How to Efficiently Utilize MSC Exosomes for Disease Treatment?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are cells that can self-renew and multidirectional differentiation. They are found in tissues and organs such as bone marrow, skeleton, fat, skin, heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, thymus, and liver. The most prevalent MSCs include fat-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs), bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs), and gingival mesenchymal stem cells. Because they are permeable and stable, MSC-EXOs are stored within cells via lysosomes and released to the extracellular matrix via paracrine signalling to engage in intercellular and signal transduction regulation. More recent studies showed an increasingly therapeutic application of MSC-EXOs in liver, kidney, brain and cardiovascular disorders. They facilitate intercellular signalling and control the activities of cells through contact, fusion and internalisation with the membranes of their targets. Furthermore, due to their anti-inflammatory function, MSC-EXOs suppress the immune system by interacting with immune effector cells, which is essential for inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
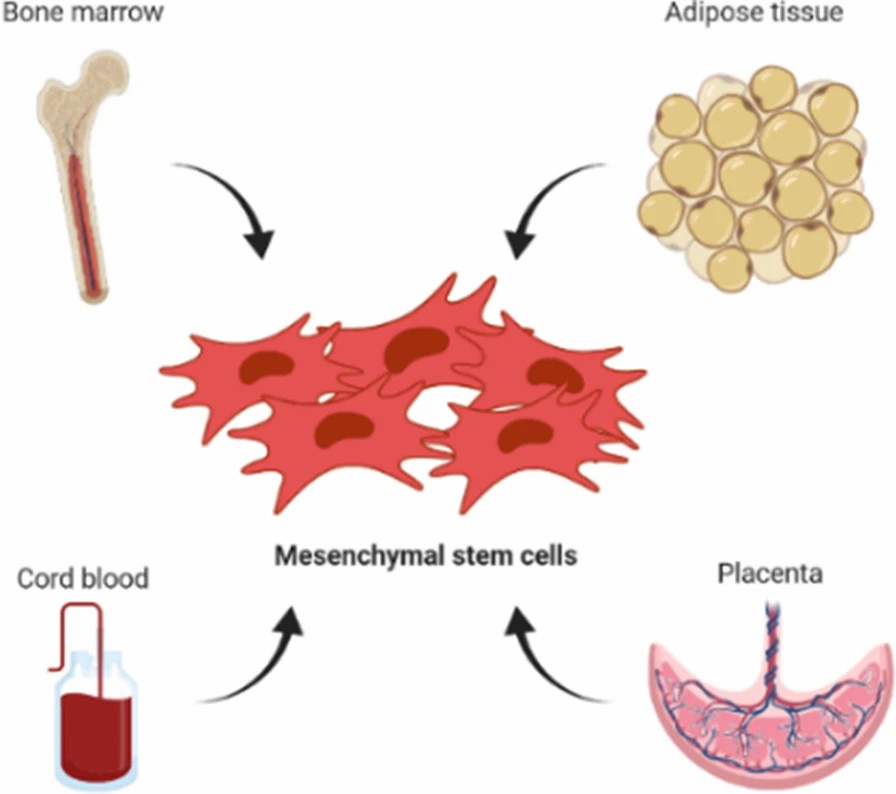 Fig. 1. The most common sources of MSC isolation (Janockova J, Slovinska L, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. The most common sources of MSC isolation (Janockova J, Slovinska L, et al., 2021).
Applications of MSC-EXOs in Disease Treatment
Cardiovascular diseases
MSC-EXOs can restore myocardial damaged tissue and help improve the function of the heart. Researchers discovered that MSC-EXOs stimulate angiogenesis and the proliferation of myocardial cells through miRNA and protein exchange. MSC-EXO microRNAs miR-126 and miR-210, for instance, control myocardial fibrosis-associated genes that are necessary for the survival and activity of myocardial cells.
Neurological disorders
MSC-EXOs protect neurons and foster neurogenesis, and molecular modifications make them compatible with the blood-brain barrier for treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. In neurodegenerative conditions like stroke, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, MSC-EXOs carrying neurotrophic factors promote survival and activity of neurons. In stroke models, MSC-EXOs narrow infarcts and improve motor function.
