Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
PC-9
Cat.No.: CSC-C4619J
Species: Human
Source: Lung
Morphology: Epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Shipping Condition: Dry Ice.
The PC-9 cell line is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line that was established from a patient with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This cell line is particularly significant in cancer research due to its responsiveness to targeted therapies and its mutation profile, which includes the presence of an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. The identification of such mutations has propelled the development of targeted treatments, making PC-9 a valuable model for studying the mechanisms of tumor growth and response to therapy in lung cancer.
PC-9 cells are often used in preclinical studies to evaluate the efficacy of EGFR inhibitors, such as gefitinib and erlotinib. These agents are effective in patients whose tumors harbor specific EGFR mutations, underscoring the importance of the PC-9 cell line in understanding the molecular pathways that drive lung adenocarcinoma. Moreover, the cell line serves as a platform for investigating resistance mechanisms that can develop during treatment, offering insights into how tumors adapt and survive in the presence of targeted therapies.
C17:0 Inhibits PC-9 and PC-9/GR Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Clone Formation
Dietary saturated fatty acids may exert antitumor effects, and screening functional fatty acids may provide candidates that may serve as adjuvants in cancer therapy. C14:0, C15:0, C16:0, C17:0, C18:0, C18:1 or C20:0 were directly added into HBE, PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. As presented in Fig. 1A and B, the results of the MTT assay indicated that these fatty acids did not affect the proliferation of HBE cells, while 4 types of fatty acids (C16:0, C17:0, C18:0, and C20:0) significantly inhibited the proliferation of PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. Furthermore, C17:0 was identified to be the most effective fatty acid against PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells, and its effects were dose-dependent (Fig. 1C and D). The effect of C17:0 in other lung cancer cells, including A549 and H1975, was also examined. Similarly, the results revealed that C17:0 inhibited cell proliferation in A549 and H1975. These results indicated that C17:0 may be a fatty acid suitable for lung cancer treatment.
The functional role of C17:0 in lung cancer cells was then studied. A wound healing assay indicated that C16:0, C17:0, and C18:0 inhibited the wound closure ratio of PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells (Fig. 2A and B). Furthermore, the impact of C17:0 on cell migration was the greatest among all fatty acids tested. The apoptosis ratio was also determined by flow cytometry. As presented in Fig. 3A, C17:0 induced 16.62 and 29.63% apoptosis in PC-9 cells and PC-9/GR cells respectively. C18:0 also performed similarly in the two cell line variants. In addition, the results of the cell clone formation assay indicated that C17:0 suppressed the proliferation of PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells (Fig. 3B). These results indicated that C17:0 treatment in PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells was able to induce lung cancer cell death.
