- You are here: Home
- Services
- Cell Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Drug Efficacy Test
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Drug Efficacy Test
- Service Details
- Workflow
- Features
- Case Studies
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
In the field of cancer research and drug development, traditional two-dimensional (2D) cell culture technology has long been widely used for drug screening and other experiments. Although this method is easy to use and cost-effective, it fails to effectively simulate the complex environment of tumors in vivo. Real tumors grow in three dimensions, with specific tissue architecture and cell-to-cell interactions. As a result, the findings obtained from 2D cultures often do not correlate with actual clinical outcomes, leading to a high failure rate of drugs in clinical trials. In contrast, three-dimensional (3D) model technology has demonstrated significant advantages in drug development and is gradually becoming a research hotspot.
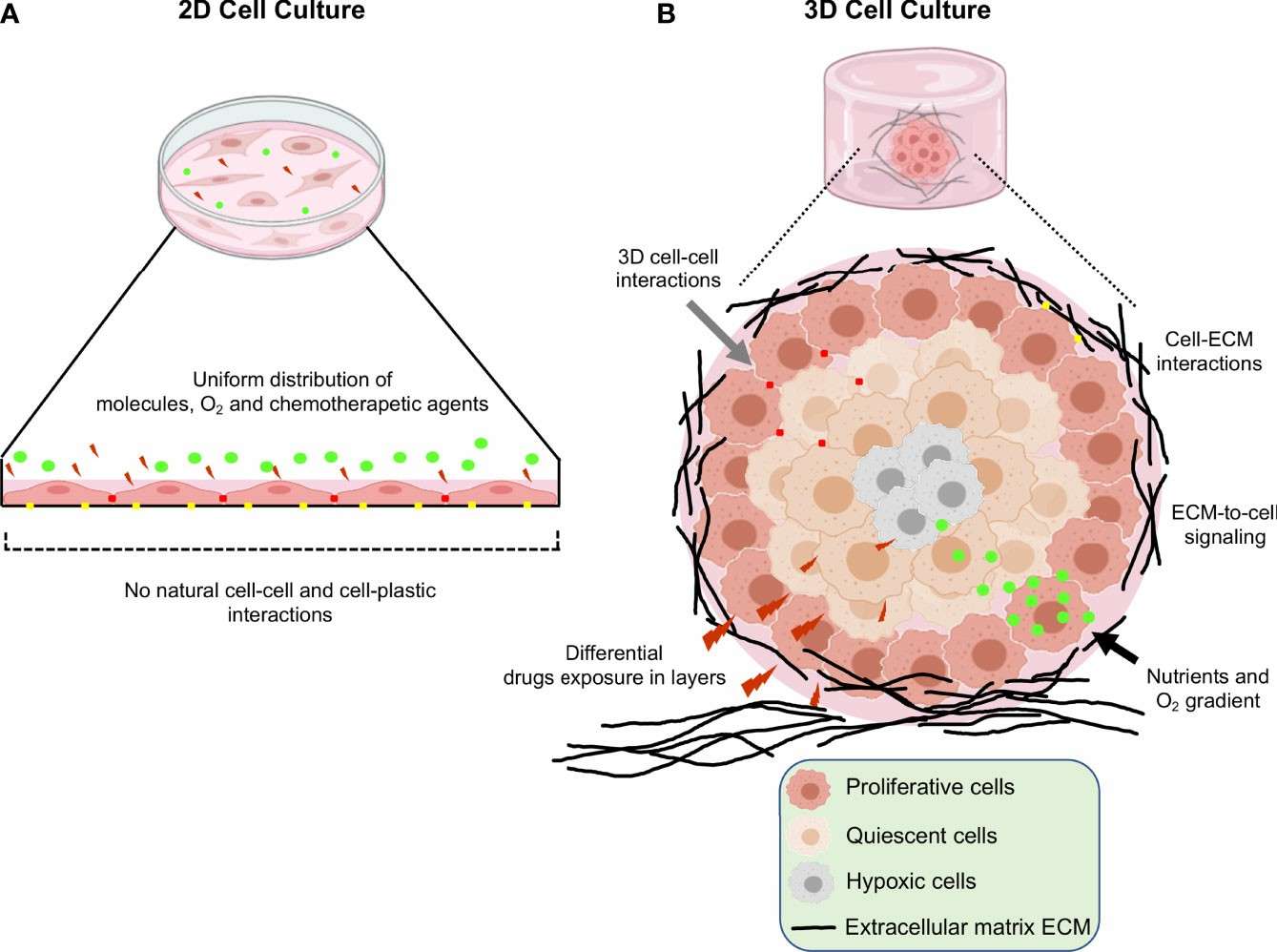 Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the main differences between 2D and 3D cell cultures (Salinas-Vera YM, Valdés J, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the main differences between 2D and 3D cell cultures (Salinas-Vera YM, Valdés J, et al., 2022).
Creative Bioarray uses 3D in vitro models for drug efficacy testing, which more accurately simulate the in vivo tumor environment. These models account for factors such as cell-cell interactions, hypoxia, drug penetration, response and resistance, and the production anddeposition of extracellular matrix, thereby providing more reliable preliminary data support for drug development.
Advantages of 3D in vitro model testing
- More accurately simulates the in vivo environment and cell-cell interactions.
- Improved prediction of drug response compared to 2D cultures.
- Reduced use of animals in preclinical testing.
- High-throughput screening capabilities for testing multiple drug candidates.
Workflow
1
Sample preparation
Based on the client's research needs, we develop a research plan and select appropriate cell lines.
2
3D model generation
3D cell models are constructed using our 3D cell culture technology.
3
Drug exposure
Test drugs are added to the 3D cell models with varying concentrations and treatment times based on research requirements.
4
Assessment of drug efficacy
During and after drug treatment, we employ a variety of advanced detection technologies and instruments, including, but not limited to, cell viability assays, proliferation and apoptosis analysis, and microscopic imaging techniques, to collect data on the cell status and drug response of the 3D tumor models.
5
Data analysis
Bioinformatics analysis methods and software are employed for in-depth data analysis, assessing the drug's efficacy on the 3D tumor model, such as its ability to inhibit tumor growth and induce apoptosis. Detailed data analysis reports are generated.
Our testing includes but not limited to:
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- ATP Content assay
- Drug Penetration and Distribution Studies…
Features

