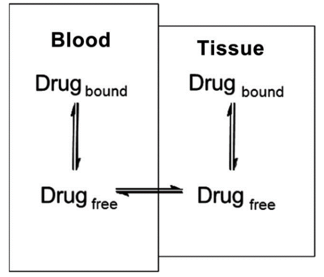
- Drug distribution describes the reversible movement of a drug from one location to another within the body. Usually, it refers to a drug transfer from the blood to various tissues.
- Theoretically, different body parts can receive different doses and remain for a different amount of time.
- The distribution of drugs in the body depends on many aspects, and its binding to tissues and plasma proteins is an important influencing factor.
- The degree of binding to plasma affects the way the drug is distributed to tissues in the body. If the compound is highly bound, it will remain in the plasma, resulting in a low volume of distribution. This may affect the therapeutic effect of the compound by limiting the amount of free compound available to act on the target molecule.
- Extensive plasma protein binding also limits the amount of free compounds available for metabolism, reducing compound clearance.
Brief Protocol
- Equilibrium dialysis is the most widely accepted method for evaluating plasma protein binding because non-specific binding effects are minimized compared to other methods (such as ultrafiltration).
- The semipermeable membrane separates the protein-containing compartment from the protein-free compartment. Equilibrate the system at 37°C. LC-MS/MS quantifies the test compound present in each compartment.
Case Study
- Dialysis membrane and matrix preparation
- Methods and Results
- Test compound and control compound were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to achieve 10 mM stock solutions.
- Prepare the T0 sample for recovery determination.
- Load the dialysis device.
- At the end of the dialysis, a 100 μL aliquot of the supernatant of all samples was taken for LC-MS/MS analysis.
The dialysis membrane strips were soaked in ultra-pure water at room temperature for approximately 1 hour. Before the experiment, the membrane was rinsed and soaked for 20 minutes in ultrapure water.
| Plasma Protein Binding Assay | |||||||
| Cmpd ID | Test Conc. | Matrix | % Unbound | %Unbound SD | %Bound | %Recovery | %Recovery SD |
| Warfarin | 2μM | Human Plasma | 1.32 | 0.1 | 98.68 | 90.5 | 5.1 |
| Sample #1 | 2μM | Human Plasma | 21.64 | 0.2 | 78.36 | 31.1 | 0.6 |
Note: Where: T is the analyte concentration or peak area ratio of analyte/internal standard on the matrix (donor) side of the membrane T0 is the analyte concentration or the peak area ratio of analyte/internal standard in the loading matrix sample at time zero. | |||||||
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Bohnert, Tonika, and Liang-Shang Gan. "Plasma protein binding: from discovery to development." Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 102.9 (2013): 2953-2994.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

