ONLINE INQUIRY
WI-38
Cat.No.: CSC-C9261W
Species: Human
Source: Lung
Morphology: fibroblast
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The WI-38 human embryonic lung cell line, one of the foundational inventions of biomedical science, was isolated and developed in 1960 by Leonard Hayflick from lung tissue from a 14-week-old female infant. WI-38 cells exhibit typical fibroblast morphology; they adhere to the substrate, cell walls are not well-defined, and their nuclei are big, round and easily distinguishable amongst many cell lines. In particular, the WI-38 cell line is not capable of differentiation, making its use and study in experiments somewhat straightforward. Although it is a finite cell line, WI-38 will survive up to 50±10 passages in vitro. By adding growth factors, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), to the culture medium, WI-38 cells can be accelerated in growth and survival.
WI-38, the original human diploid cell line for human vaccine development, is prized for its diploid stability and vulnerability to viruses. It not only enables the replication and spread of viruses, but also serves as a scale that is roughly matched to human physiological reality for intensive studies of viral infection processes, virus-host cell interactions, and vaccine development and evaluation. The WI-38 cell line is the target of many widely used global vaccines such as rubella, rabies, adenovirus, poliovirus (polio), measles, varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles). Further, WI-38 cells are often used to create cell senescence models to investigate the molecular determinants of cell ageing and potential anti-aging agents.
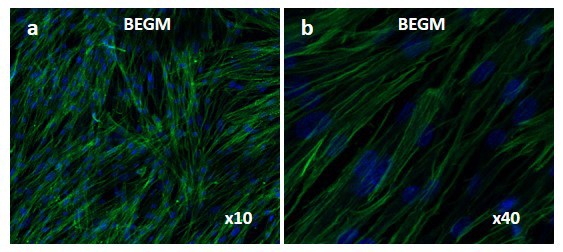 Fig. 1. Laser confocal images of WI-38 cells cultured in fresh bronchial epithelial growth medium (BEGM). Green: anti-vimentin labeled intermediate filaments; Blue: nuclei (Boublil L, Martinon L, et al., 2013).
Fig. 1. Laser confocal images of WI-38 cells cultured in fresh bronchial epithelial growth medium (BEGM). Green: anti-vimentin labeled intermediate filaments; Blue: nuclei (Boublil L, Martinon L, et al., 2013).
Shikonin Alleviates LPS-Induced WI-38 Cell Injury
Pneumonia is an inflammatory disease caused by exposure to a range of microbes. Even though several preclinical studies indicate that shikonin, a natural naphthoquinone, can reduce lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation, the mechanism behind pneumonia is unclear. Wang et al. built an in vitro model of pneumonia by treating WI-38 cells with LPS, and examined the role of shikonin in LPS-induced injury to WI-38 cells.
An MTT assay measured the effect of LPS on WI-38 cell viability in a specific time-dependent manner (Fig. 1A). Apoptosis was more rapid in LPS-treated WI-38 cells based on elevated Bax, cleaved-caspase-3 (C-caspase-3) and apoptotic activity, as well as reduced Bcl-2 expression (Fig. 1B and C). In LPS-treated WI-38 cells, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1, IL-18, TNF-) were higher than in controls, suggesting a serious inflammatory response (Fig. 1D). Shikonin significantly enhanced cell viability as shown in Figure 2A. LPS also increased the expression of Bax and C-caspase-3; however, shikonin reversed these effects. Shikonin, on the other hand, reversed the decreased expression of Bcl-2 caused by LPS (Fig. 2B). Shikonin inhibited LPS-induced cell death (Fig. 2C). Shikonin reduced LPS-induced IL-6, IL-1, IL-18 and TNF-a productions (Fig. 2D). In summary, shikonin reduces LPS-induced WI-38 cell damage by improving cell viability and inhibiting cell death and inflammation.
