ONLINE INQUIRY

Mouse Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C4737Z
Species: Mouse
Source: Liver
Cell Type: Endothelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Never can cryopreserved cells be kept at -20 °C
Mouse Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells (MHSECs) originate from mouse liver tissue and form a major component of the sinusoidal walls. These flat, thin cells have numerous fenestrated structures and exhibit adherent growth in vitro. The hepatic sinusoid is a unique structure in liver circulation, mixing blood from the hepatic artery and portal vein and allowing it to flow through the liver parenchyma. MHSECs are adjacent to hepatocytes, Kupffer cells (liver macrophages), and stellate cells, creating a complex liver microenvironment. They contact blood on one side and connect to the space of Disse on the other. MHSECs are highly permeable, allowing rapid exchange of molecules through their fenestrations. They also phagocytose and remove waste and denatured macromolecular lipids from the blood. In the immune system, MHSECs play key roles in antigen presentation and recruiting immune cells to maintain liver immune homeostasis.
MHSECs are used to construct liver disease models like hepatitis and cirrhosis to study disease mechanisms and treatments. In liver regeneration and tissue engineering research, they help create liver tissue models with liver-specific vasculature, providing an essential foundation for regenerative medicine research.
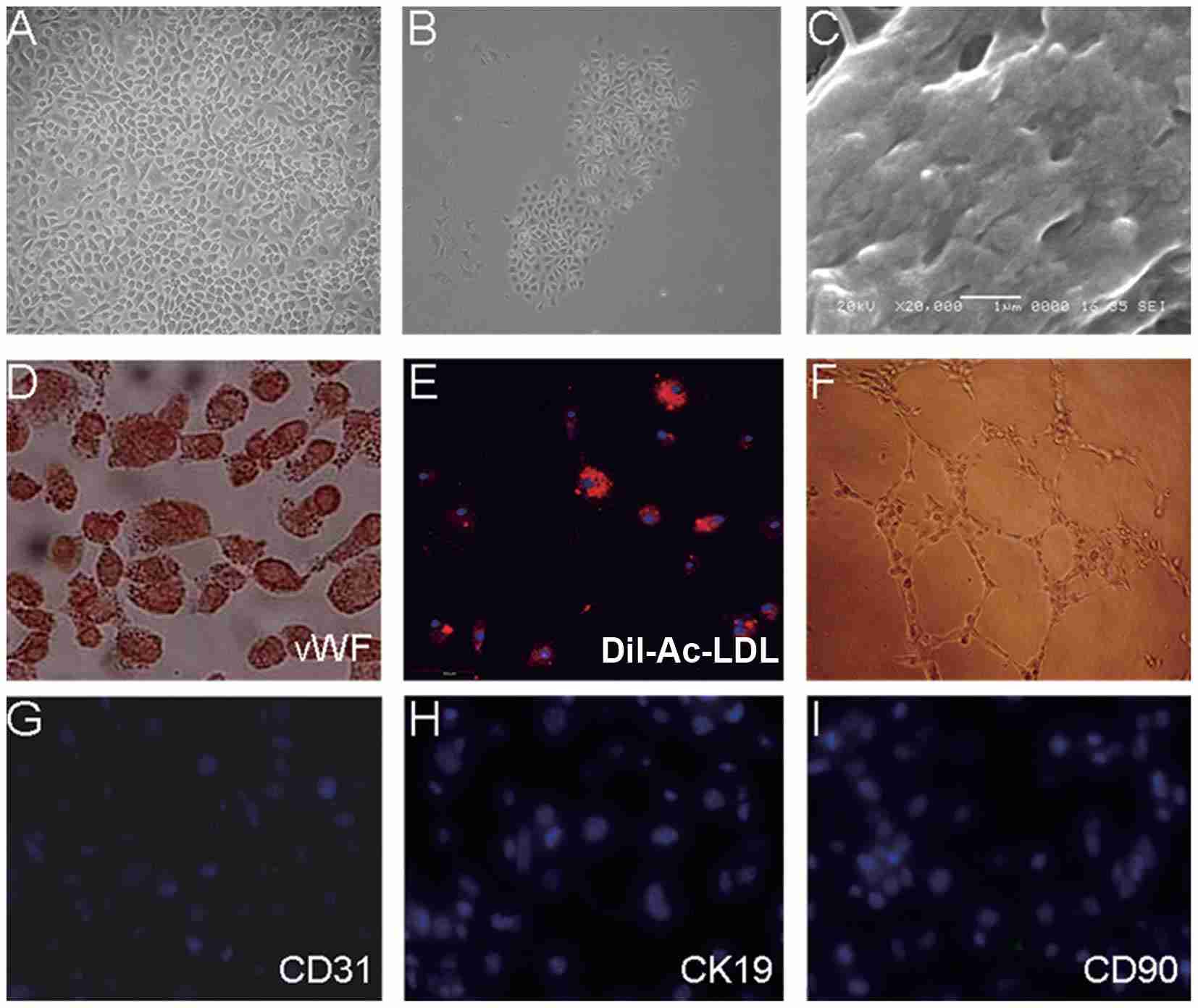 Fig. 1. Characterization of mouse hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (Zhao X, Zhao Q, et al., 2015).
Fig. 1. Characterization of mouse hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (Zhao X, Zhao Q, et al., 2015).
Effects of Curcumol on Ferroptosis and Tube Forming Ability of Hepatic Sinus Endothelial Cells
