ONLINE INQUIRY
Human Intestinal Fibroblasts (HIF)
Cat.No.: CSC-7769W
Species: Human
Source: Intestine
Morphology: Fibroblasts
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
HIF are isolated from human intestinal tissue. HIF are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 10^5 cells in 1 ml volume. HIF are characterized by their spindle morphology and immunofluorescent method with antibody to fibronectin. HIF are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast and fungi.
Never can primary cells be kept at -20 °C.
The human intestinal fibroblasts (HIF) originate from human intestinal tissue found in the submucosa and lamina propria which serves as a vital component for intestinal structure and function. These cells interact closely with epithelial cells, immune cells and vascular endothelial cells which creates the complex intestinal microenvironment. HIF cells produce and release a variety of extracellular matrix components including collagen, fibronectin, and laminin. These matrices serve as crucial substrates that support cell attachment and survival while also playing a key role in controlling cell growth, differentiation and migration which is vital for repairing and regenerating intestinal tissue. During intestinal immunity cells produce cytokines and chemokines including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) which control the recruitment and activation of immune cells and kickstart immune responses. HIF cells have strong links to multiple diseases because fibroblast growth together with extracellular matrix enlargement creates intestinal strictures in Crohn's disease. Thus, the cell line functions as a vital model system to explore inflammatory bowel diseases including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis along with various cell interactions including adhesion migration and signaling.
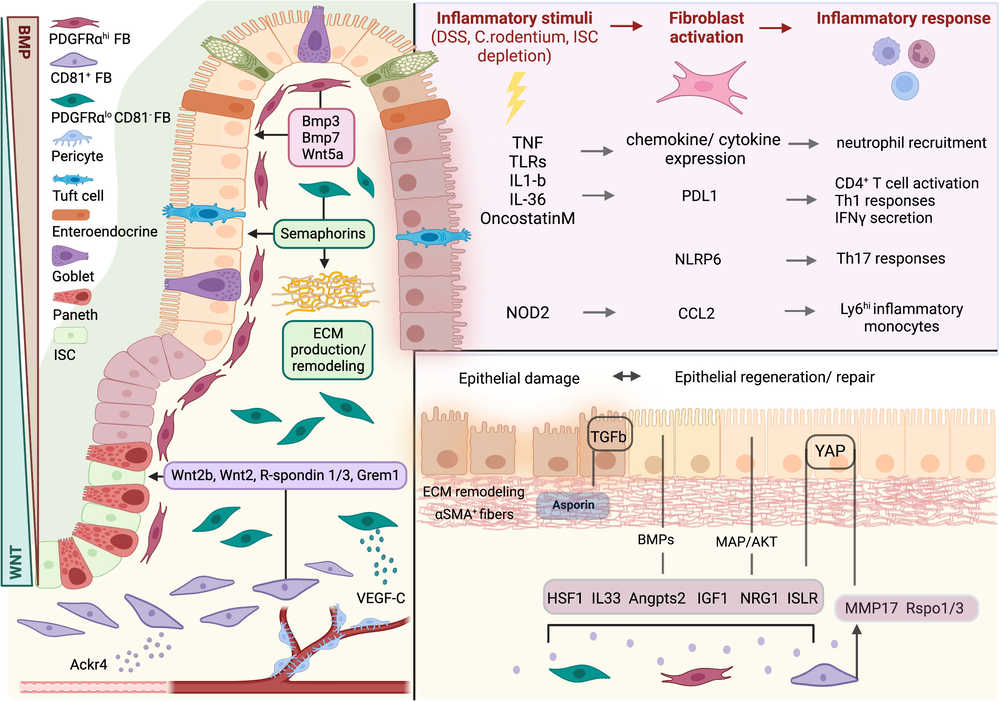 Fig. 1. Fibroblasts in intestinal homeostasis, damage, and repair (Chalkidi N, Paraskeva C, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Fibroblasts in intestinal homeostasis, damage, and repair (Chalkidi N, Paraskeva C, et al., 2022).
P2X7 Regulates the Expression of Col1a1 in Human Intestinal Fibroblasts
Intestinal fibrosis, a common complication in Crohn's Disease (CD), often requires surgery due to a lack of pharmacological treatments. The P2X7 receptor might play a role in this complication but its exact function is unknown. Lis-López et al. aimed to investigate the involvement of the P2X7 receptor in CD-related intestinal fibrosis, particularly focusing on its effects in human intestinal fibroblasts.