Liver diseases
In liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, MSC-EXOs reverse the course of the disease through their anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects. They discovered that MSC-EXO miRNA and proteins kill fibroblasts and, hence, halt liver fibrosis.
Immune diseases
MSC-EXOs are potent immunomodulators; they can suppress multiple subsets of immune cells, including B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages and natural killer cells, pro-antigen-presenting cells. In autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, MSC exosomes can tame immune cells and inhibit overlying immune cells, reducing inflammation and disease symptoms. They can, for example, decrease inflammation through suppressing Th17 cells and controlling regulatory T-cell numbers.
Cancer
As a cancer therapy, MSC-EXOs not only directly kill cancer cells (by transporting anticancer compounds) but also indirectly suppress tumour growth (by controlling the tumor microenvironment and inhibiting angiogenesis). Studies have revealed that MSC-EXOs can also carry tumor suppressor proteins such as p53 that help to suppress the growth of cancer cells. But some studies show MSC-EXOs can promote the growth and migration of cancer cells and boost their tumorigenicity, so serving as a "double-edged sword" in the fight against cancer.
Wound healing
MSC-EXOs have also been demonstrated to speed wound healing by increasing proliferation, differentiation and localisation of components of skin cells and promoting immune cell differentiation. Subcutaneous injection of exosomes sourced from iPSC-MSC, for example, may promote wound healing in animals by encouraging the production of type I and III collagen and elastin by fibroblasts. Additionally, MSC-EXOs exhibit tissue regenerative activity for the treatment of epidermolysis bullosa (EB) and idiopathic macular hole retinal detachments.
