Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
MKN-74
Cat.No.: CSC-C9495L
Species: Human
Source: stomach
Morphology: polygonal
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Histopathology: adenocarcinoma, tubular
Differentiation: moderately differentiated
Note: Mycoplasma-eliminated cells by MC-210
vWA: 16,20
FGA: 23
Amelogenin: X
TH01: 6
TPOX: 8,11
CSF1P0: 12
D5S818: 11
D13S317: 11
D7S820: 9
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
The MKN-74 cell line is a well-established human gastric cancer cell line that has been widely used in research related to gastric adenocarcinoma. This cell line was derived from a 37-year-old male patient of Mongoloid descent, and the histopathological analysis revealed that the tumor was a moderately differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma. Importantly, the MKN-74 cell line has been specifically treated to eliminate potential Mycoplasma contamination, which is a common issue that can affect the reliability and reproducibility of cell-based experiments.
The MKN-74 cell line, with its origin from a moderately differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma, provides a relevant in vitro model for researchers to investigate the biological characteristics and behavior of this common subtype of gastric cancer. Researchers can utilize this cell line to investigate various aspects of tumor biology, including cell growth, invasion, metastasis, and response to various therapeutic agents. The availability of this Mongoloid-derived, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma cell line provides important representation and diversity within the broader landscape of gastric cancer cell line models, enabling more comprehensive and inclusive research approaches.
Anti-proliferative Effects of Astragalosides on Human Gastric Cancer MKN-74 Cells
Radix astragali mainly contains saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, amino acids, and other chemical constituents of which total astragalosides have immunomodulatory, anti-viral, hepatoprotective, and gastric mucosa protective effects. The inhibition of human gastric cancer MKN-74 cell growth by total astragalosides was investigated and the inhibitory effect of total astragalosides on the proliferation of human gastric cancer MKN-74 cells by MTT assay (Fig. 1). As can be seen from the experimental results, the MTT assay found that astragalosides could relatively pronouncedly inhibit the proliferation of MKN-74 cells, and the inhibitory effect was enhanced with the increase of astragaloside dose and the extension of processing time, which showed a dose-and time-dependence.
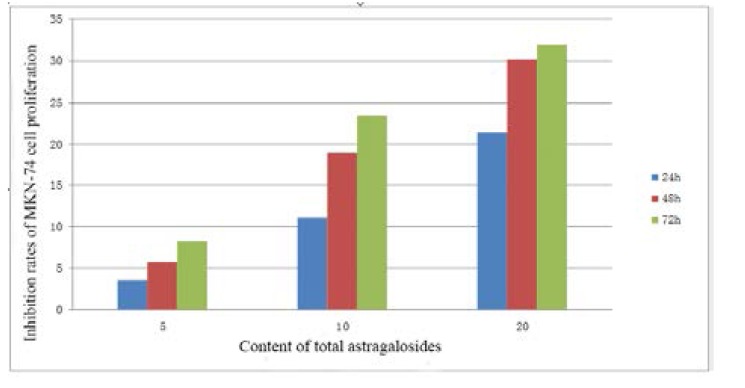 Fig. 1 Inhibition rates of different concentrations of total astragaloside on MKN-74 cell proliferation. (OuYang Y, et al., 2014)
Fig. 1 Inhibition rates of different concentrations of total astragaloside on MKN-74 cell proliferation. (OuYang Y, et al., 2014)
Role of Bile Acids in Cellular Invasiveness of Gastric Cancer MKN-74 Cells
Bile acids have been implicated in the development of digestive tract malignancy by epidemiological, clinical, and animal studies. The growth and transformation signaling by most of the bile acids is thought to be related to the induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and increased production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The highly hydrophobic bile acids such as chenodeoxycholic acid (CD) and deoxycholic acid can promote carcinogenesis and stimulate the invasion of colon cancer cells. On the contrary, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells.
The effect of CD in MKN-74 cells was first examined with regard to COX-2 expression. MKN-74 cells were exposed to 100, 200, or 400 μM CD for 24 h, then cells were collected and fractionated into the membrane (M) and cytosolic (C) extracts as described in Methods. Western blot analyses were performed using COX-2 antibody. As shown in Fig. 2a, with exposure to 10 nM PKC activator PMA as a positive control, a dose-dependent induction of COX-2 protein expression by CD was demonstrated; similar results were noted in primary gastric adenocarcinoma SK-GT5 cells (Fig. 2c). Furthermore, a time-course induction of COX-2 without affecting COX-1 was seen after exposing to 200 μM CD at different time interval for MKN-74 cells (Fig. 2b).