Primary human intestinal fibroblasts (HSIFs) underwent transient transfection with P2X7-specific siRNA and TGF-β treatment for 24 hours. As shown in Figure 1A, TGF-β reduced P2X7 expression but significantly increased COL1A1, COL5A1, α-SMA, and TGF-β levels compared to untreated fibroblasts. P2X7 receptor silencing elevated COL1A1 expression under basal conditions and enhanced COL4 and COL5A1 expression in TGF-β-treated fibroblasts. However, it did not significantly affect COL3, COL5A2, COL6A3, α-SMA, or VIMENTIN expression (Fig. 1B). Western blot analysis indicated increased COL1A1 protein levels in siRNA-transfected HSIFs compared to untreated cells (Fig. 1C). Immunofluorescence confirmed that TGF-β treatment, P2X7 silencing, and their combination elevated COL1A1 protein levels compared to non-transfected and untreated fibroblasts (Fig. 1D).
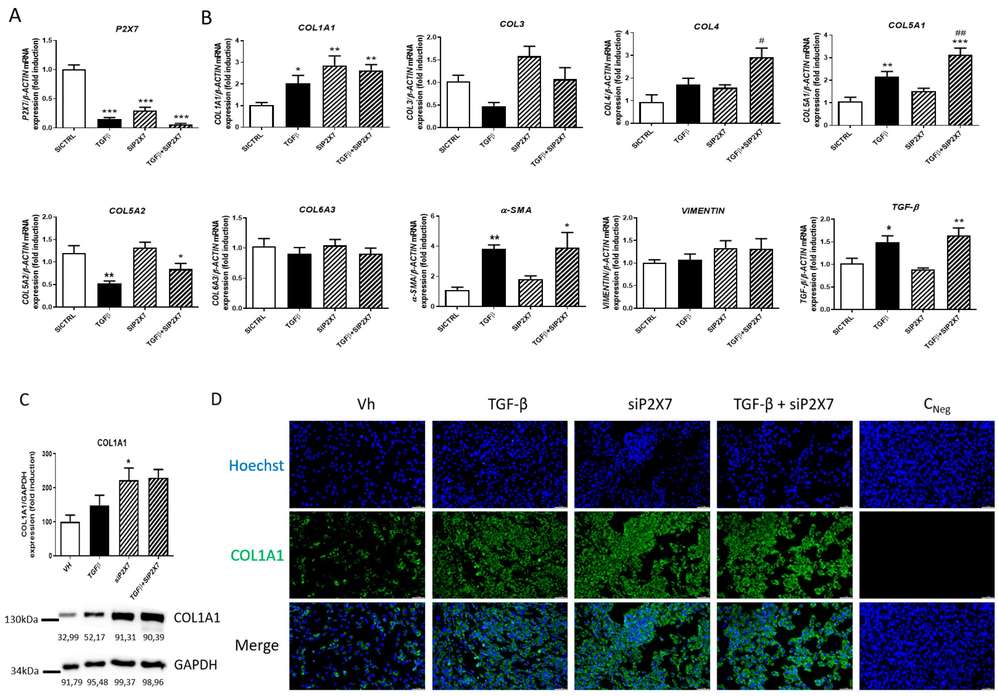 Fig. 1. P2X7 regulates collagen expression in HSIFs (Lis-López L, Bauset C, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. P2X7 regulates collagen expression in HSIFs (Lis-López L, Bauset C, et al., 2023).
CAV1 is Decreased in Activated Fibroblasts Induced by TGF-β1 and Inhibits Fibroblast Activation In Vitro
Crohn's disease (CD) often leads to intestinal fibrosis through excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins which cause bowel wall thickening and narrowing without proper treatment. Although Caveolin-1 (CAV1) functions as an antifibrotic agent its specific involvement in intestinal fibrosis is still unknown.
