- You are here: Home
- Applications
- Skin
- Cosmetics
- Skin Anti-Wrinkle
Applications
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Skin Anti-Wrinkle
Skin aging may occur simultaneously with two different biological processes: (i) intrinsic aging; and (ii) extrinsic aging.
Intrinsic aging is a slow process that causes changes in tissue structure and impairs the function of the skin in the absence of additional factors. The clinical features of intrinsically aged skin are usually not evident until old and are characterized by fine lines and occasionally exaggerated expression lines. Functionally, intrinsically aged skin is drier and less elastic than more youthful skin.
In contrast, externally aged skin shows obvious and coarse wrinkles, mottled hyperpigmentation, and a significant loss of elasticity and retraction. The two main environmental effects that contribute to extrinsic aging are (i) long-term exposure to solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation (called photoaging) and (ii) smoking.
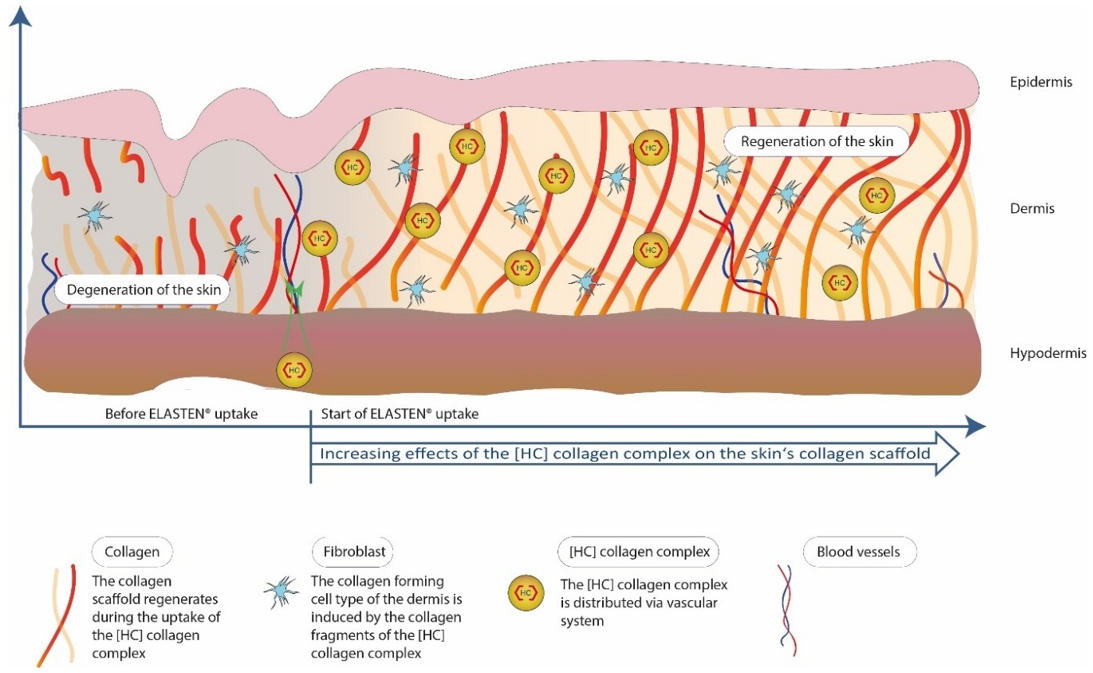 Figure 1. A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density (Bolke, et al. 2019).
Figure 1. A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density (Bolke, et al. 2019).
Dermal fibroblasts produce collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid. However, factors such as UV rays and aging cause damages to fibroblasts, so that the skin becomes less firm and less elastic, and wrinkles occur.
Creative Bioarray provides in vitro skin model-based testing services to evaluate the anti-wrinkle efficacy of active substances.
Your Needs
- To screen cosmetic formulations for skin anti-wrinkle
- To evaluate the anti-wrinkle effect of products
- To fully understand how skin tissue forms wrinkles
- To look for a CRO performing skin anti-wrinkle efficacy testing
- Need a custom in vitro skin model
Our Capability
In vitro skin models available
- Normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK)
- Reconstructed human epidermis (RHE)
- Full thickness skin model
Efficacy and Screening Tests available
- Evaluating the anti-wrinkle efficacy of active substances/compounds
- Evaluating the anti-wrinkle effect of different formulations
- Customized testing based on customer needs
Endpoints
- Cell viability
- The activity of antioxidant-related enzymes
- Inhibition of collagen degradation ability
- Elastase inhibition ability
- Inhibition of cellular senescence (apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential)
- In vitro tissue morphology
- Collagen/collagen fibril production
- Elastin/elastin fiber production
- Hyaluronic acid production
- Related gene expression assays (MMP-1, NEP, HAS-1)
Techniques
- qPCR, qPCRarray, RT-PCR
- ELISA
- Western-Blotting
- Specific immuno-labeling
- Histology (Fontana/Masson staining)
- RNA extraction
- Protein extraction
- Macroscopy
Study Examples
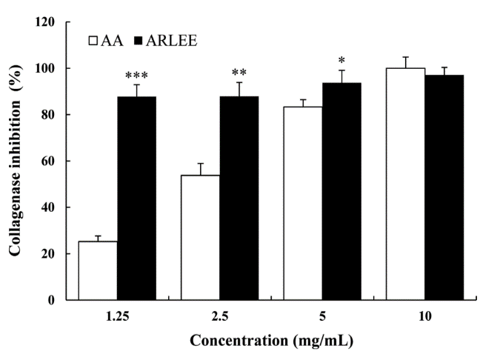 Figure 2. Collagenase activity inhibition of ARLEE relative to the control ascorbic acid. AA: ascorbic acid, ARLEE: A. rossii leaf ethanol extract (Ha, et al. 2015).
Figure 2. Collagenase activity inhibition of ARLEE relative to the control ascorbic acid. AA: ascorbic acid, ARLEE: A. rossii leaf ethanol extract (Ha, et al. 2015).
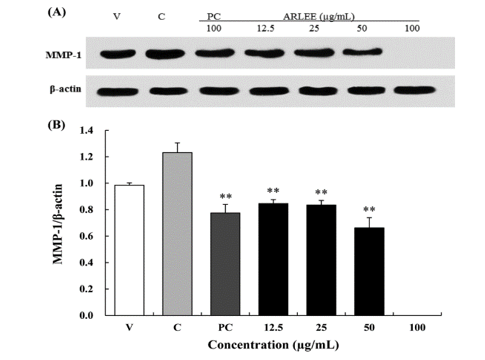 Figure 3. Effect of ARLEE on MMP-1 protein expression in human dermal fibroblasts.
Figure 3. Effect of ARLEE on MMP-1 protein expression in human dermal fibroblasts.
In vitro Skin Models
References
- Bolke, Liane, et al. "A collagen supplement improves skin hydration, elasticity, roughness, and density: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, blind study." Nutrients 11.10 (2019): 2494.
- Ha, Bi Gyeon, et al. "Antioxidant Activity and Anti-wrinkle Effects of Aceriphyllum rossii Leaf Ethanol Extract." Toxicological research 31.4 (2015): 363-369.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

