Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
OCI-Aml-3
Cat.No.: CSC-C9119W
Source: acute myeloid leukemia
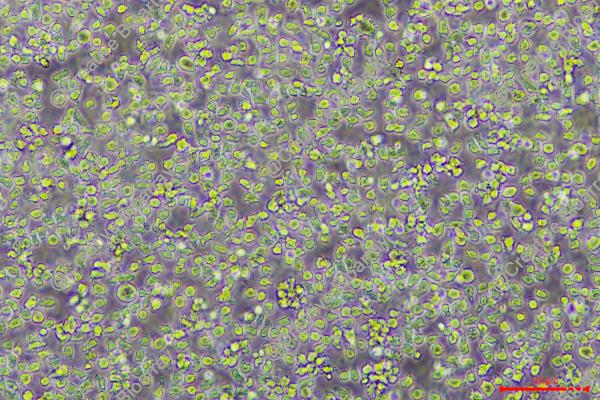
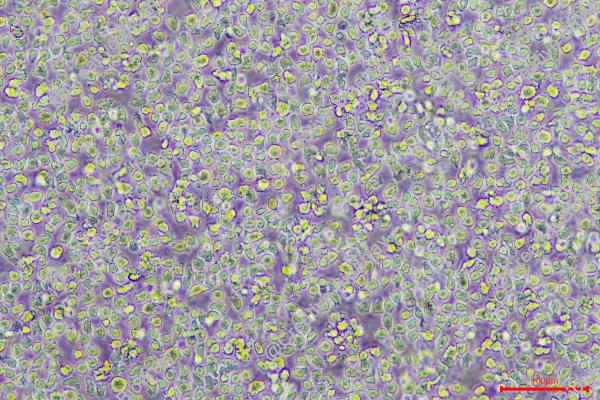
Morphology: single, mostly round cells growing in suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
The OCI-AML3 cell line is a well-known and widely used cell line in AML research. It was established from the peripheral blood of a 57-year-old male patient diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) of the French-American-British (FAB) subtype M4 in 1987. This cell line has been extensively characterized and has specific genetic mutations that are representative of AML.
Two significant genetic mutations found in OCI-AML3 cells are the NPM1 gene mutation and the DNMT3A R882C mutation. The NPM1 gene mutation is of type A, which refers to mutations that involve the nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) gene. NPM1 mutations are one of the most common genetic alterations in AML and are associated with a favorable prognosis. The DNMT3A R882C mutation is specific in the DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) gene at the amino acid position 882. DNMT3A mutations are recurrent in AML and have been implicated in leukemogenesis.
Due to its relevance to AML biology and the presence of these specific mutations, the OCI-AML3 cell line serves as a valuable model for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying leukemia development and progression. Researchers use this cell line to investigate various aspects of AML, such as the effects of genetic mutations on cellular processes, signaling pathways involved in leukemogenesis, and responses to different therapeutic agents.
Additionally, the OCI-AML3 cell line is frequently employed in drug testing and development studies. Researchers use it to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of potential anti-leukemic compounds and to explore novel therapeutic targets for AML treatment.
Proteomic Analysis of Nucleostemin in OCI-AML-3 Cell Line
Nucleostemin (NS; a product of the GNL3 gene) is a nucleolar-nucleoplasm shuttling GTPase whose levels are high in several solid and hematological neoplasms, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). It plays a role in telomere maintenance, response to stress stimuli, and favoring DNA repair.
To investigate the role of NS in AML with NPM1 mutation, the OCI-AML 3 cell line bearing the most common NPM1 mutation was used as a model system. Preliminarily, basal NS expression in a panel of AML cell lines was assessed. First of all, the study observed a strong expression of NS in OCI-AML 3 SCR control cells, which was markedly reduced after 72 h of doxycycline treatment. NS protein levels were less than 10% in shNS OCI-AML 3 cells in comparison with the SCR control (Fig. 1A). In addition, mRNA expression levels of NS in silenced cells were significantly reduced by at least of 50%-as compared to the SCR control (Fig. 1B).