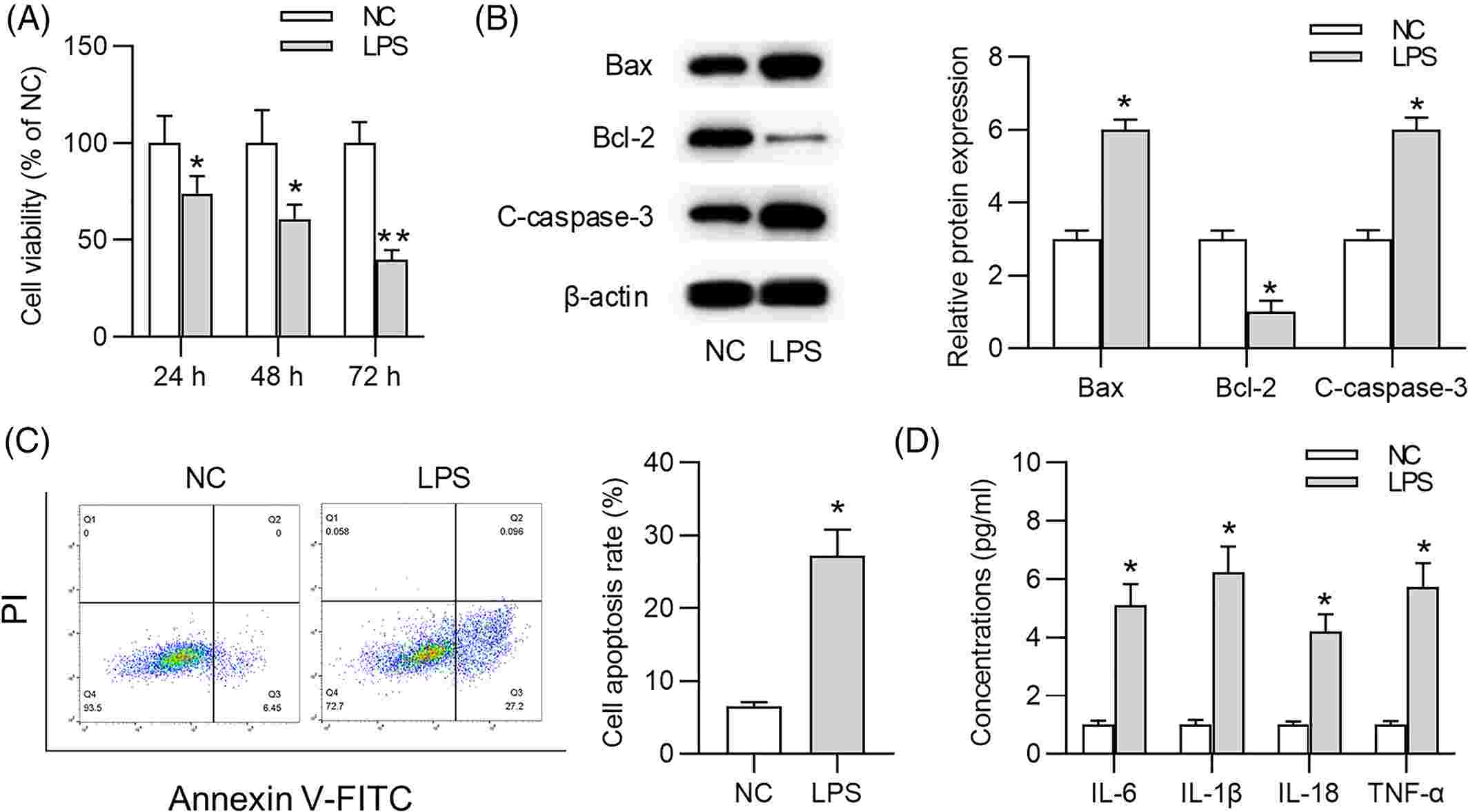 Fig. 1. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to WI-38 cell damage and inflammatory response (Wang J, Chen Z, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to WI-38 cell damage and inflammatory response (Wang J, Chen Z, et al., 2021).
