Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
MKN-45
Cat.No.: CSC-C0453
Species: Human
Source: gastric adenocarcinoma
Morphology: both spindle-shaped or oval cells growing in monolayers and single round cells or clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Publications
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +
The MKN45 cell line was established from a tissue sample obtained from a 62-year-old woman diagnosed with a poorly differentiated, medullary-type adenocarcinoma of the stomach. This aggressive form of gastric cancer is characterized by the proliferation of highly anaplastic tumor cells with a lack of glandular differentiation.
By deriving the MKN45 cell line directly from the patient's primary gastric tumor, researchers were able to create a valuable in vitro model that faithfully represents the biological and molecular features of this malignancy. The establishment of the MKN45 line provided a renewable and reliable resource for investigating the underlying mechanisms driving the development and progression of poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma.
Since its initial characterization, the MKN45 cell line has been widely utilized in gastric cancer research. Investigators have leveraged this model to elucidate key signaling pathways, identify genetic and epigenetic alterations, and evaluate the efficacy of various therapeutic agents against this aggressive form of stomach cancer. The availability of the MKN45 cells has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the complex biology of gastric adenocarcinoma and informing the development of more effective treatment strategies for affected patients.
Suppressive Activity of MT-2 Cells on Primary Human PB CD4 Cells and Mouse CD4 Cells
The MKN-45 cell line was established from a liver metastasis of a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Some growth factors (GFs) and supplements, such as FGF-2 and EGF, are used to support the spheroid formation in serum-free spheroid culture of MKN-45 cells. There is no significant difference between the groups of FBS- GF- and FBS- GF+ in terms of the size and viability of spheroids. However, the group of FBS- GF- had a 2 times higher number of spheroids when compared to the group of FBS- GF+ (p = 0.04) (Fig. 1).
Expression changes in OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, MUC1, CD24, and CD90 genes were analyzed by qRT-PCR to monitor whether spheroid bodies grown in different culture systems cause enrichment of cells expressing stem cell markers (Fig. 2). The results indicated that MKN-45 spheroids from two different culture systems showed different expression patterns of stem cell markers. The addition of the GFs significantly decreased the expression of OCT4, MUC1, NANOG, SOX2, CD24, and CD90 (p = 0.02, p = 0.0003, p = 0.0006, p = 0.03, p = 0.001, and p = 0.001, respectively). Gene expression changes in spheroid cells are shown in Fig. 2. CD44 levels were analyzed using a flow cytometer (Fig. 2B-2D). The ratio of CD44-positive cells decreased in spheroids compared to parental cells. The parental cells also had a larger CD44 population (77.6%). (Fig. 2C, 2F, 2G). The FBS- GF- group had an elevated level of CD44 high expression (18.3%) (Fig. 2C) compared to the group of FBS- GF+ (12.7%) (Fig. 2D).