Chronic liver conditions cause fibrosis of the liver because of chronic inflammation and overrepair, which eventually result in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. These HSECs, the lifeline for liver health and resistance to disease, are damaged in pathology and neovascularised (an unusual and difficult feature of liver fibrosis). Ferroptosis, the programmable cell death triggered by iron build-up and oxidative stress, produces a lot of ROS. ROS accumulation has been correlated with angiogenesis in many studies, but ROS accumulation and angiogenesis in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells have not yet been identified.
The way that curcumol mediated ferroptosis and angiogenesis in HSECs was researched by Wang's team to better understand its molecular defence against liver fibrosis, opening up new therapeutic targets for chronic liver disease prevention and treatment. WB and RT-PCR experiments showed that curcumol reduced SLC7A11 and GPX4 but increased ACSL4 (Fig. 1A-B). It also increases iron ions in HSEC (Fig. 1C), enhances ROS expression (Fig. 1D), and shortens mitochondria length (Fig. 1E). Thus, curcumol induces ferroptosis in HSEC. Angiogenesis experiments revealed that curcumol inhibits angiogenesis by decreasing CD31 and VWF expression after VEGF stimulation and reduces new blood vessel formation (Fig. 2A-C). Therefore, curcumol hinders angiogenesis. To investigate the targets of curcumol's regulation of HSEC ferroptosis and to further clarify the mechanism of action of curcumol's inhibition of angiogenesis. They used si P53 and Ferropto-1, to perform functional replication experiments. Results showed that curcumol targets P53 to influence ferroptosis and angiogenesis. siP53 rescues curcumol-induced changes in iron deposition, ROS levels, and mitochondrial features (Fig. 3A-D). Curcumol's inhibition of migration and angiogenesis can be reversed by siP53 or Ferrostatin-1 (Fig. 3E-F). P53 is crucial for curcumol's effect on ferroptosis, further suggesting that curcumol-induced HSEC ferroptosis is a key mechanism for its inhibition of angiogenesis.
