Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
OCI-AML-2
Cat.No.: CSC-6981J
Species: Homo sapiens (human)
Source: Peripheral blood
Morphology: Single, round to oval cells in suspension
Culture Properties: Suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
OCI-AML-2 cells are a well-known cell line that was established in 1986 from the peripheral blood of a 65-year-old man diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), specifically classified as French-American-British (FAB) subtype M4. These cells have been widely utilized in research studies aimed at understanding the biology of AML and investigating potential therapeutic approaches.
These cells exhibit key features of AML, including abnormal proliferation, impaired differentiation, and the ability to form colonies in vitro. The OCI-AML-2 cell line has been extensively used to investigate the genetic and molecular alterations associated with AML, such as chromosomal abnormalities and mutations in genes involved in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis.
Furthermore, OCI-AML-2 cells have been employed in preclinical drug screening assays to test the efficacy and toxicity of various therapeutic agents. They have helped researchers evaluate potential treatment strategies and identify novel therapeutic targets for AML.
Isolation of Daunorubicin-Resistant AML-2 Sublines
An attempt was made to isolate resistant sublines of acute myelogenous leukemia (OCI-AML-2) cells by chronic exposure to gradually increasing concentrations of daunorubicin to determine the mechanism of its resistance to this drug. Five drug-resistant AML-2 sublines are developed from the wild-type AML-2 line. The resistant AML-2 sublines selected for resistance to daunorubicin were named AML-2/D100, /D250, /D500, and /D 1,000. These resistant sublines appeared to be similar to the wild-type AML-2 cell line in cell size, while they showed slightly increased doubling times of 30 h, 30 h, 43 h, and 43 h, respectively, as compared to 22 h in the parental cell line. The AML-2/D100, /D250, /D500, and /D1,000 were approximately 3-, 6-, 18-, and 23-fold resistant to daunorubicin in comparison to the AML-2 cell line in terms of IC50 (Fig. 1 and Table 1).
As shown in Table 1, the AML-2/D100 and/D250 sublines displayed low levels of cross-resistance to doxorubicin (4-fold), vincristine (26-fold), and VP-16 (10-fold). The AML-2/D500 showed an intermediate level of cross-resistance to doxorubicin (7-fold), vincristine (74-fold), and VP-16 (14-fold). The AML-2/D1,000 subline was resistant to doxorubicin (16-fold), vincristine (248-fold), and VP-16 (37-fold).
 Fig. 1 Cytotoxicity of daunorubicin in the parental AML-2 cell line and its daunorubicin-resistant sublines. (Choi CH, Ling V, 1997)
Fig. 1 Cytotoxicity of daunorubicin in the parental AML-2 cell line and its daunorubicin-resistant sublines. (Choi CH, Ling V, 1997)
Table 1. Relative resistance of daunorubicin-resistant AML-2 sublines to a variety of anticancer drugs. (Choi CH, Ling V, 1997)
| Cell line | Relative resistance | |||
| DNR | DOXO | VCR | VP-16 | |
| AML-2/WT | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| AML-2/D100 | 3 | 4 | 26 | 10 |
| AML-2/D250 | 6 | 4 | 26 | 10 |
| AML-2/D500 | 18 | 7 | 74 | 14 |
| AML-2/D1,000 | 23 | 16 | 248 | 37 |
In Vivo Anti-tumor Effects of either Free VTX or PEG-VTX on OCI-AML-2 Mouse Models
A novel polyethylene glycol (PEG)-drug conjugate of VTX (PEG-VTX) was evaluated for its cytotoxic effects on AML both in vitro and in vivo. In the OCI-AML-2 xenograft model, the clinical dosage was mimicked by orally administering free VTX daily for 2 weeks at a dose of 100 mg/kg/day: the total VTX dosage was 1400 mg/kg (Fig. 2 upper panel). PEG-VTX was intravenously administered at 100, 200, or 300 mg/kg once a week for 2 weeks: the total VTX dosages were 16, 32, and 48 mg/kg. Intravenous PEG-VTX showed a weaker growth-inhibitory effect even at the highest dose (300 mg/kg), compared with 100 mg/kg of oral-free VTX (Fig. 2 middle panel and Table 2). The doses of converted API and VTX, however, were much smaller in PEG-VTX (48 mg/kg) than in free VTX (1400 mg/kg). In addition, and most importantly, the treatments of intravenous PEG-VTX even at the highest dose (300 mg/kg) caused no body weight loss in the treated mice, while the treatments of oral-free VTX (100 mg/kg) caused >16% body weight loss (Fig.2 lower panel).
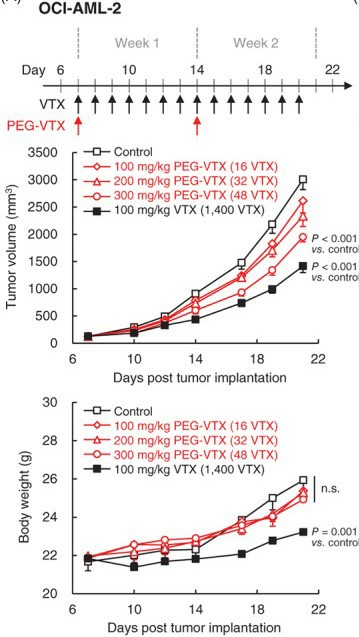 Fig. 2 In vivo anti-tumor effects of either free VTX or PEG-VTX on OCI-AML-2 xenograft mouse model. (Ando H, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 In vivo anti-tumor effects of either free VTX or PEG-VTX on OCI-AML-2 xenograft mouse model. (Ando H, et al., 2022)
Table 2. TGI of free VTX and PEG-VTX on OCI-AML-2 xenograft mouse model. (Ando H, et al., 2022)
| Treatment | TGI (%) |
| 100 mg/kg PEG-VTX (16 VTX) | 13.1 |
| 200 mg/kg PEG-VTX (32 VTX) | 22.4 |
| 300 mg/kg PEG-VTX (48 VTX) | 35.2 |
| 100 mg/kg VTX (1400 VTX) | 52.9 |
A diagnosis of leukemia is usually made by analyzing a patient's blood sample through a complete blood count (CBC) or microscopic evaluation of the blood, or by using flow cytometry.
OCI-AML-2 cells were established in 1986 from the peripheral blood of a 65-year-old man diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML FAB M4) at the time of diagnosis.
Yes, OCI-AML-2 cells are commonly used in preclinical drug screening assays. They provide a valuable model for testing the effectiveness of various therapeutic agents and help researchers assess their potential in treating AML.
OCI-AML-2 cells may exhibit specific genetic and molecular alterations commonly found in AML, such as chromosomal abnormalities and mutations in genes involved in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. These characteristics make them valuable for studying the genetic basis of AML.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Good results
Our lab has used these cell products to develop new cancer treatments and gotten good experimental results!
25 Apr 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Satisfied
I recently purchased the OCI-AML-2 cell line from Creative Bioarray, and overall, I'm satisfied with the product.
13 Oct 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Expected characterizations
The OCI-AML-2 cells exhibited the expected characteristics of AML, allowing me to conduct my research effectively. The customer support team was responsive and assisted when needed.
23 Dec 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review