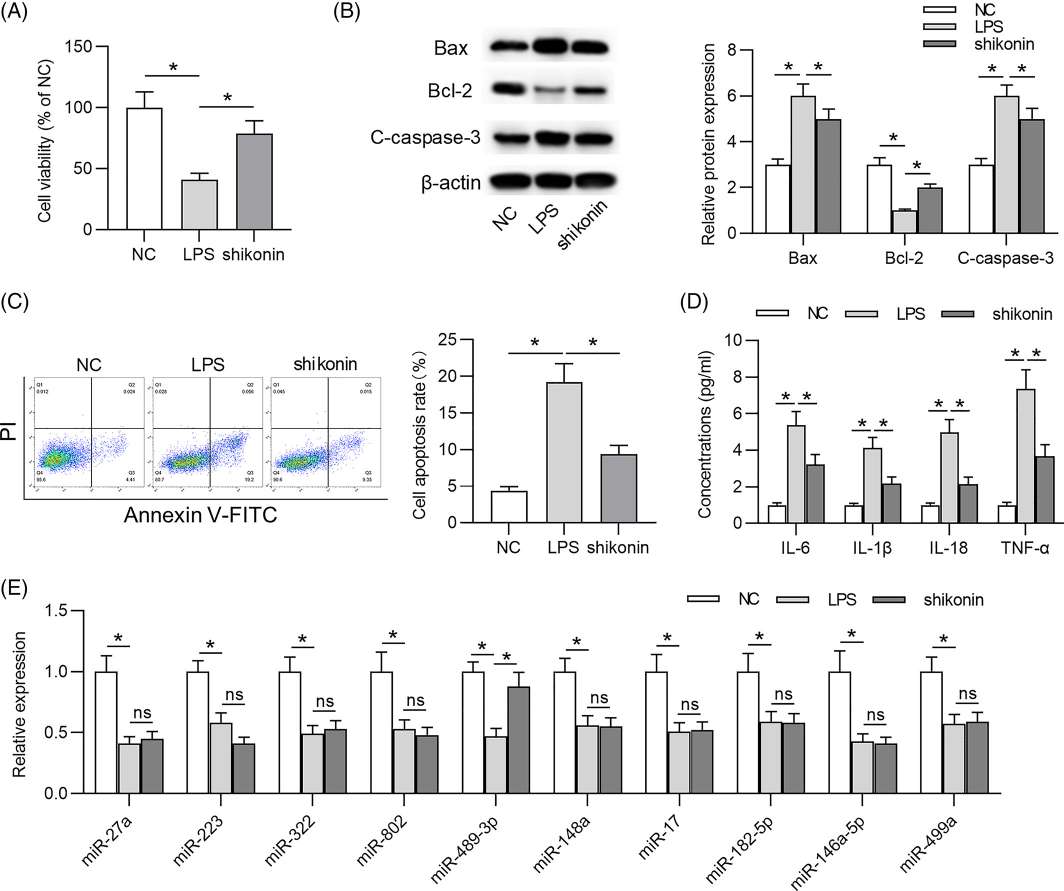 Fig. 2. Shikonin alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cell injury on WI-38 cells (Wang J, Chen Z, et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. Shikonin alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cell injury on WI-38 cells (Wang J, Chen Z, et al., 2021).
Histamine-Evoked Elevation in [Ca2+]i in WI-38 was Mainly Mediated by H1R
Histamine, an inflammatory mediator released by mast cells, causes asthmatic airway remodeling and chronic airflow restriction. H1R coordinates histamine's effects by increasing intracellular Ca2+ in human pulmonary fibroblasts, though the mechanism of action is not well understood. Therefore, Berra-Romani et al. aim to understand how histamine-induced [Ca2+]i increases in foetal human pulmonary WI-38 fibroblasts are achieved.
