Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
RAJI
Cat.No.: CSC-C8231L
Species: Homo sapiens (human)
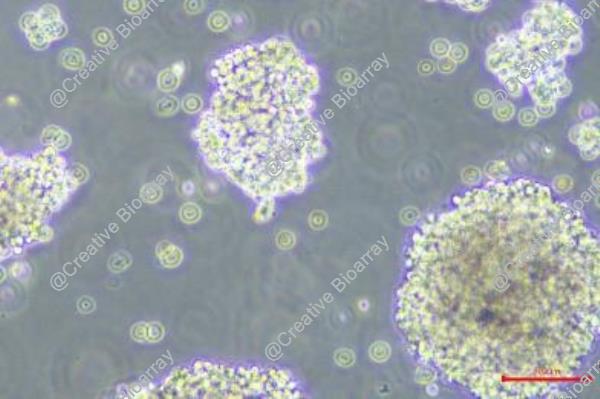
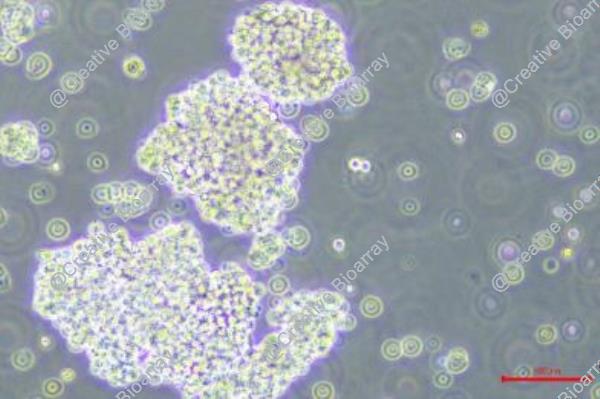
Morphology: Lymphoblastoid
Culture Properties: Suspension (partly in clusters or clumps)
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
RAJI is a cell line that was established in 1963 from a case of Burkitt's lymphoma, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, in an 11-year-old black male. The cell line has been widely used in research to study various cancer biology and immunology aspects.
RAJI cells exhibit a distinctive growth pattern. They grow as single cells without attachment, meaning they do not adhere to a substrate or surface, and can also form macroscopically visible clumps consisting of hundreds of cells. This characteristic growth pattern makes RAJI cells easy to handle and study in laboratory settings. One of the distinctive characteristics of the RAJI cell line is its association with the latent Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) genome. These cells test positive for EBNA (Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen) and are sometimes referred to as a "non-producer" due to deletions in the EBV genome that prevent the formation of virus particles.
RAJI cells have been extensively used in research, particularly in studies focusing on lymphomas, virology, immune responses, and cancer biology. Their unique properties, including the presence of the EBV genome and resistance to VSV, make them a valuable tool for investigating viral interactions, cellular immune responses, and potential therapeutic interventions related to EBV-associated diseases.
Meloxicam on RAJI Cell Line Proliferation and Apoptosis
Meloxicam, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, inhibits the production of PGE2 by blocking Cox-2 activity. The study aimed to study the effect of meloxicam on the proliferation and apoptosis of Raji cell lines.
The effects of meloxicam were examined on the viability of Raji cells by using the MTT assay. Raji cells were treated with meloxicam at the specified concentrations (0-200 μM) for 24 hours. The percentage of cell viability was averaged to 89.67 ± 1.53%, 79.33 ± 5.51%, 74.67 ± 1.53%, 74.33 ± 4.73%, 68.67 ± 3.22%, 72.33 ± 1.53%, and 76.67 ± 3.51%, respectively. As shown in Fig. 1, a significant decrease in cell viability was observed in Raji cells treated with meloxicam (p < 0.05). Fig. 2 shows that meloxicam treatment for 24 hours causes an increase in Raji cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.05). The percentage of apoptotic cells was averaged at 18.4 ± 1.8%, 23.53 ± 2.2%, and 25.57 ± 1.6%, respectively. Morphological changes in the Raji cells after being treated with meloxicam were observed using SEM (Fig. 3). After treatment with meloxicam, many blebs extrude from the cytoplasm giving the cell a foamy shape, indicating an apoptosis process occurred. These findings suggest that meloxicam has anticancer properties by inhibiting Raji cell proliferation and inducing Raji cell apoptosis in vitro.
 Fig. 1 Raji cell viability was treated with various concentrations of meloxicam for 24 hours. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 Raji cell viability was treated with various concentrations of meloxicam for 24 hours. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
 Fig. 2 The flow cytometry histogram of the percentage of Raji cells after 24 hours of incubation with various concentrations of meloxicam. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 The flow cytometry histogram of the percentage of Raji cells after 24 hours of incubation with various concentrations of meloxicam. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
 Fig. 3 Representative scanning electron microscopy of Raji cells. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
Fig. 3 Representative scanning electron microscopy of Raji cells. (Asmarani YK, et al., 2022)
B10 Inducing RAJI Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphoid cells originating in matured B or T cells. The study isolates a natural stilbene B10 (3-methoxy 5-hydroxy stilbene) from Cajanus cajan (Pigeon Pea) for its anti-proliferative efficacy against human lymphoma (Raji) cells.
To confirm the apoptotic effect of B10 in Raji cells, PI /AnnexinV-FITC dual staining analysis was performed at 24 and 48 h of B10 treatment for 12, 18, and 24 µM concentrations. The flow cytometric analysis revealed dose and time-dependent enhancement in apoptosis rates after B10 treatment (Fig. 4A and 4B). Additionally, the PI-stained flow cytometric cell cycle analysis revealed that G1 and S phases got arrested by B10 treatment, both dose and time-dependently (Fig. 4C and 4D). The western blot protein expression analysis of apoptotic and cell cycle proteins was carried out. In accordance, there was a significant increase in expression of APAF-1, cleaved caspase3, cleaved caspase9, cleaved PARP1, and decreased expression of cyclin D1 compared to control in both dose and time-dependent manner after B10 treatment (Fig. 4E and 4F). Thus, the results could reveal the selective inhibitory effects of B10 on lymphoma, suggesting it is a probable innovative chemotherapeutic agent.
 Fig. 4 B10 aggravates dose/time-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in Raji cells. (Varier KM, et al., 2022)
Fig. 4 B10 aggravates dose/time-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in Raji cells. (Varier KM, et al., 2022)
Sodium bicarbonate improves the pH control of media incubated in a 5-10% CO2 atmosphere and provides cells with carbonate ions that are essential for the metabolic functions of most cells. Additionally, this buffer is non-toxic to cells in culture.
RAJI cells grow both as single cells without attachment and as macroscopically visible clumps containing many hundreds of cells.
RAJI cells are called "non-producers" because the EBV genome in these cells carries deletions that prevent the formation of virus particles.
Yes, RAJI cells are positive for EBNA (Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen), which is a marker for the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV).
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Easy to culture
The cells could be easily passaged or expanded for larger-scale experiments.
21 Mar 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Beneficial resources
Additional guidance or troubleshooting resources specific to the RAJI cell line from Creative Bioarray would have been beneficial.
03 Oct 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Promote delivery
The delivery of the RAJI cells was prompt, and the packaging ensured their integrity during transportation.
11 Dec 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need