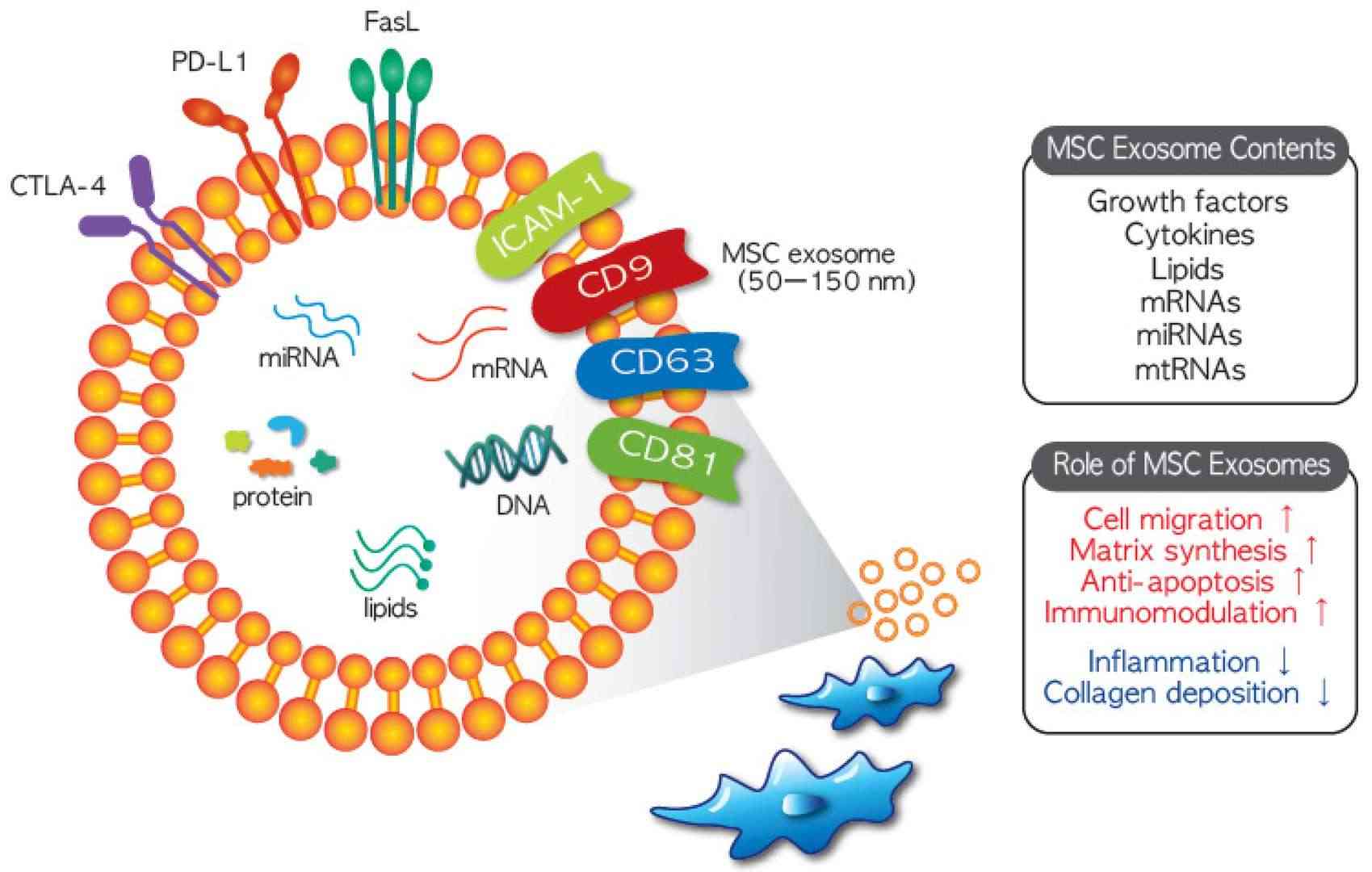 Fig. 2. Composition and therapeutic function of MSC exosomes (Lee B C, Kang I,et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. Composition and therapeutic function of MSC exosomes (Lee B C, Kang I,et al., 2021).
Pre-Conditioning Approaches to Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of Exosomes
- 3D culture techniques and microenvironment modification: The 3D culture methods such as porous scaffolds recreate physiological anatomical conditions in vivo, increasing the yield and efficacy of MSC-EXOs. Using bioreactors and microcarriers to culture cells on a large scale is a way to boost exosome production.
- Chemical or cytokine pre-conditioning of MSCs: Pre-conditioning MSCs with chemicals or cytokines stimulates the production of exosomes and change internal structure. These pro-inflammatory cytokines (for example, IFN-γ and TNF-α) greatly enhance MSC therapeutic activity by creating exosomes with abundant anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective compounds. Certain chemicals, such as imidazoles and sodium nitroprusside, enhance the biological functions of exosomes by controlling exosome production factors.
- Gene editing: Modifying genes involved in exosome production and secretion through overexpression or knockout improves exosome quantity and efficacy. Overexpression of phospholipase D2 significantly raises exosome yield. Specific miRNA overexpression can also enhance exosome functions in cardiac, neuroprotective, and antitumor applications.
- Hypoxic MSC pre-conditioning: Culturing MSCs under hypoxic conditions releases exosomes with enhanced therapeutic effects. These exosomes improve angiogenesis, myocardial repair, and immune modulation. Hypoxia-preconditioned exosomes often exhibit superior protective effects in cardiovascular disease models.
- Cellular stress and other factor treatments: Cellular stress, such as altering osmotic pressure, can trigger exosome release. MSC exosomes, treated with bioactive factors like thrombin and H2O2, exhibit superior regeneration and repair capabilities in specific diseases.