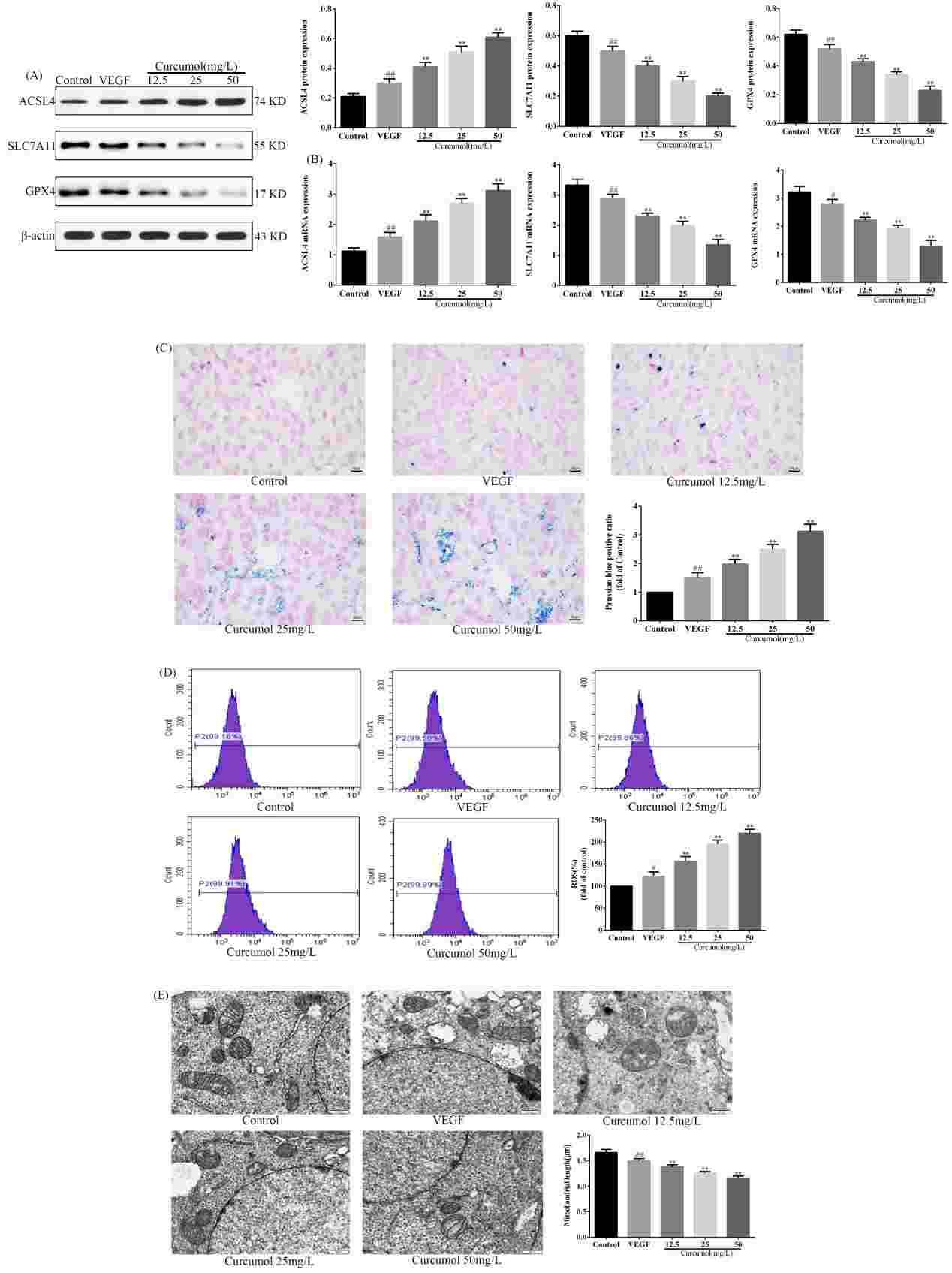 Fig. 1. Curcumol induces ferroptosis in HSEC (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Curcumol induces ferroptosis in HSEC (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
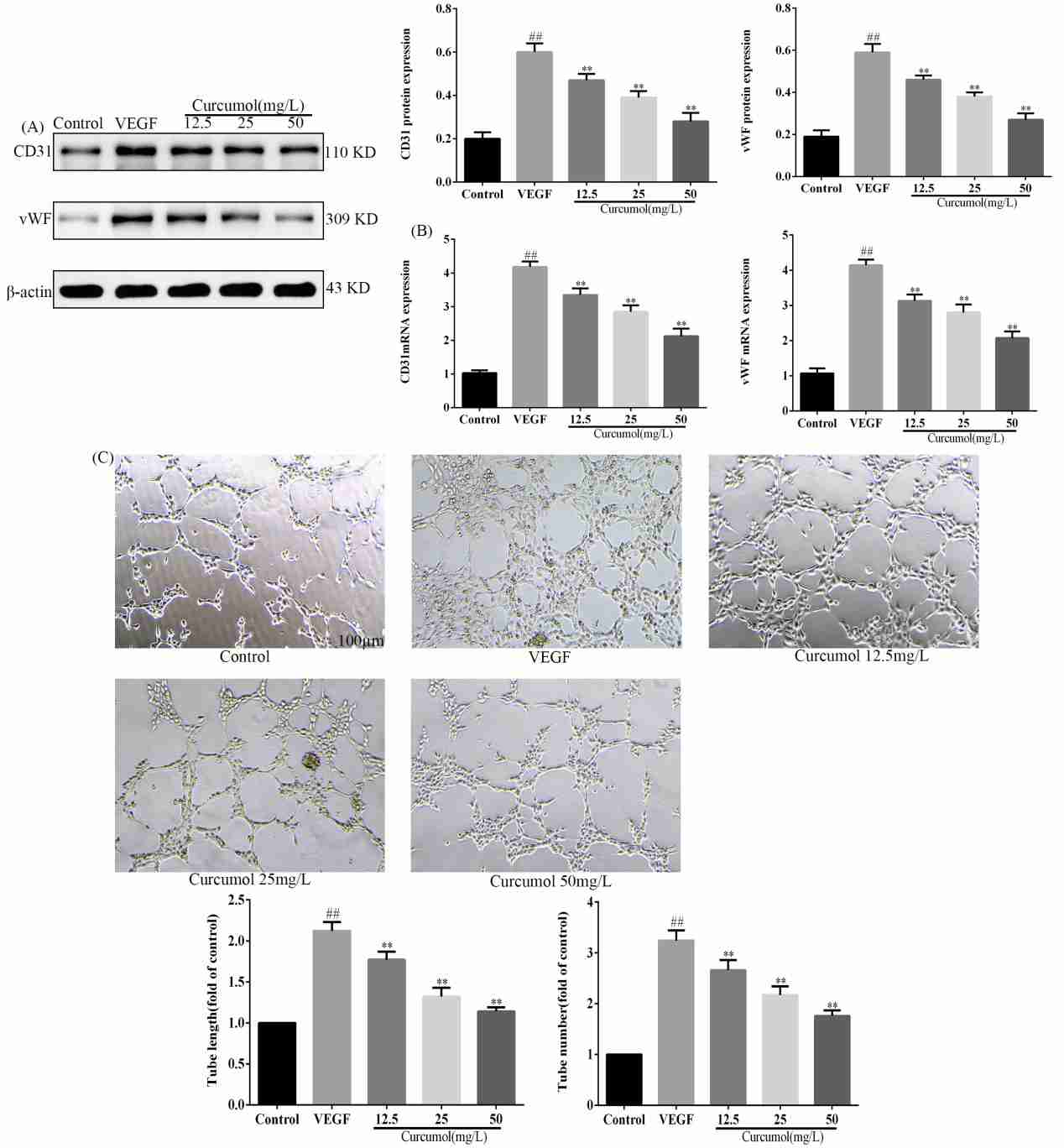 Fig. 2. Effect of curcumol on angiogenesis (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Effect of curcumol on angiogenesis (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
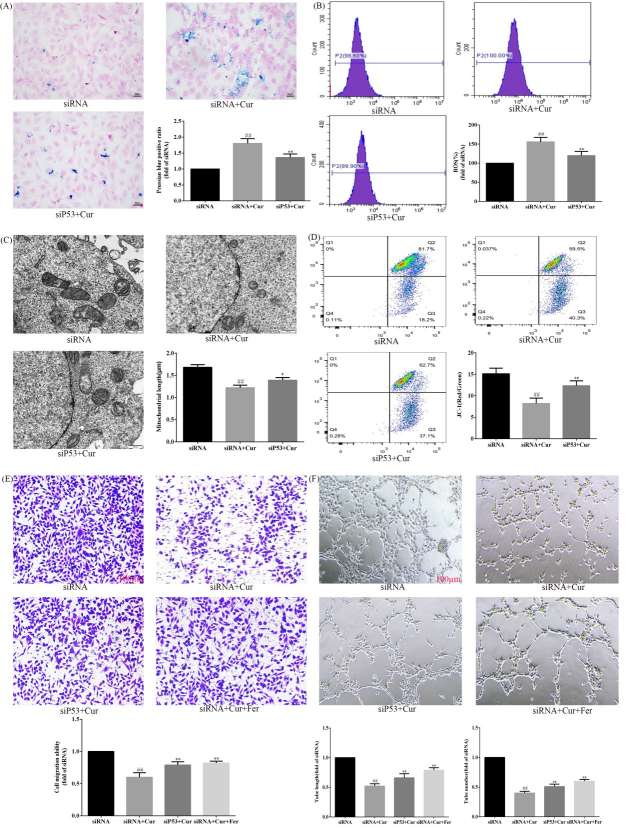 Fig. 3. Curcumol targets P53 to regulate ferroptosis mediated angiogenesis (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Curcumol targets P53 to regulate ferroptosis mediated angiogenesis (Wang J, Huang N, et al., 2024).
Platelet Promoting Effect In Vitro on CD133BMSC Adhesion to Endothelium is Conserved for Rodent Micro Endothelium and LSEC
