- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
- Monosodium Iodoacetate (MIA)-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Monosodium Iodoacetate (MIA)-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
Creative Bioarray provides a monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis (OA) model for our clients to study the disease mechanisms or evaluate the efficacy of drug candidates. With our services, you can obtain reliable and accurate results, providing valuable insights into drug development.
OA is the most common form of arthritis among middle-aged and elderly individuals. Its etiology is complex and involves multiple factors, with the underlying pathogenic mechanisms remaining elusive. While the progression of the disease is typically slow, it can result in significant pain and disability, negatively impacting the quality of life. Given the challenges in studying OA in humans, animal models have become crucial in assessing the development of the disease and evaluating innovative treatment strategies.
Currently, the most utilized type of chemical induction is MIA, which has an inhibitory activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase glycolysis and induces the death of chondrocytes. In both rodents and non-rodents, the intra-articular injection causes chondrocyte destruction. When administered in rats, it causes cartilage lesions with loss of proteoglycan matrix and functional alterations with stiffness that are analogous to those seen in human osteoarthritis.
Our Monosodium Iodoacetate (MIA)-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
- Available Animal
Rat - Modeling Method
After anesthetization, rats are given a single intra-articular injection of MIA through the infrapatellar ligament of the right knee. - Endpoints
- Behavioral test
- Histology analysis (knee joint): H&E staining, Safranin-O/Fast Green staining
- Mankin score
- Serum analysis: cytokine, SOD, MDA, etc.
- Body weight
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
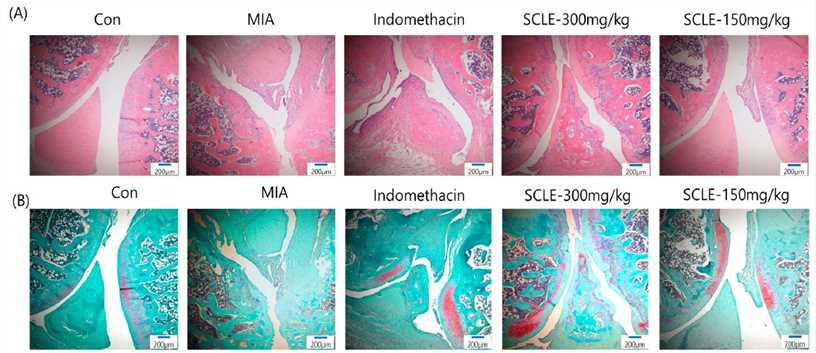 Fig. 1 Histopathological features of knee joint tissues in monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis (OA) rats. Knee joint tissues histopathological changes with (A) H&E and (B) Safranin-O/Fast Green
Fig. 1 Histopathological features of knee joint tissues in monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis (OA) rats. Knee joint tissues histopathological changes with (A) H&E and (B) Safranin-O/Fast Green
Meanwhile, we also provide other OA models that maybe you are interested in:
- Papain-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
- Medial Meniscal Tear (MMT)-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Transection (ACLT)-Induced Osteoarthritis (OA) Model
Quotation and Ordering
With years of experience in disease models, the scientists at Creative Bioarray are eager to collaborate with our clients to create a customized design tailored to your unique needs. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Lee, Y.M., et al. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Schisandra chinensis leaf extracts and monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats and acetic acid-induced writhing in mice. Nutrients, 2022, 14(7): 1356.
- Longo, U.G., et al. Induced models of osteoarthritis in animal models: a systematic review. Biology, 2023, 12(2): 283.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