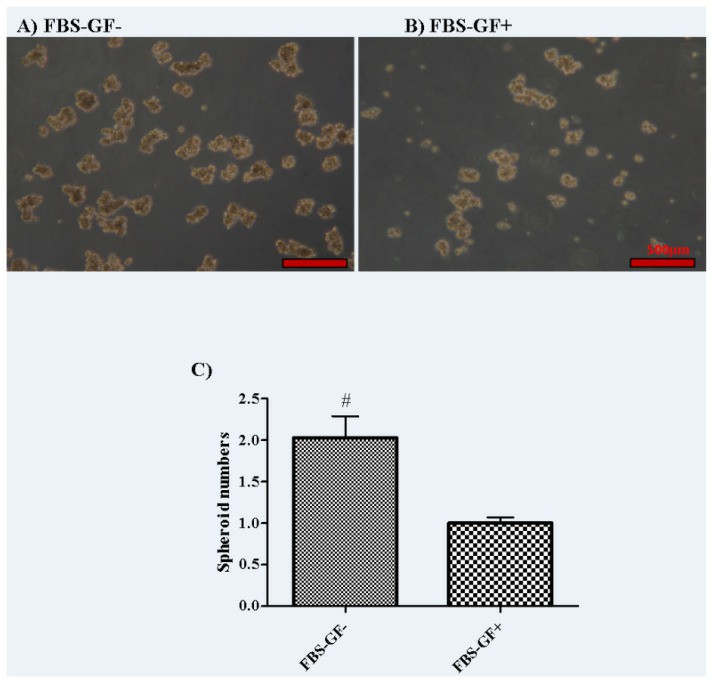 Fig. 1 Comparison of the effect of GFs, FBS-positive, and GF–FBS-free conditions on spheroid-forming activity in the MKN45 cell line. (Türksoy Terzioğlu Ö and Terzioğlu G, 2023)
Fig. 1 Comparison of the effect of GFs, FBS-positive, and GF–FBS-free conditions on spheroid-forming activity in the MKN45 cell line. (Türksoy Terzioğlu Ö and Terzioğlu G, 2023)
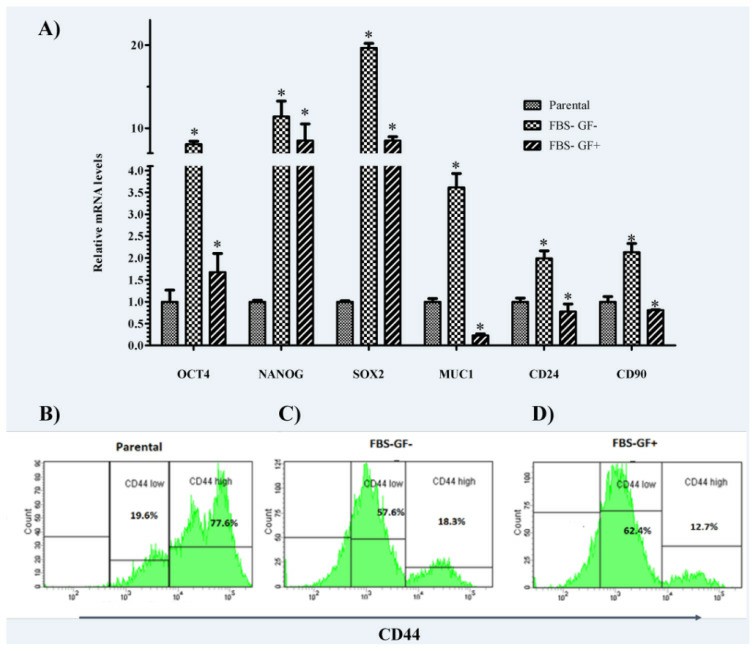 Fig. 2 Stem cell-related genes were upregulated in spheroid-derived cells over parental counterparts. (Türksoy Terzioğlu Ö and Terzioğlu G, 2023)
Fig. 2 Stem cell-related genes were upregulated in spheroid-derived cells over parental counterparts. (Türksoy Terzioğlu Ö and Terzioğlu G, 2023)
Effects of Magnolol and/or Cisplatin on MKN-45 Cells
Gastric cancer is the most common type of gastrointestinal cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death. Magnolol, used in treating gastrointestinal disorders, has been shown to have anti-cancer properties. Cisplatin is one of the most commonly used medications to treat gastric cancer. However, cisplatin does not work for all patients.
According to MTT data, magnolol treatment reduced cell viability dose-dependently (Fig. 3). The algorithm of cisplatin's effect on MKN-45 cells was similar to that of magnolol (Fig. 3). However, the combination of magnolol and cisplatin resulted in a substantially more significant reduction in cell viability (Fig. 3). IC50 values of magnolol, cisplatin, and their combination were 6.53, 7, and 3.25 µM, respectively.
According to the results of proliferation analysis, the cell growth rate was reduced to 62% and 59% of the control group after 24 h of treatment with magnolol and cisplatin, respectively (p < 0.05). However, the combination of the two medications decreased cellular proliferation by 55.5% compared to the control (p < 0.05). The tendency of lower cell proliferation in all treatment groups relative to the control group persisted until the fifth day of therapy. In the groups treated with magnolol, cisplatin, and magnolol plus cisplatin for five days, the proliferation amount reduced to 38.0%, 36.5%, and 36.7% of the control, respectively (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4). Following magnolol injection, the ability of MKN-45 cells to form colonies was significantly reduced. The cells that received cisplatin therapy showed a more significant decrease in colony formation. The cells that were given a combination of magnolol and cisplatin had the least ability to form colonies (Fig. 5A-E).