Previous studies have shown that CD133 bone marrow stem cells (BMSC) aid in liver regeneration after resection, influenced by factors like hepatocyte growth factor and stroma-derived factor-1 (SDF-1). Platelets have been implicated in hepatic injury mediation and liver regeneration by interacting with liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and releasing factors that promote hepatocyte proliferation. Lehwald et al. employed in vitro co-culture systems and a re-perfused rat liver model to examine how platelets enhance CD133 BMSC adhesion and homing to endothelial cells, particularly under shear stress conditions. Key interactions involving platelet receptors such as P-selectin were analyzed.
They found that CD133BMSC adhesion to all types of EC were increased in the presence of platelets under shear stress. This platelet effect was mostly diminished by antagonization of P-selectin and its ligand P-Selectin-Glyco-Ligand-1 (PSGL-1). Inhibition of PECAM-1 as well as SDF-1 receptor CXCR4 had no such effect. Next, they tested the impact of platelets in an allogeneic rodent equivalent of their human shear-stress co-culture model. Murine platelets (mPRP) had a similar adhesive enhancing effect for mouse (m) CD133BMSC to murine dermal micro-endothelial cells (dMEC) when contrasted to platelet-poor conditions (mPRP vs. mPPP 1.44-fold (+/− 0.17); Fig. 4a). Further, stimulation of platelets with the strong platelet activator ADP exhibited a little more pronounced effect on CD133BMSC adhesion (Fig. 4b). However, when directly compared to non-activated platelet co-incubation, they noted only a non-significant trend (+ ADP vs. − ADP; p = 0.072). To prove the platelet effect in the same setting for hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, they utilized mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (mLSEC) in their flow chamber system and observed a comparable positive platelet effect of mCD133BMSC adhesion to mLSEC (1.31-fold (+/− 0.09); Fig. 4c).