Customized service solutions

High-throughput drug screening
Innovative and professional technical support

Detailed reports and data interpretation
Case Studies
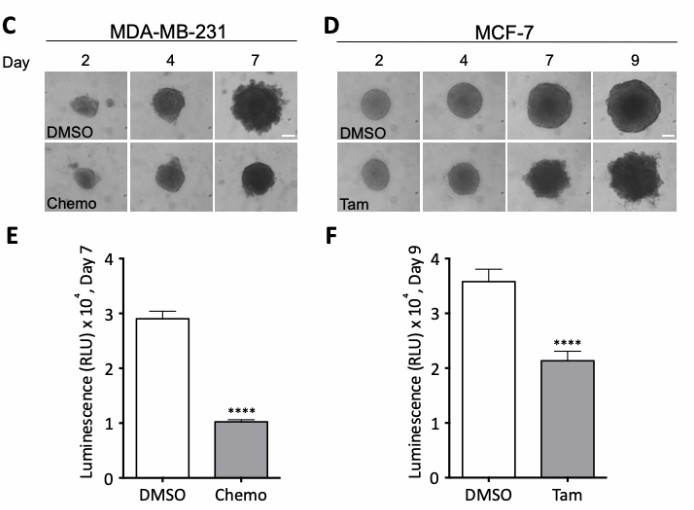 Fig. 2. Effects of treatment regimens on spheroid morphology and cell viability. (Rolver MG, Elingaard- Larsen LO, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. Effects of treatment regimens on spheroid morphology and cell viability. (Rolver MG, Elingaard- Larsen LO, et al., 2019).
FAQ
1. Can your 3D models be used for testing other types of drugs?
Our 3D models are not limited to anticancer drugs and are suitable for testing the efficacy of other types of drugs as well.
2. How do you ensure the accuracy of 3D cultures?
We use validated biomaterials, optimized culture media, and precise operating procedures to ensure that each model's construction and performance meet high standards.
3. What are the differences compared to 2D testing results?
Since 3D models are closer to the in vivo tumor environment, cell growth states and drug sensitivity may differ significantly from 2D tests. In 3D testing, factors such as tumor tissue barriers and cell-cell interactions may affect drug penetration and efficacy, generally resulting in more accurate reflection of the drug's real efficacy in vivo.
References
- Salinas-Vera YM, Valdés J,et al. Three-Dimensional 3D Culture Models in Gynecological and Breast Cancer Research. Front Oncol. 2022. 12:826113.
- Rolver MG, Elingaard-Larsen LO, Pedersen SF. Assessing Cell Viability and Death in 3D Spheroid Cultures of Cancer Cells. J Vis Exp. 2019 Jun 16;(148).
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