The effect of CD on PKCα activation was then examined. MKN-74 cells were exposed to 100, 200, or 400 μM CD for 24 h; then cells were collected and fractionated as described. Western blot analyses were performed using COX-2 and PKCα antibodies. As shown in Fig. 3a, induction of COX-2 protein expression was associated with activation of PKCα, as demonstrated by translocation from cytosolic fraction to membrane fraction.
The effect of UDCA on COX-2 expression was further examined. MKN-74 cells were exposed for 8 h to a single drug alone including PMA, CD, and UDCA, 10 nM PMA with 200 μM UDCA, or 200 μM CD with 200 μM UDCA; then cells were collected and fractionated as described. Western blot analyses were performed using COX-2 antibody. As shown in Fig. 3b, UDCA did not affect PMA- or CD-induced COX-2 protein expression.
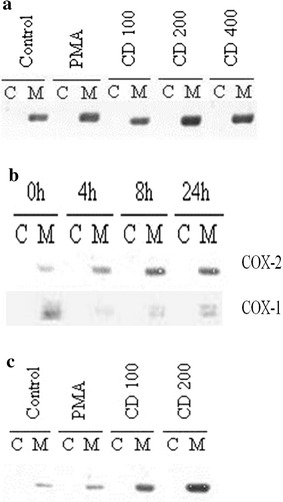 Fig. 2 (a) Western blot analysis of COX-2 in MKN-74 after treatment with 10 nM PMA, 100, 200, and 400 μM CD, respectively for 24 h. (b) Western blot analysis of COX-2 and COX-1 in MKN-74 after treatment with 200 μM CD for 0, 4, 8, and 24 h, respectively. (c) Western blot analysis of COX-2 in SK-GT5 after treatment with 10 nM PMA, 100 and 200 μM CD, respectively for 24 h. (Wu YC, et al., 2018)
Fig. 2 (a) Western blot analysis of COX-2 in MKN-74 after treatment with 10 nM PMA, 100, 200, and 400 μM CD, respectively for 24 h. (b) Western blot analysis of COX-2 and COX-1 in MKN-74 after treatment with 200 μM CD for 0, 4, 8, and 24 h, respectively. (c) Western blot analysis of COX-2 in SK-GT5 after treatment with 10 nM PMA, 100 and 200 μM CD, respectively for 24 h. (Wu YC, et al., 2018)
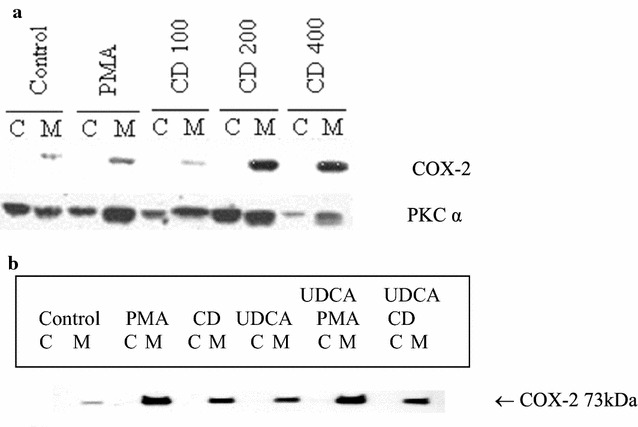 Fig. 3 (a) Induction of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 by CD required activation of PKCα in MKN-74 cells. (b) UDCA did not affect PMA- or CD-induced COX-2 protein expression. (Wu YC, et al., 2018)
Fig. 3 (a) Induction of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 by CD required activation of PKCα in MKN-74 cells. (b) UDCA did not affect PMA- or CD-induced COX-2 protein expression. (Wu YC, et al., 2018)
Tumor cells are observed under the microscope and marked on the bottom of the culture flask or culture dish, and then the unmarked area is scraped off with sterile adhesive.
The MKN-74 cell line is classified as a moderately differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma, a common subtype of gastric cancer.
Mycoplasma contamination is a common issue in cell culture that can affect the reliability and reproducibility of experimental results. The MKN-74 cell line has been specifically treated to eliminate Mycoplasma, ensuring that researchers can work with a contaminant-free cell line.
The MKN-74 cell line provides a relevant in vitro model for researchers to investigate the biological characteristics and behavior of moderately differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma, a common subtype of gastric cancer. This cell line can be used for various studies, including cell growth, invasion, metastasis, and drug response.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
No contamination
During our experiments, the cells grew well without any contamination.
19 July 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Comprehensive documentation
The documentation provided with the cells is comprehensive, covering the cell line's origin, histopathological characteristics, and Mycoplasma-free status.
15 Jan 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliable results
The cells have performed reliably in my studies, and I've been able to generate high-quality, reproducible data.
23 May 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need