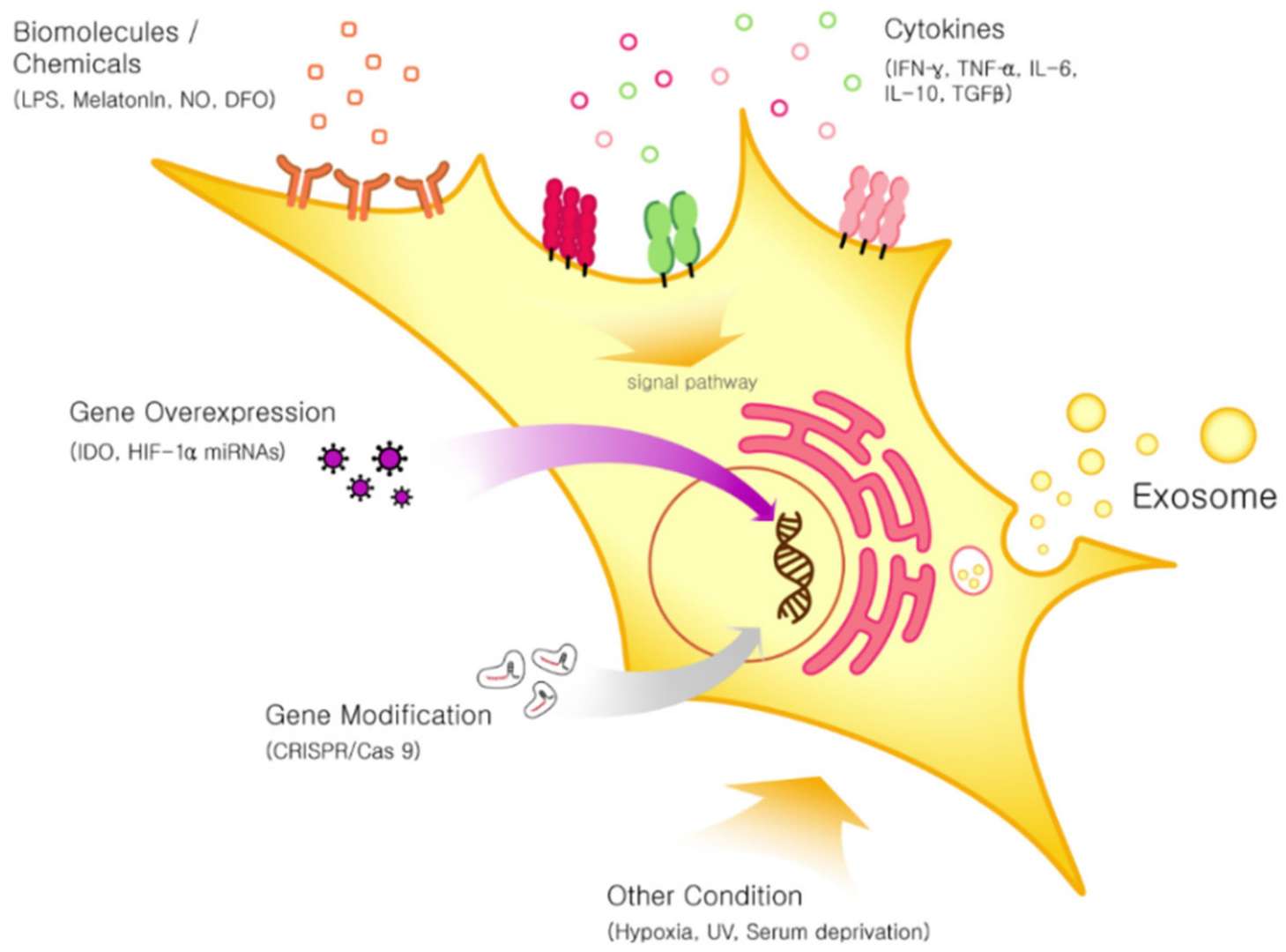 Fig. 3. Pre-conditioning approaches for MSC to enhance the secretion and therapeutic efficacy of exosomes (Joo HS, Suh JH, et al., 2020).
Fig. 3. Pre-conditioning approaches for MSC to enhance the secretion and therapeutic efficacy of exosomes (Joo HS, Suh JH, et al., 2020).
| Products & Services | Description |
| Exosome Applications | Creative Bioarray offers a complete set of services for exosome application including but not limited to exosome transfection, exosome labeling, and exosome targeting. |
| Exosome Analysis | Creative Bioarray provides diverse exosomal species analysis to help you understand your exosome compositions. |
| Exosome Identification | Creative Bioarray provides comprehensive support for your exosome identification by including the morphology assay, purity, and quantity assay, particle size distribution analysis, and exosome-specific markers expression. |
| Exosome Isolation Tools | Creative Bioarray aims to develop the best quality exosome isolation tools with optimized conditions to help our customers obtain pure exosomes with a higher yield. |
References
- Janockova J, Slovinska L, et al. New therapeutic approaches of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. J Biomed Sci. 2021. 28(1), 39.
- Lee B-C, Kang I, et al. Therapeutic Features and Updated Clinical Trials of Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC)-Derived Exosomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021. 10(4), 711.
- Joo HS, Suh JH, et al. Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives on Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a New Therapeutic Agent. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. 21(3), 727.

