Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY

IMR-5
Cat.No.: CSC-6268W
Species: Human
Source: thyroid
Morphology: continuous culture, grown as monolayer, morphology neuroblastic-like
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Tumor: neuroblastoma
Scientists widely study the biological properties of neuroblastoma and its treatment responses using the IMR-5 cell line which originates from human neuroblastoma cells. Neuroblastoma represents a malignant tumor which develops from neural crest cells and primarily affects children. The IMR-5 cell line displays standard adherent growth patterns which researchers frequently use to examine tumor proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis mechanisms.
Researchers utilize the IMR-5 cell line for drug screening, toxicity assessment, gene expression studies and fundamental neuroblastoma research across multiple scientific disciplines. For example, research shows Cannabinol can decrease IMR-5 cell proliferation and invasion by blocking the AKT signaling pathway and increasing miR-34a levels. Moreover, the IMR-5 cell line serves as a model for studying the mechanisms of apoptosis. Experiments demonstrate that this cell line does not show caspase-activated DNase (CAD) activity during apoptosis but researchers can regain DNA degradation functionality by introducing recombinant caspase-3 externally. These studies reveal both the distinct biological properties of the IMR-5 cell line with new targets and treatment mechanisms for neuroblastoma.
TW-37 Reduces Viability of Neuroblastoma Cell Lines, with Strongest Effect in Cell Lines with N-Myc Amplification
High-risk neuroblastoma, particularly with N-Myc amplification, presents a significant therapeutic challenge in pediatric oncology. Despite various treatment strategies, the prognosis remains poor, with low survival rates. Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 are crucial in influencing treatment outcomes by modulating apoptotic pathways. The potential of TW-37, an inhibitor of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2, to serve as a single-agent treatment has been explored to enhance chemotherapy efficacy.
Klenke's team investigated the cytotoxic effects of TW-37 on neuroblastoma cell lines. Cell lines were treated with varying concentrations of TW-37 to evaluate its effect. A notable decrease in cell viability across all lines was shown by MTT-assay. IC50 values were 0.96 μM for SY5Y (Fig. 1a), 0.83 μM for SKNAS (Fig. 1b), 0.28 μM for IMR-5 (Fig. 1c), and 0.22 μM for Kelly cells (Fig. 1d). N-Myc amplified lines (IMR-5 and Kelly) were more sensitive, indicated by lower IC50 values, compared to lines without amplification (SY5Y