What Is the Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Drug Delivery?
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective and impermeable barrier that separates the circulatory system from the brain and the central nervous system (CNS). This specialized structure is essential for maintaining delicate homeostasis and protecting sensitive neural tissue from potentially harmful substances. Composed of a complex network of specialized endothelial cells, tight junctions, astrocytes, and pericytes, the BBB acts as a gatekeeper, strictly controlling the passage of molecules, nutrients, and even therapeutic agents into the brain.
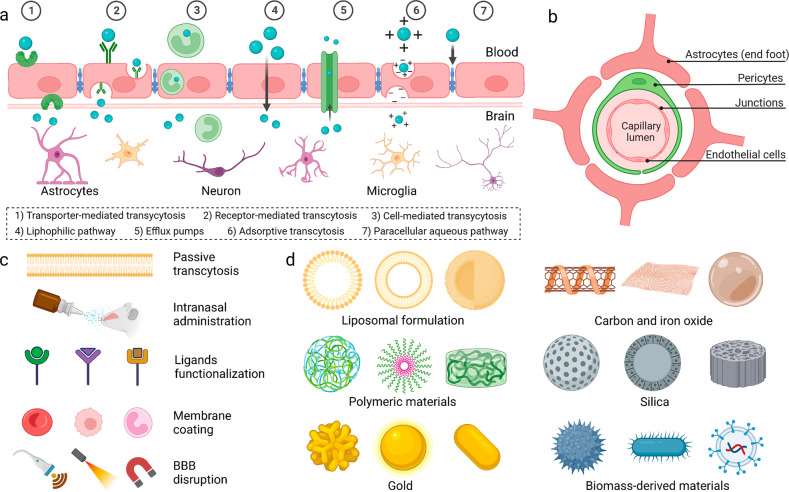 Fig.1 Strategies and materials for BBB regulation and brain-targeted drug delivery. (Wu D, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Strategies and materials for BBB regulation and brain-targeted drug delivery. (Wu D, et al., 2023)
BBB Structure and Physiology
The unique anatomy and physiology of the BBB are the key factors that contribute to its remarkable barrier function. The endothelial cells lining the blood vessels in the brain are connected by tight junctions, which drastically limit the paracellular transport of molecules. Additionally, the presence of various efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, actively pumps out substances that attempt to cross the barrier, further enhancing the BBB's protective capabilities.
The involvement of astrocytes and pericytes in the BBB's structure and function cannot be overstated. Astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support, while pericytes play a crucial role in regulating blood flow and maintaining the BBB's integrity. This intricate interplay of cellular components ensures the BBB's ability to selectively allow the passage of essential nutrients and molecules while effectively blocking the entry of potentially harmful substances.
| Features | Details |
| Endothelial cell tight junctions | The endothelial cells lining the blood vessels in the brain are a critical component of the BBB. These cells are connected by tight junctions, specialized protein complexes that create a highly impermeable seal between the cells. This tight arrangement significantly restricts the paracellular transport of molecules, preventing the free flow of substances into the brain. |
| Efflux transporters | Another key feature of the BBB is the presence of various efflux transporters, such as the well-known P-glycoprotein (P-gp). These specialized proteins actively pump out a wide range of molecules, including many therapeutic drugs, from the brain tissue back into the bloodstream. This active transport mechanism further enhances the barrier's ability to protect the CNS from potentially harmful substances. |
| Astrocyte involvement | Astrocytes, a type of glial cell, play a crucial role in the structure and function of the BBB. These star-shaped cells provide structural support and contribute to maintaining the BBB's integrity. Astrocytes help regulate the expression of tight junction proteins and actively participate in the transport of molecules across the barrier. |
| Pericyte regulation | Pericytes, another type of specialized cell, are closely associated with the endothelial cells of the BBB. These cells contribute to the regulation of blood flow and the modulation of the barrier's permeability. Pericytes can influence the expression of tight junction proteins and the activity of efflux transporters, further enhancing the BBB's selective barrier function. |
Challenges of Drug Delivery Across the BBB
The very features that make the BBB so effective in protecting the brain also pose significant challenges to the delivery of therapeutic agents. The tight junctions and the presence of efflux transporters severely limit the permeability of the barrier, making it difficult for many drugs to reach their intended targets within the CNS. Furthermore, the lipophilic nature of the BBB presents an additional hurdle, as many drug candidates are unable to passively diffuse across the barrier due to their physicochemical properties.
The enzymatic degradation of drugs at the BBB level is another formidable obstacle. The presence of various metabolic enzymes can rapidly break down drug molecules, reducing their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
Strategies to Overcome the BBB
Lipid-based drug delivery systems
Nanoparticles, with their unique physicochemical properties, can be engineered to evade efflux transporters and permeate the tight junctions of the BBB. Similarly, liposomes, which are lipid-based vesicles, can be optimized to mimic the structure of the BBB, thereby facilitating the transport of encapsulated drugs.
Receptor-mediated transcytosis
Utilizing receptor-mediated transcytosis involves targeting specific receptors on the BBB, such as transferrin or insulin receptors, to facilitate the transport of drugs across the barrier. This targeted approach can enhance drug delivery efficiency and specificity to the brain tissues while minimizing off-target effects.
Modulation of tight junctions
Tight junction modulators are substances that can alter the integrity of the tight junctions in the BBB, temporarily increasing permeability to allow drug molecules to pass through. By modulating tight junctions, drug delivery to the brain can be enhanced, allowing for improved therapeutic outcomes.
Intranasal drug delivery
Intranasal drug delivery offers a non-invasive route to bypass the BBB by directly delivering therapeutic agents to the brain via the nasal mucosa. This method can provide a rapid onset of action, avoid first-pass metabolism, and enhance drug bioavailability in the brain.
Invasive techniques
Invasive techniques such as convection-enhanced delivery and focused ultrasound involve more direct methods to overcome the BBB. Convection-enhanced delivery utilizes pressure differentials to infuse drugs directly into the brain tissue, while focused ultrasound can transiently disrupt the barrier to enhance drug penetration.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
| Service/Product Types | Description |
| In vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Assay Service | With decades of operational experience and a technology platform for BBB research, Creative Bioarray has established multiple in vitro BBB Models. |
| In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay | Creative Bioarray has established a simple, reliable, and efficient in vivo assay that has been successfully applied to several genetic and experimental mouse models. |
| Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA) | Creative Bioarray is a reliable PAMPA provider. Over the past years, we have developed expertise in PAMPA. |
Reference
- Wu D, et al. (2023). "The blood-brain barrier: structure, regulation, and drug delivery." Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8 (1): 217.

