Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
HCA-1 is a human endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line derived from female endometrial tissue. Endometrial adenocarcinoma represents a prevalent malignant tumor that occurs mainly in the endometrial layer of the female reproductive system. Pathological examination reveals that the tumor displays glandular hyperplasia and cellular atypia along with elevated levels of mitotic figures. HCA-1 cells show epithelial-like morphology with adenocarcinoma cell features such as enlarged nuclei and variable cellular structures when grown in vitro.
Researchers use HCA-1 cell line as a representative model of endometrial adenocarcinoma to investigate its pathogenesis and explore its molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. In clinical practice this approach aids in assessing chemotherapy effectiveness while also allowing for patient outcome predictions and the creation of tailored treatment strategies. HCA-1 serves as a tool for early-stage screening and assessment of drugs that show potential antitumor properties during drug development.
Reduced Expression of Gangliosides with GM2-Determinant in Cervical Carcinoma-Derived Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation into Nude Mice
Glycosphingolipids' altered expressions in cancer cells contribute significantly to tumorigenicity and metastasis through changes in glycosyltransferase activities. Cervical carcinoma-derived cell lines express gangliosides with GM2 determinants prominently, unlike other carcinomas. Tanaka et al. employed subcutaneous transplantation of cervical carcinoma cells into nude mice and uses TLC-immunostaining for ganglioside quantification. By comparing ganglioside profiles in transplanted cells to those in original tissues and cultured cells, researchers aim to uncover differences in glycolipid expression.
Previously reported findings show all cells had high concentrations of gangliosides with GM2-determinant: SKG-IIIb and HeLa cells had GM2 alone; HCSC-cells had GM2 and GalNAc-GM1b; HCA-1 cells had GM2, GalNAc-GM1b, and GalNAc-GD1a. However, Fig. 1 shows these gangliosides disappeared in transplanted cells, but GM1, a GM2 derivative, was present. In transplanted HCA-1 and HCSC-1 cells, new expression of GM1b was seen, indicating reduced GalNAc-GM1b synthesis. GM3, absent in cultured HCSC-1 cells, appeared in the transplanted ones due to decreased GM2 synthesis, leading to GM3 accumulation. GalNAc-GM1b in cultured HCA-1 and HCSC-1 cells matched GM1b in their transplanted counterparts, suggesting stable GM1b synthesis. GM2 levels in cultured cells didn't correlate with GM3 in transplanted cells, while GM1 expression remained stable across both cell types. Ganglioside expression in patient tissues was analyzed using TLC-immunostaining with anti-GM3 (5H6), CTB, and anti-GM2 (YHD-06) antibodies, as shown in Fig. 2. GM3 and GM1 were found in all tissues examined, but GM2 appeared in only three of 14 tissues at less than 0.02 μg/mg dry weight, including SCC-patient 4, adenocarcinoma-patient 5, and small cell carcinoma-patient 1. GM3 was the predominant ganglioside, comprising over 84% of total gangliosides, while GM1 was less than 12%, at 0.01–0.06 μg/mg. GM1b, GalNAc-GM1b, and GalNAc-GD1a were undetectable in lipid extracts from 1 mg of dry tissue.