and SKNAS). Protein analysis revealed Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 expression, with SKNAS showing lower Bcl-2 levels (Fig. 1e). Treatment with 1 μM TW-37 increased apoptotic cells in N-Myc amplified lines, with Kelly cells most affected, whilst no significant change was found in non-amplified lines (Fig. 1f, 1g). Proliferation was notably inhibited in SKNAS, IMR5, and Kelly, but not in SY5Y (Fig. 1h). In Kelly cells, selective knockdown of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 with siRNA mimicked the TW-37 effects, increasing apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation (Fig. 2b, 2c, 2e, 2f). Mock transfection showed little change. These in vitro results provide strong evidence for the impact of TW-37 on cell viability and proliferation in neuroblastoma cell lines.
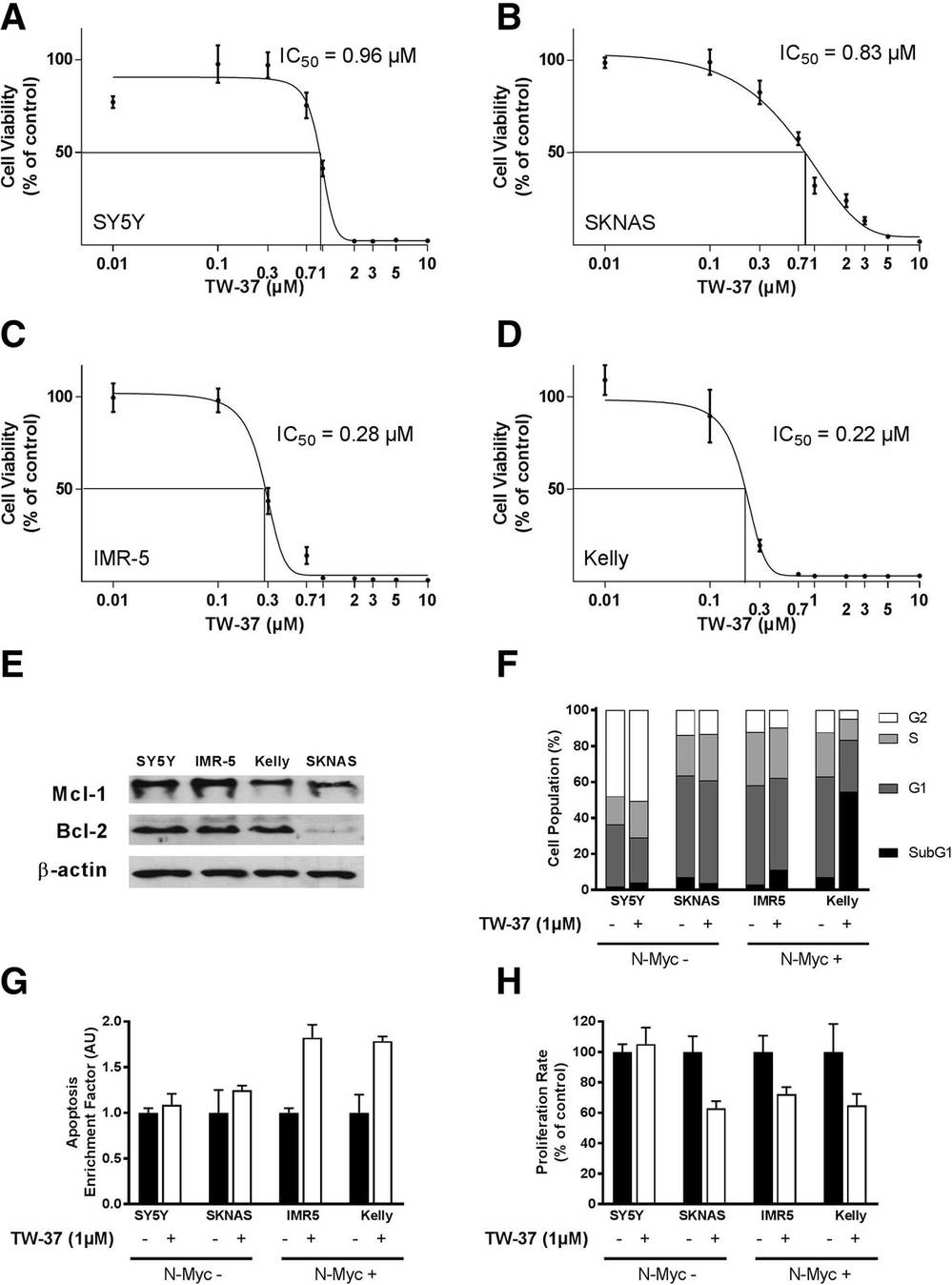 Fig. 1. Cell viability, measured in MTT-assay in Kelly (a), IMR-5 (b), SKNAS (c) and SY5Y (d) cells 72 h after treatment with variable concentrations of TW-37 (Klenke S, Akdeli N, et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. Cell viability, measured in MTT-assay in Kelly (a), IMR-5 (b), SKNAS (c) and SY5Y (d) cells 72 h after treatment with variable concentrations of TW-37 (Klenke S, Akdeli N, et al., 2019).
CBN Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Angiogenesis of Neuroblastoma
The prognosis of high-risk neuroblastoma is poor due to its high relapse rate. Cannabinol (CBN) is a phytocannabinoid, structurally similar to endocannabinoids and primarily found in Cannabis sativa, which interacts with the endocannabinoid system, although its specific effects on neuroblastoma tumorigenesis remain unclear.
In this study, Wang et al. employed the neuroblastoma cell lines IMR-5 and SK-N-AS to investigate how cannabinol (CBN) affects neuroblastoma and to understand its molecular mechanisms. They investigated CBN's role in neuroblastoma by examining cannabinoid receptor expression among both normal and neuroblastoma cell lines. Western blotting showed differential CBR1 and CBR2 expression (Fig. 2A and B). They used p53 wild-type IMR-5 (high CBR1, low CBR2) and p53 mutant SK-N-AS (low CBR1, high CBR2) lines. CBN's IC50 was 20.23 µM for IMR-5 and 29.88 µM for SK-N-AS. MTT assays revealed CBN reduced proliferation in both lines dose-dependently (Fig. 3A); low doses (15 µM) inhibited, while high doses (30 µM for IMR-5, 25 µM for SK-N-AS) induced cell death. CBN caused S-phase arrest in IMR-5 and reduced apoptosis in SK-N-AS (Fig. 3B and C). Additionally, SK-N-AS media treated with 15 or 20 μM CBN significantly reduced angiogenesis and invasion, with moderate effects seen in IMR-5 media (Fig. 3D and E).