Intestinal fibrosis involves excessive ECM protein deposition by activated myofibroblasts. Primary human intestinal fibroblasts and CCD-18Co cells were cultured to examine how CAV1 influences fibrogenesis. α-SMA expression increased slightly and CAV1 expression declined at RNA and protein levels in CCD-18Co cells upon TGF-β1 stimulation (Fig. 2A, C). Treatment with TGF-β1 resulted in elevated α-SMA and fibronectin and CTGF levels while reducing CAV1 expression at both protein and RNA levels in primary fibroblasts (Fig. 2D, E, G). TGF-β1 activation of fibroblasts in vitro resulted in a decrease of CAV1 expression. Fibroblast activation is crucial in intestinal fibrosis. They then investigated if CAV1 downregulation affects this process. The results showed that siRNA-mediated CAV1 knockdown significantly worsened TGFβ1-induced ECM deposition and fibroblast activation in primary human intestinal fibroblasts (Fig. 3A-C). Conversely, overexpressing CAV1 via a Flag-tagged plasmid enhanced CAV1 levels and reduced fibrosis marker expression (Fig. 3D-F). In CCD-18Co cells, CAV1 knockdown had minimal impact on preventing fibroblast activation at the RNA level.
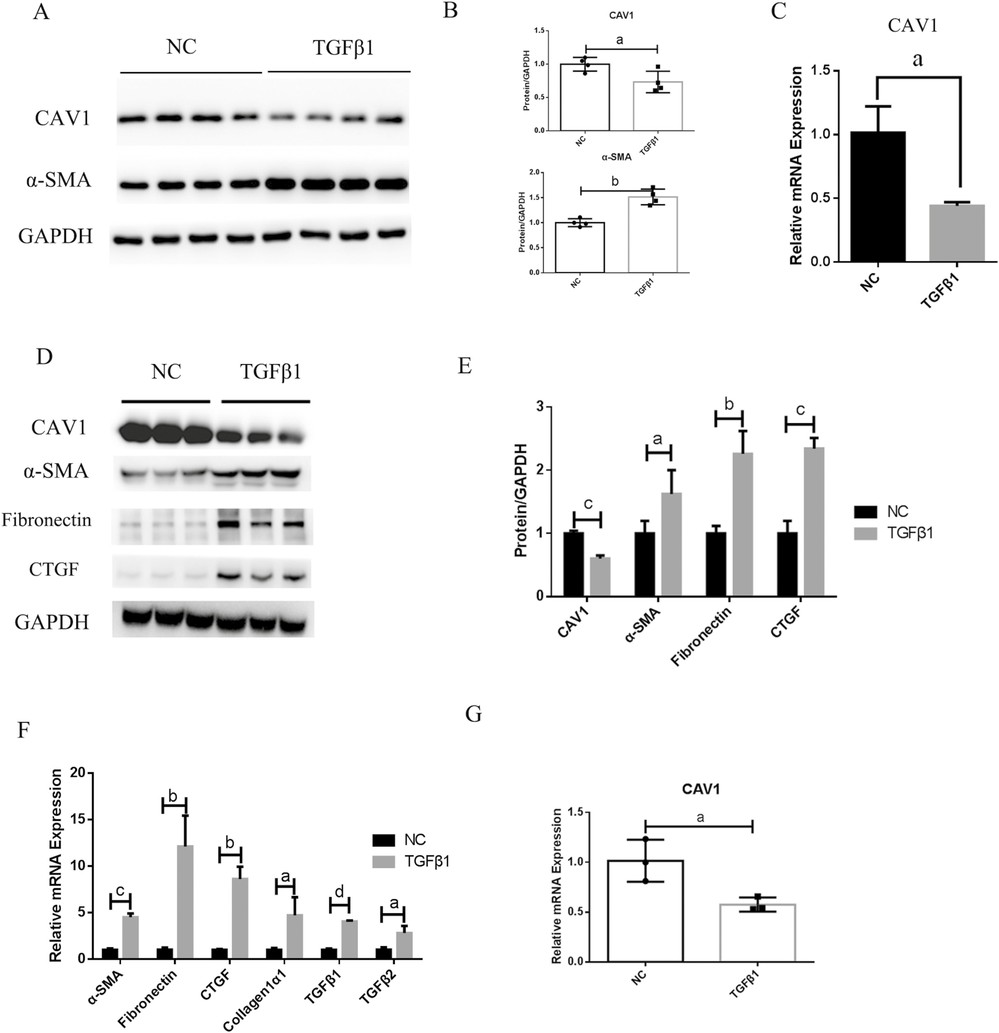 Fig. 2. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) expression is decreased in activated fibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) in vitro (Yu M, Zhu W, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) expression is decreased in activated fibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) in vitro (Yu M, Zhu W, et al., 2022).