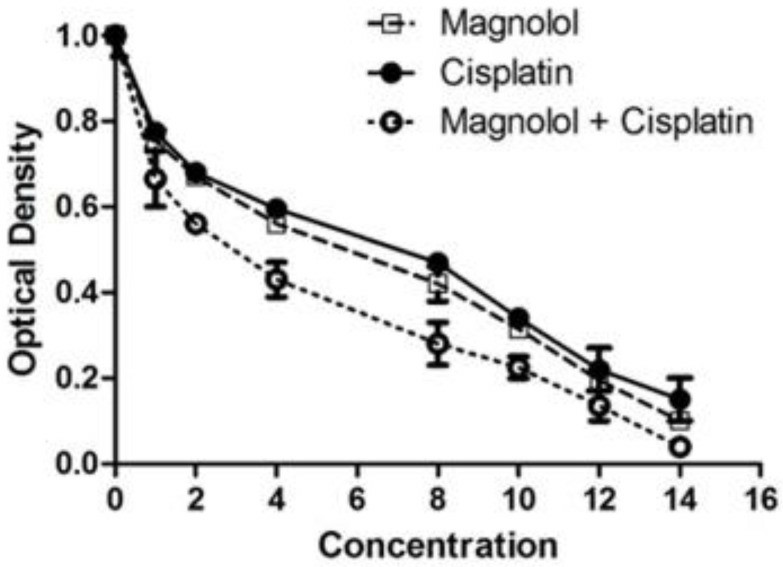 Fig. 3 Changes in MKN Cells' viability following magnolol and/or cisplatin therapy. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
Fig. 3 Changes in MKN Cells' viability following magnolol and/or cisplatin therapy. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
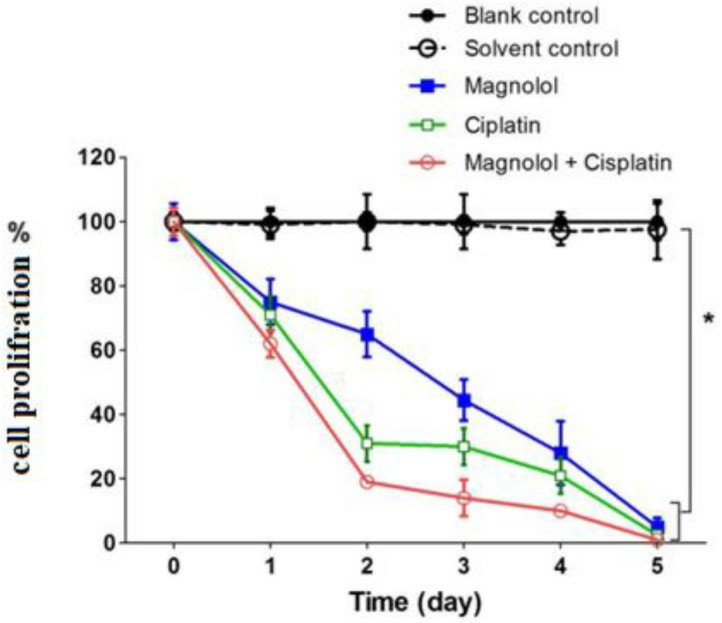 Fig. 4 Proliferation assay following treatment of MKN-45 cells with magnolol and/or cisplatin. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
Fig. 4 Proliferation assay following treatment of MKN-45 cells with magnolol and/or cisplatin. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
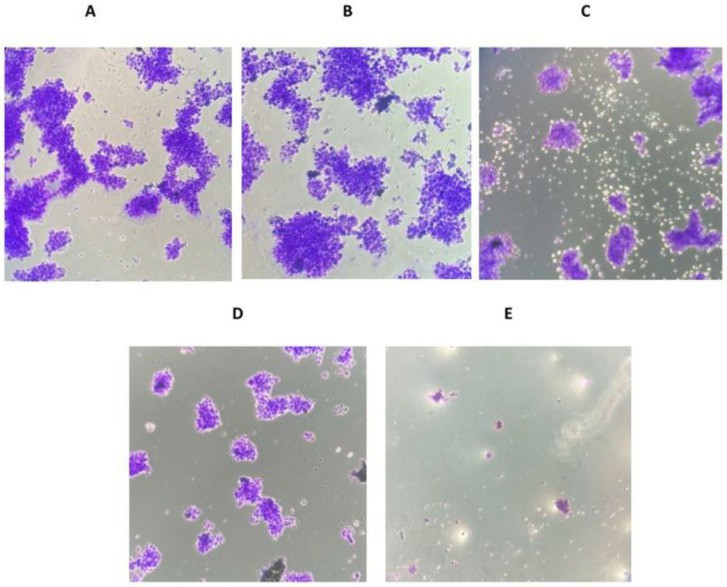 Fig. 5 The effect of magnolol and/or cisplatin on colony formation in MKN-45 cells. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
Fig. 5 The effect of magnolol and/or cisplatin on colony formation in MKN-45 cells. (Naghashpour M, et al., 2023)
Fibroblasts are more sensitive to enzymes, so they can be removed more easily than tumor cells when digested with trypsin or collagenase. The digestion can be observed under the microscope and terminated immediately after the fibroblasts are shed, and the treatment can be repeated several times to obtain purer tumor cells.
The MKN-45 cell line has been used to explore various pathways involved in gastric cancer. For instance, researchers have investigated the gene expression status of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in this cell line.
Studies have shown that MKN-45 cells respond to various treatments, including plant-based drugs. This information is valuable for the development and testing of new therapies for gastric cancer.
The recommended incubation medium for MKN45 cells is 80% RPMI-1640 + 20% h.i. FBS.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Detailed instruction
Each product comes with a detailed instruction manual that includes the protocol for that cell culture, media composition, etc., which is very friendly for novice experimenters.
23 Apr 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Good performance
Our lab has been using the MKN-45 cells from Creative Bioarray in our studies on cancer progression and metastasis. And the cells have consistently performed well.
06 Jan 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Helpful technical team
The team at Creative Bioarray has also been very helpful, providing all the necessary information and support.
15 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need