- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Osteoporosis Model
- Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis (GIO) Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis (GIO) Model
If you are looking for a robust and reliable provider of disease models to support your osteoporosis research, Creative Bioarray is the perfect partner for you. Our glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) model is designed to meet the highest standards of scientific rigor and can provide you with the data you need to advance your research goals.
Glucocorticoids, commonly employed for their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, are associated with a significant iatrogenic complication: GIO. Prolonged exposure to high doses of glucocorticoids leads to osteoporosis in a considerable number of patients. It is well-established that excess glucocorticoids directly impact bone cells, including osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes, disrupting their proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and other vital functions. These cellular alterations are believed to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of GIO.
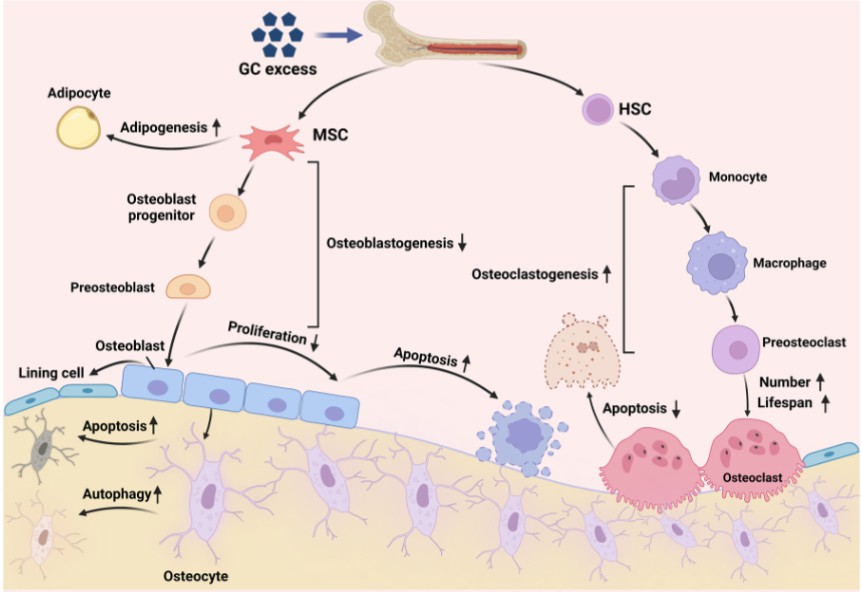 Fig. 1 Effects of GC excess on bone cell. GC, glucocorticoids
Fig. 1 Effects of GC excess on bone cell. GC, glucocorticoids
Our Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis (GIO) Model
- Available Animal
Rat - Modeling Method
Animals are treated with glucocorticoids (such as hydrocortisone or dexamethasone) to induce osteoporosis. - Endpoints
- Body weight
- Histology analysis: H&E staining
- Bone mineral density (BMD)
- Micro-CT
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
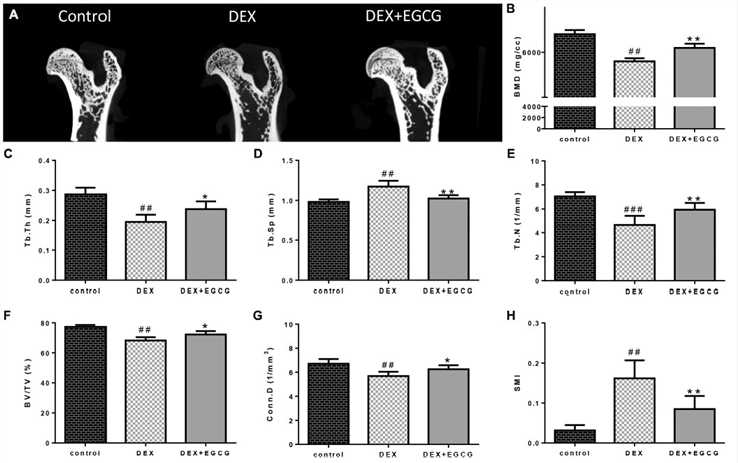 Fig. 2 Effects of EGCG on trabecular bone micro-architecture in GIO rats. (A) micro-CT of proximal femurs. (B) Data from BMD measurements of femurs by DXA. The following computed tomographic indices were analyzed in the defined region of interest (ROI): (C) Tb.Th, (D) Tb.Sp, (E) Tb.N, (F) BV/TV, (G) Conn.D, and (H) SMI.
Fig. 2 Effects of EGCG on trabecular bone micro-architecture in GIO rats. (A) micro-CT of proximal femurs. (B) Data from BMD measurements of femurs by DXA. The following computed tomographic indices were analyzed in the defined region of interest (ROI): (C) Tb.Th, (D) Tb.Sp, (E) Tb.N, (F) BV/TV, (G) Conn.D, and (H) SMI.
Furthermore, we also provide other osteoporosis models that maybe you are interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is dedicated to sharing our extensive expertise in drug efficacy studies with our clients to facilitate and accelerate their drug development process. We specialize in developing and validating disease models that mimic human pathologies, providing a rigorous testing environment for your drug candidates. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly. We look forward to cooperating with you.
References
- Chen, M., et al. Pathogenic mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Cytokine & growth factor reviews, 2023, 70: 54-66.
- Liu, S., et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis of rats in vivo and in vitro. Frontiers in pharmacology, 2018, 9: 447.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