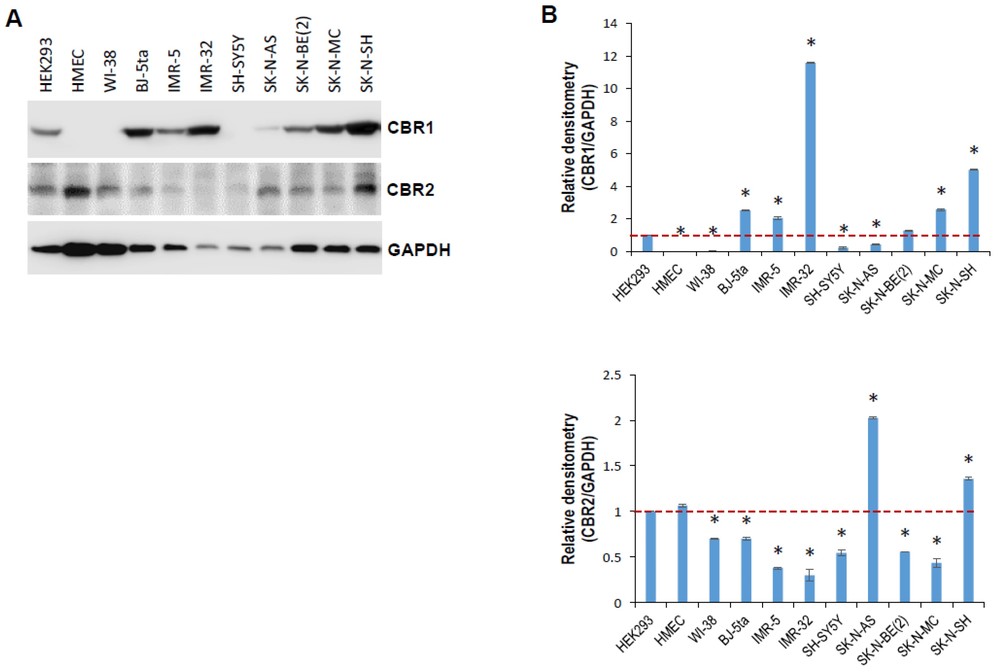 Fig. 2. Expression of cannabinoid receptors CBR1 and CBR2 in normal and neuroblastoma cell lines (Wang B, Li D, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. Expression of cannabinoid receptors CBR1 and CBR2 in normal and neuroblastoma cell lines (Wang B, Li D, et al., 2022).
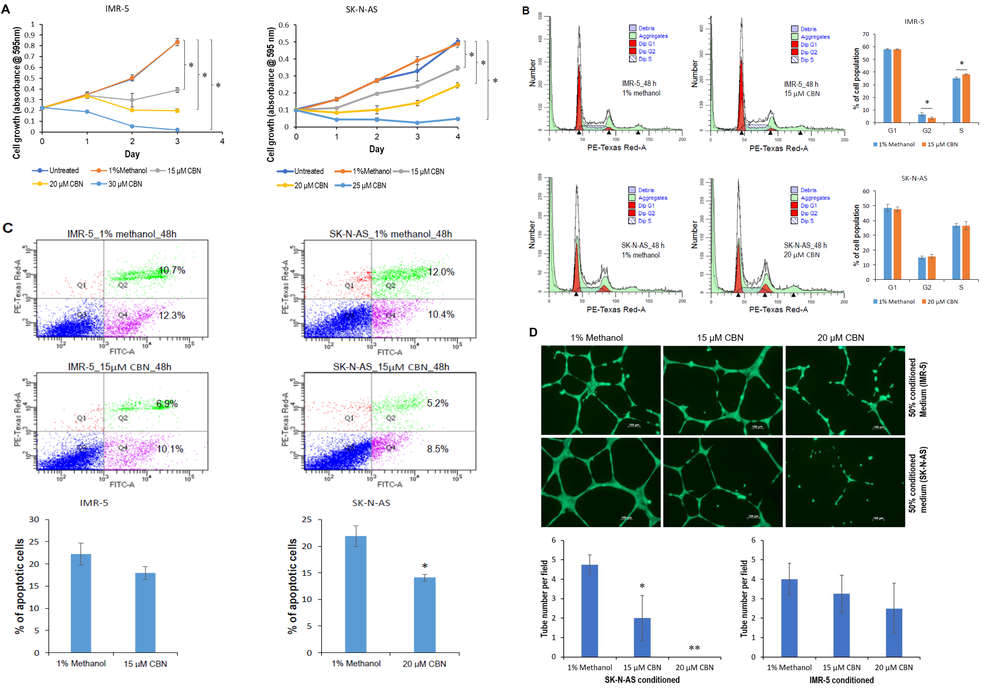 Fig. 3. Anti-neuroblastoma effect of CBN via inhibition of AKT pathway and transactivation of miR-34a (Wang B, Li D, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. Anti-neuroblastoma effect of CBN via inhibition of AKT pathway and transactivation of miR-34a (Wang B, Li D, et al., 2022).
Special care should be taken to avoid bacterial contamination of the digestive fluid.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Consistent experimental results
The experimental results with IMR-5 are consistent and the product is available at a good price.
23 Jan 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need