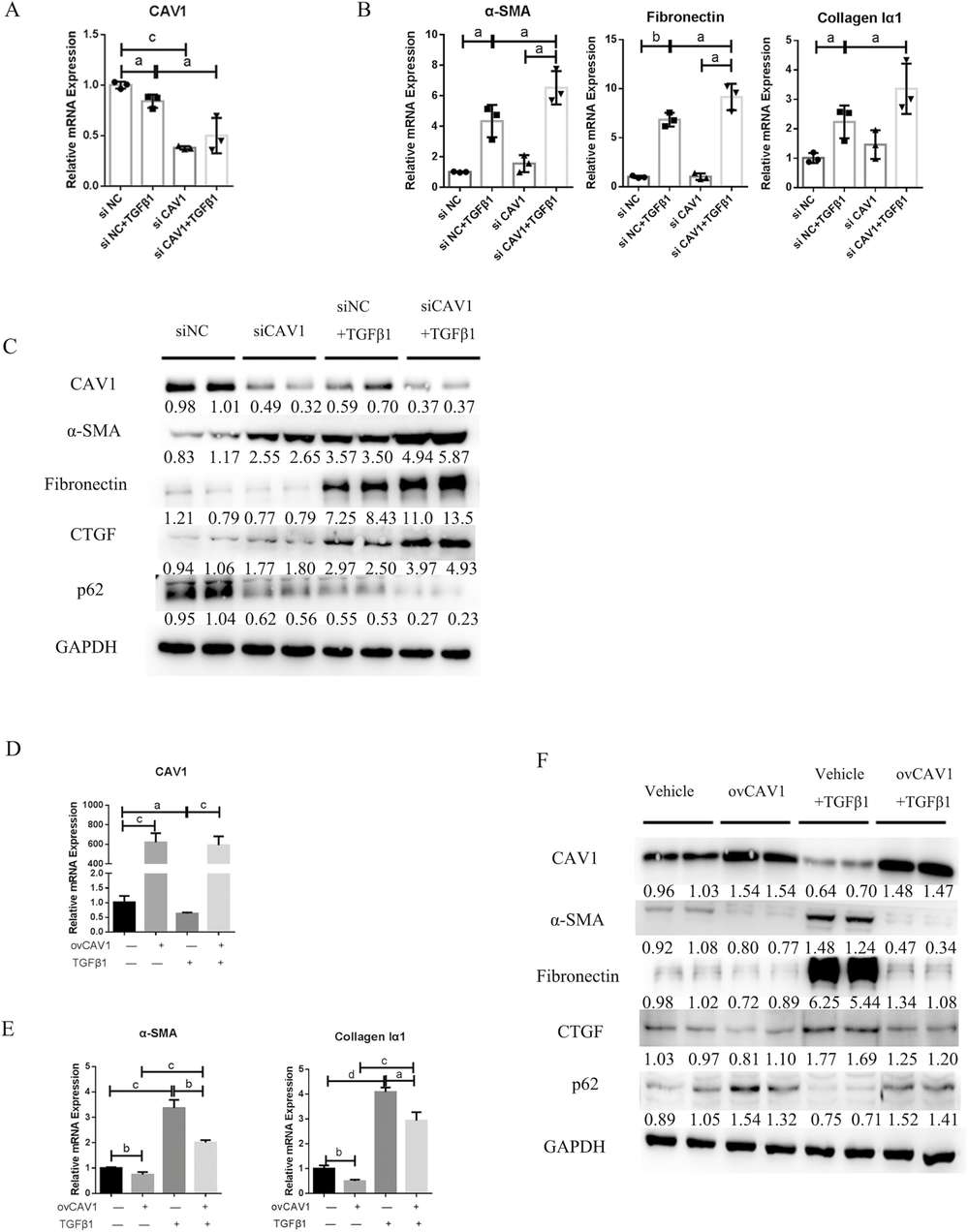 Fig. 3. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) modulates primary human intestinal fibroblast activation in vitro (Yu M, Zhu W, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) modulates primary human intestinal fibroblast activation in vitro (Yu M, Zhu W, et al., 2022).
Our cells can be handled at biosafety level 1, but caution is always recommended when handling human tissue derived products. Hope this helps.
Ask a Question
Write your own review