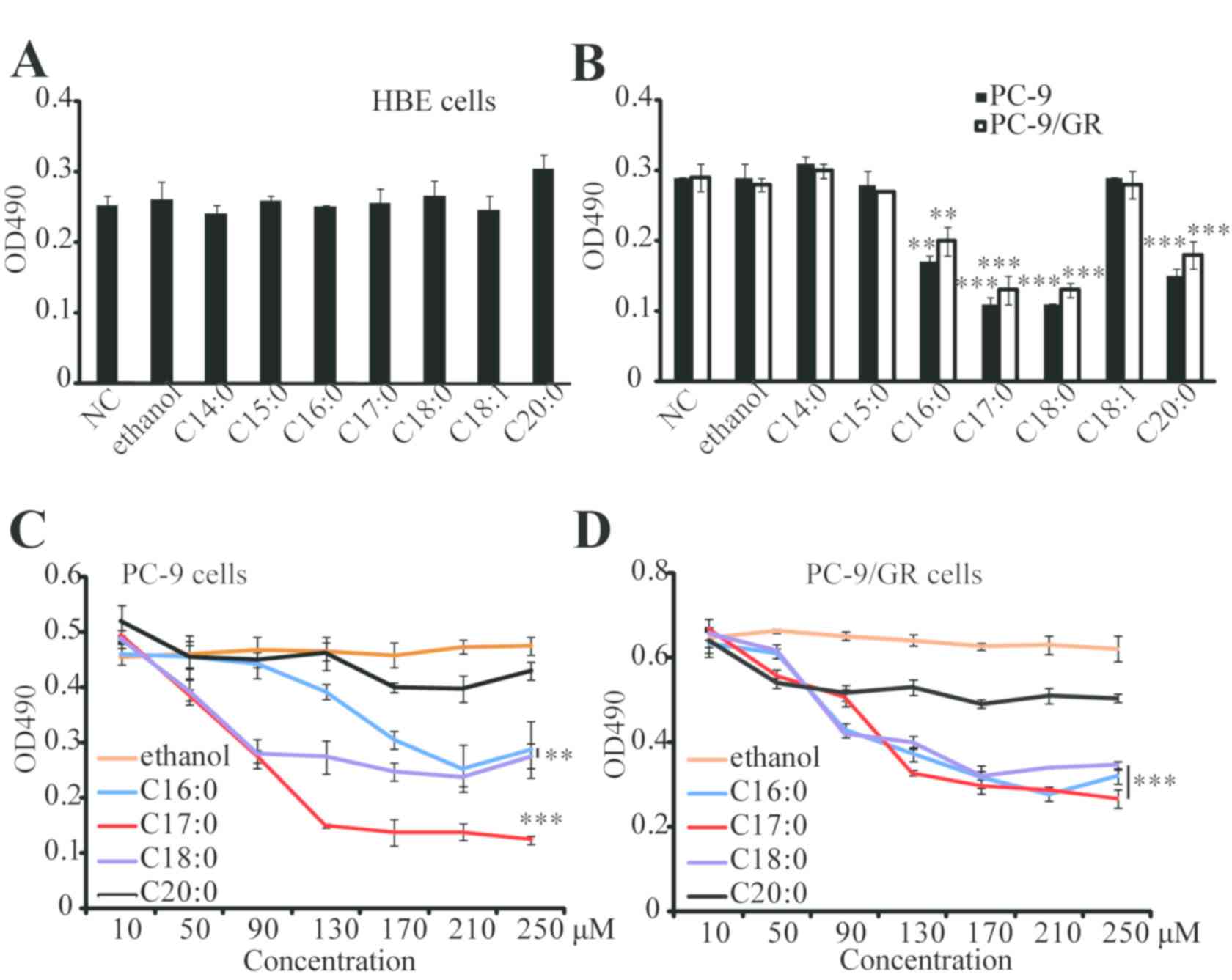 Fig. 1 C17:0 inhibits PC-9 and PC-9/GR cell proliferation. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
Fig. 1 C17:0 inhibits PC-9 and PC-9/GR cell proliferation. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
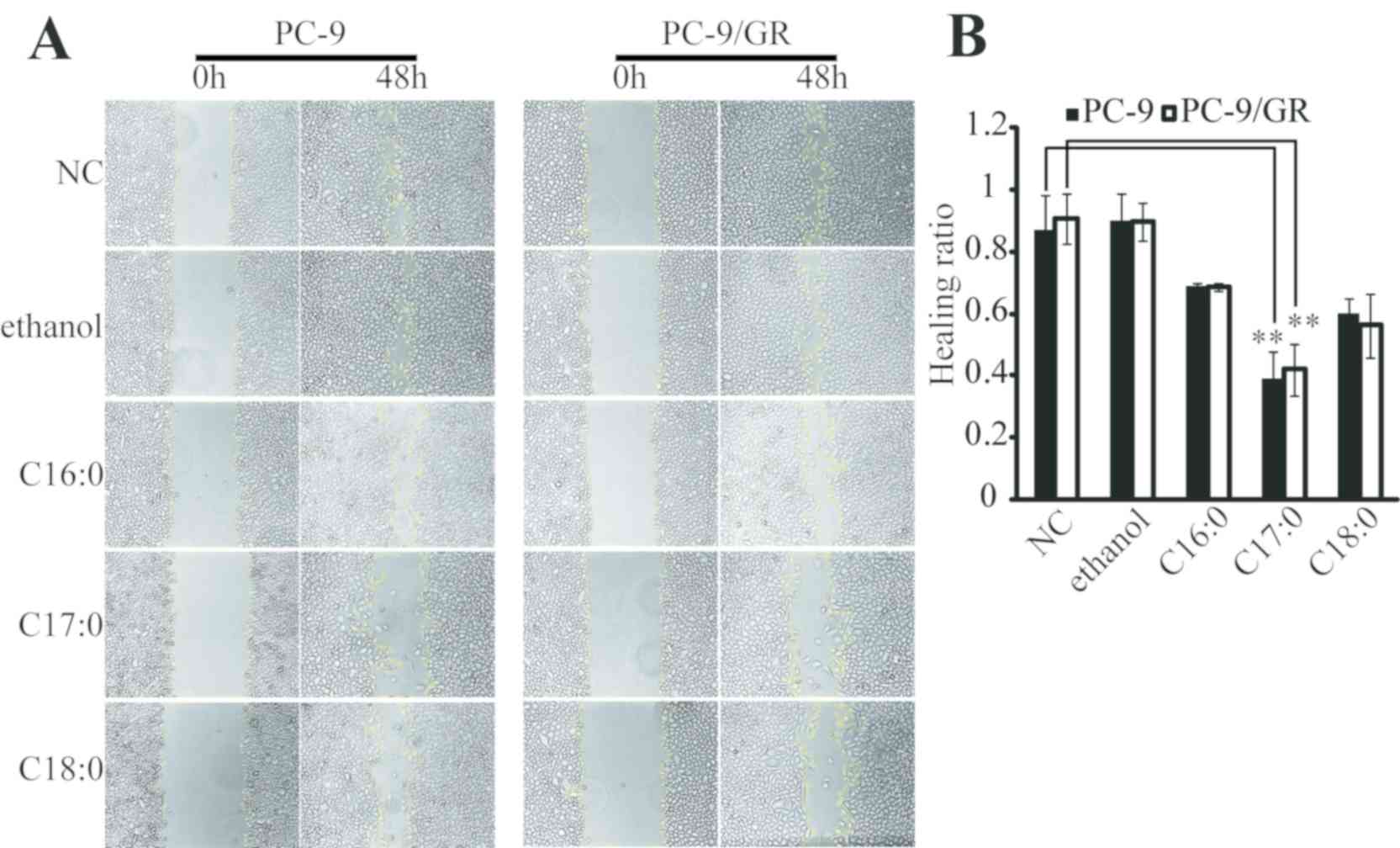 Fig. 2 C17:0 inhibits wound healing in PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
Fig. 2 C17:0 inhibits wound healing in PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
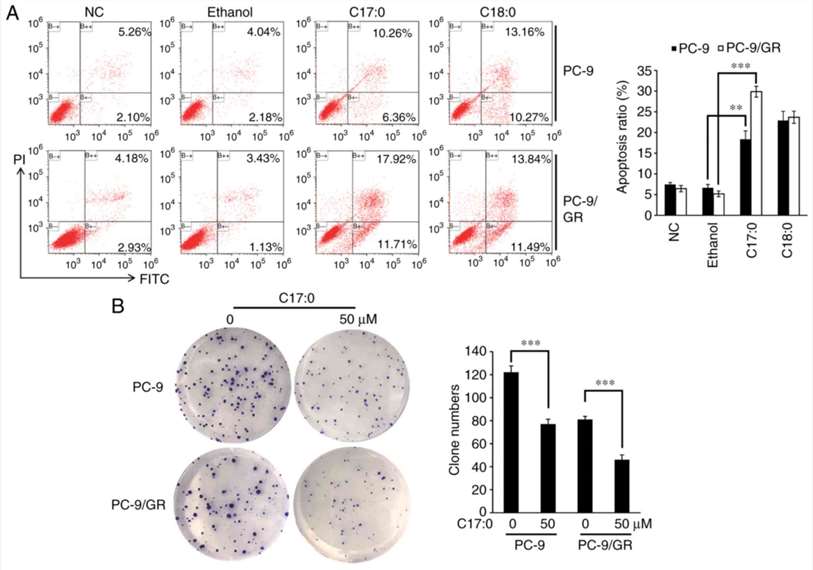 Fig. 3 C17:0 promotes apoptosis, while it inhibits clone formation in PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
Fig. 3 C17:0 promotes apoptosis, while it inhibits clone formation in PC-9 and PC-9/GR cells. (Xu C, et al., 2019)
Increased Sensitivity of EGFR-TKI-Resistant Cells to Gemcitabine and Vinorelbine
EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are widely used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harboring EGFR-activating mutations. PC-9 cells harboring an EGFR-activating mutation (EGFR exon 19 deletion) were used. The established EGFR-TKI-resistant cells were designated as PC-9ER and PC-9GR cells. PC-9ER cells became resistant to erlotinib by acquiring the EGFR T790M gatekeeper mutation (i.e., a mutation that sterically hinders inhibitor interaction), whereas PC-9GR cells became resistant to gefitinib through activation of the FGF2-FGFR1 pathway. First, the resistance of PC-9ER and PC-9GR cells to EGFR-TKIs was confirmed. The proliferation of PC-9 parent cells was inhibited by erlotinib and gefitinib at 0.01 µM; however, the proliferation of PC-9ER and PC-9GR was not significantly inhibited by even 3 mM erlotinib or gefitinib (Fig. 4A). To