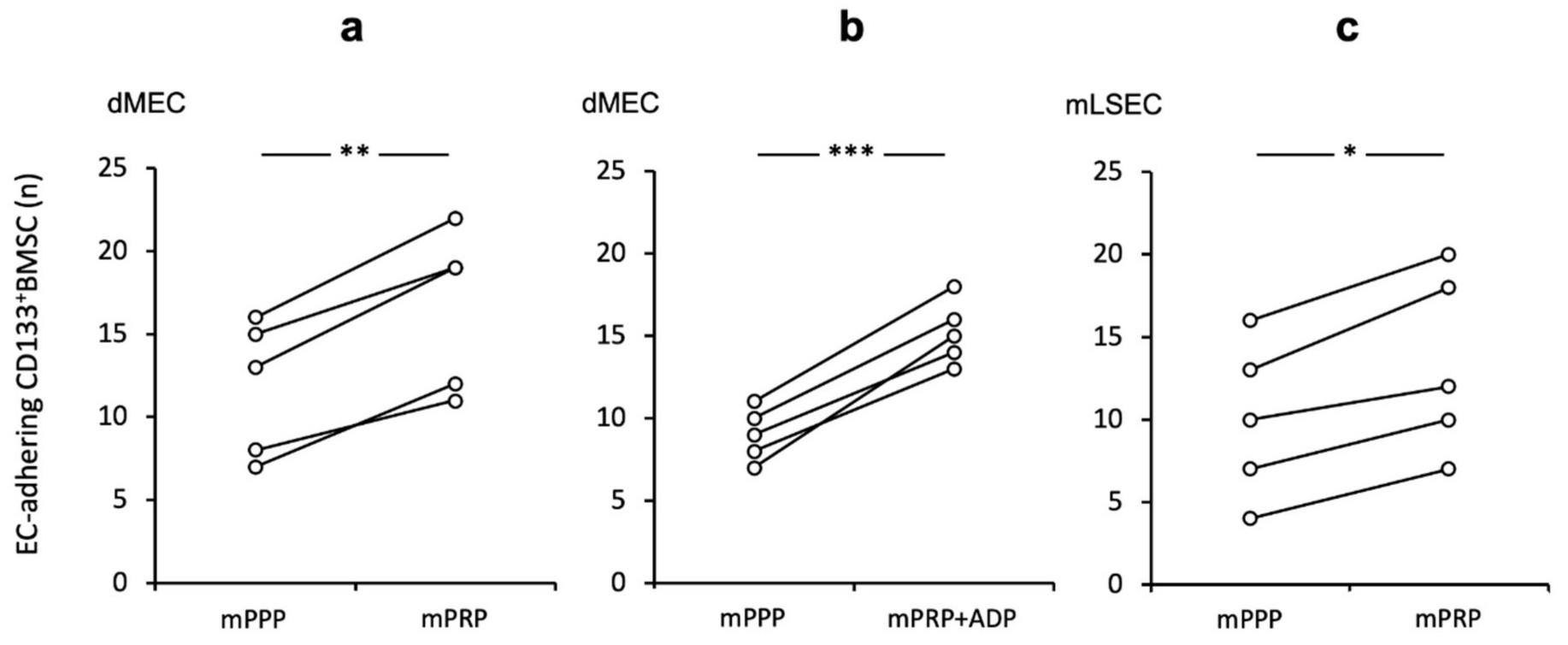 Fig. 4. Augmented CD133BMSC adherence to endothelium subsequent to platelet co-incubation in a murine shear-stress model Adherence of CD133BMSC to murine endothelial cells co-incubated with mouse platelet rich plasma (mPRP) was tested by pairs under different conditions: control and treatment at a time (Lehwald N, Duhme C, et al., 2020).
Fig. 4. Augmented CD133BMSC adherence to endothelium subsequent to platelet co-incubation in a murine shear-stress model Adherence of CD133BMSC to murine endothelial cells co-incubated with mouse platelet rich plasma (mPRP) was tested by pairs under different conditions: control and treatment at a time (Lehwald N, Duhme C, et al., 2020).
Ask a Question
Write your own review