Their findings demonstrated that histamine provoked a variety of intracellular Ca2+ discharges that were inhibited by pyrilamine (H1R inhibitor) and slowed by ranitidine (H2R inhibitor). Those Ca2+ signals were regulated by Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum via InsP3 receptors and controlled by store-operated Ca2+ channels (SOCs). Various HR antagonists were used to identify which HR isoform caused intracellular Ca2+ activation in WI-38 (pyrilamine: H1R, ranitidine: H2R, clobenpropit: H3R, NJ7777120: H4R). After a preincubation with these antagonists, histamine was administered. Arachidonic acid (AA) was also used to confirm cell viability in conditions where histamine did not induce a [Ca2+]i rise. It turned out that H1R inhibition suppressed the histamine-induced Ca2+ signal completely (Fig. 3A), H2R inhibition reduced the Ca2+ signal significantly (Fig. 3B), while H3R (Fig. 3C) and H4R blockage (Fig. 3D) had no significant effect. Statistical comparisons (Fig. 3E) showed that H1R and, to a lesser extent, H2R are required for Ca2+ uptake in WI-38 cells, but not H3R or H4R.
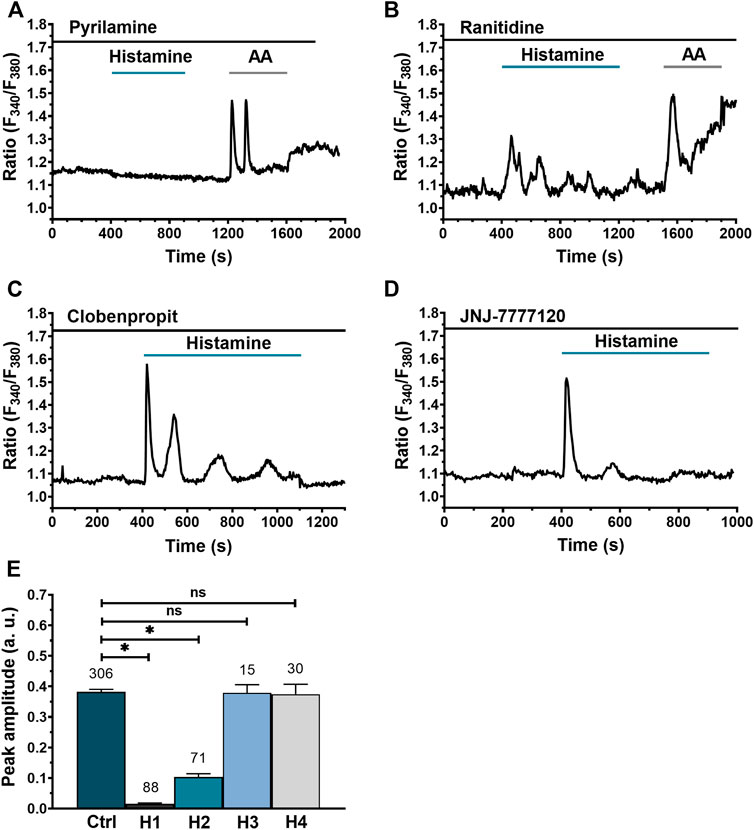 Fig. 3. Histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts do not involve Gαi/o activation but require PLC and ER Ca2+ release (Berra-Romani R, Vargaz-Guadarrama A, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. Histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts do not involve Gαi/o activation but require PLC and ER Ca2+ release (Berra-Romani R, Vargaz-Guadarrama A, et al., 2022).
WI-38, derived from the embryonic lung tissue of a 3-month-gestation female in 1962, is the first human diploid cell line used in the preparation of human vaccines.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 5 Scientist has reviewed this product
Reliable products
I highly recommend Creative Bioarray for their professionalism and reliable products.
10 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliable products
I highly recommend Creative Bioarray for their professionalism and reliable products.
10 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliable products
I highly recommend Creative Bioarray for their professionalism and reliable products.
10 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliable products
I highly recommend Creative Bioarray for their professionalism and reliable products.
10 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliable products
I highly recommend Creative Bioarray for their professionalism and reliable products.
10 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need