examine whether EGFR-TKI-resistant cells exhibit altered sensitivity to cytotoxic agents, the sensitivity of PC-9, PC-9ER and PC-9GR cells was evaluated by MTS assay with or without cytotoxic agents. The cytotoxic agents included in the present study were cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine, all of which are widely used in the clinic for the treatment of patients with NSCLC. The sensitivity of EGFR-TKI-resistant cells to cisplatin, docetaxel, and pemetrexed was comparable with that of PC-9 parent cells. By contrast, increased sensitivity of EGFR-TKI-resistant cells to gemcitabine and vinorelbine was observed (Fig. 4B). These results indicated that EGFR-TKI-resistant cells had increased sensitivity to gemcitabine and vinorelbine.
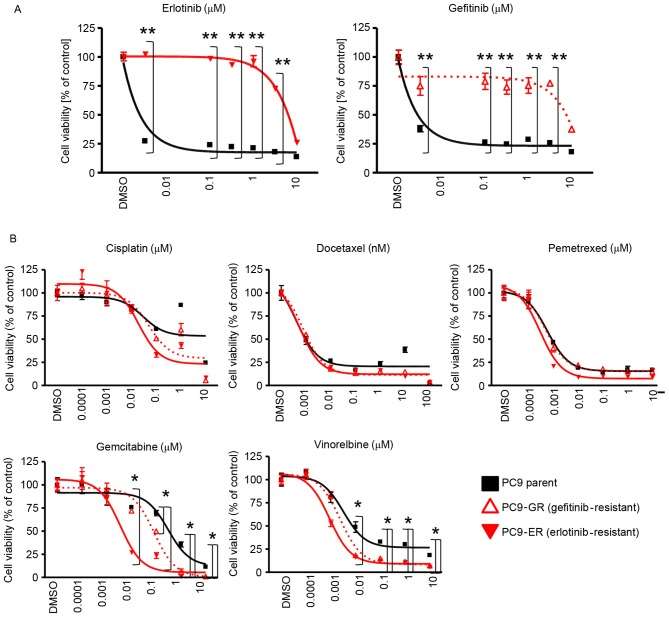 Fig. 4 Sensitivity of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor-sensitive and resistant cell lines to cytotoxic agents. Results of MTS assay for PC-9, PC-9GR, and PC-9ER cells. (Hamamoto J, et al., 2017)
Fig. 4 Sensitivity of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor-sensitive and resistant cell lines to cytotoxic agents. Results of MTS assay for PC-9, PC-9GR, and PC-9ER cells. (Hamamoto J, et al., 2017)
Trypan blue cell exclusion depends on the integrity of the cellular membrane while MTT assay depends on intracellular activity to metabolize reagents and give a color for absorbance measurement.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Highly recommended
I had a great experience purchasing tumor cells from Creative Bioarray. The product arrived on time and was packaged securely. Highly recommended!
20 Jan 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review