To further shed light on the role of NS expression in OCI-AML 3 cells, the study performed a shotgun proteomics analysis of shNS cells and their SCR control. 1298 proteins for OCI-AML 3 SCR and 1452 proteins for OCI-AML 3 shNS were identified and quantified. Among them, 1245 proteins were in common between the two conditions, as reported in the Venn diagram of Fig. 1C, consisting of 82.5% of all identified proteins. OCI-AML 3 cells with silenced NS significantly triggered biological processes related to down-regulation of cell movement, cell viability, and homologous recombination as well as significantly up-regulated mechanisms linked to cell death of cancer cells and bone marrow lesions.
 Fig. 1 NS expression, silencing, and differential proteomics analysis of OCI-AML 3 cells. (Cela I, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 NS expression, silencing, and differential proteomics analysis of OCI-AML 3 cells. (Cela I, et al., 2022)
Pim Kinase Inhibitor Inducing Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Death
Pim kinases are serine/threonine kinases with multiple substrates that affect survival pathways. The imidazo pyridazine compound SGI-1776 inhibits Pim-1, Pim-2, and Pim-3. It was evaluated in AML cell lines (MV-4-11, MOLM-13, and OCI-AML-3). The phosphorylation of traditional Pim kinase targets, c-Myc (Ser62), and 4E-BP1 (Thr36/Thr47) decreased in actively cycling AML cell lines MV-4-11, MOLM-13, and OCI-AML-3 (Fig. 2).
Treatment of AML cells with SGI-1776 results in a concentration-dependent induction of apoptosis. A significant reduction of levels of antiapoptotic proteins Mcl-1 was observed. In OCI-AML-3, RNA synthesis was inhibited to 80% and 50% of control at 1 and 10 μM SGI-1776, respectively (Fig. 3A). The MV-4-11 and MOLM-13 cell lines also showed inhibition of RNA synthesis, and further studies found that inhibition of RNA synthesis was associated with reduced levels of the MCL-1 transcript and impaired protein translation. MV-4-11, MOLM-13, and OCI-AML-3 cells were treated with SGI-1776 and then stained with either annexin/PI or DiOC6/PI to assess cell survival. There was a dose-dependent increase in annexin/PI-positive cells in all 3 lines (Fig. 4). To sum up, Pim kinase inhibition may be a new strategy for AML treatment.
 Fig. 2 Immunoblot analysis of Pim kinase targets in AML primary cells treated with SGI-1776. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
Fig. 2 Immunoblot analysis of Pim kinase targets in AML primary cells treated with SGI-1776. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
 Fig. 3 Effect of SGI-1776 in AML cell lines. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
Fig. 3 Effect of SGI-1776 in AML cell lines. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
 Fig. 4 Induction of cell death by SGI-1776 in AML cell lines. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
Fig. 4 Induction of cell death by SGI-1776 in AML cell lines. (Chen LS, et al., 2011)
Specimens collected after antibiotic exposure may reduce culture-based bacterial detections. The impact on culture-independent diagnostic tests is unclear.
OCI-Aml-3 cells carry an NPM1 gene mutation (type A) and the DNMT3A R882C mutation.
Yes, OCI-Aml-3 cells are widely used in research studies related to acute myeloid leukemia, particularly those focusing on NPM1 and DNMT3A mutations.
Like any cell line, OCI-Aml-3 cells may have specific characteristics or limitations that need to be taken into account, such as their genetic background and potential differences from primary patient samples.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Grateful
We are grateful for the availability of such a wide variety of tumor cell types in Creative Bioarray.
10 Mar 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Well-characterized
In our experiments, the OCI-Aml-3 cells exhibited the characteristic features of AML, expressing relevant markers and displaying the expected growth pattern. This consistency in phenotype made the cells suitable for our research objectives.
02 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
High viability
The OCI-Aml-3 cells arrived on time, and the packaging was secure, ensuring their viability upon arrival. The provided documentation was thorough, offering detailed protocols for culturing and maintaining the cells. This was particularly helpful for researchers new to working with this cell line.
11 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need