- You are here: Home
- Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
- Drug-Drug Interaction
- UGT Inhibition
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
UGT Inhibition
Creative Bioarray provides customers with the UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) enzymes inhibition test to help study the metabolic pathways of the tested drugs except for CYPs.
UGT Inhibition Assay Introduction
- Why do we need the UGT inhibition assay?
- Uridine 5'-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) are a family of enzymes that perform Phase II conjugative metabolism (glucuronidation), which usually follows the Phase I oxidative metabolism performed by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes or other oxidative metabolic steps (Soars et al. 2004).
- UGT enzymes catalyze the attachment of a glucuronic acid moiety to varied drugs and other xenobiotics, also on endogenous compounds like bilirubin. This conjugation promotes their excretion.
- Glucuronidation caused by UGT is a crucial pathway for drug metabolism in humans and other mammals.
- Regulatory agencies began to require UGT inhibition studies as part of drug-drug interaction (DDI) to determine whether clinical DDI studies are needed.
- Mechanism of UGT involving metabolism
- Glucuronidation involves adding (or combining) glucuronic acid directly into the drug itself or the oxidative metabolite of the drug. The addition of glucuronide causes the conjugate to be more polar and ionize at physiological pH. These features facilitate excretion through the kidneys. The liver can also excrete glucuronic acid through bile.
- UGT enzyme can catalyze the connection of glucuronic acid moiety to the hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, or sulfhydryl group of the target compound.
- If the activity of UGT is impaired, the result may increase the toxicity of the drug. Otherwise, UGT will dispose of these drugs. The direct action of drugs that inhibit UGT may result in impaired UGT activity.
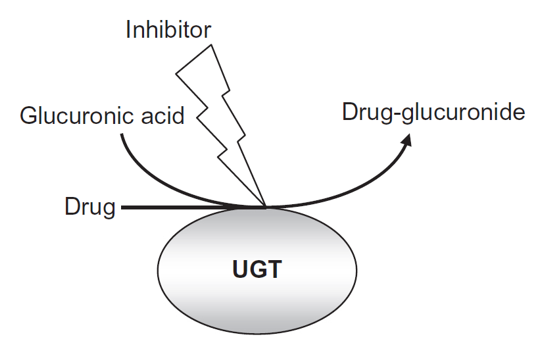 Figure 1. The catalytic reaction of UGT(Brody, 2018).
Figure 1. The catalytic reaction of UGT(Brody, 2018).
Brief Protocol
- The known UGT substrates were incubated with recombinant UGT enzymes, alamethicin, uridine-5'-diphospho-α-d-glucuronic acid (UDPGA), and a series of test compound concentrations at 37°C.
- The protein concentration and time point depend on the specific UGT and have been previously determined by protein linearity and time linearity studies. Characterized enzyme kinetics of every reaction has previously determined the substrate concentration. The range of test compound concentration depends on the plasma Cmax, the solubility of the test compound, and the degree of plasma protein binding.
- At the end of the incubation, the formation of UGT isoform-specific metabolites was monitored by LC-MS/MS at each test compound concentration. The reduction in metabolite formation compared to the vehicle control is used to calculate the IC50 value (the concentration of test compound that produces 50% inhibition).
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Soars, Matthew G., et al. "AN ASSESSMENT OF UDP-GLUCURONOSYLTRANSFERASE INDUCTION USING PRIMARY HUMAN HEPATOCYTES." Drug Metabolism and Disposition, vol. 32, no. 1, Jan. 2004, pp. 140–48. DOI.org (Crossref).
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