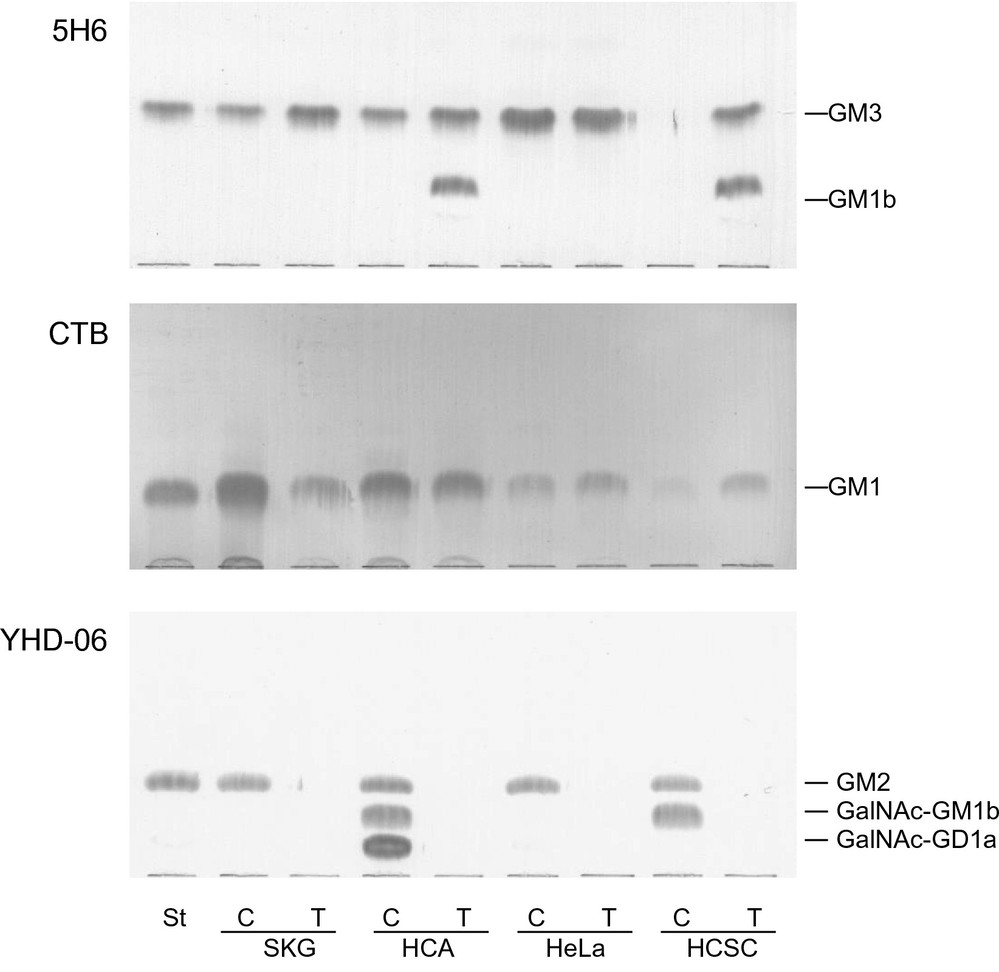 Fig. 1. TLC-immunostaining with anti-GM3 (5H6) antibodies, CTB and anti-GM2 (YHD-06) antibodies of lipid extracts from cultured (C) and transplanted (T) cervical carcinoma-derived cells (Tanaka K, Murakami I, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. TLC-immunostaining with anti-GM3 (5H6) antibodies, CTB and anti-GM2 (YHD-06) antibodies of lipid extracts from cultured (C) and transplanted (T) cervical carcinoma-derived cells (Tanaka K, Murakami I, et al., 2023).
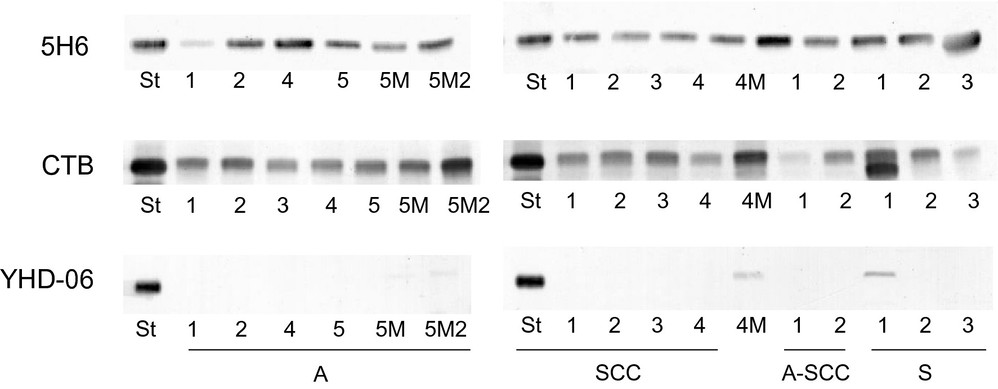 Fig. 2. TLC-immunostaining with anti-GM3 (5H6) antibodies, CTB and anti-GM2 (YHD-06) antibodies of lipid extracts from the tissues of patients with several types of cervical carcinoma (Tanaka K, Murakami I, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. TLC-immunostaining with anti-GM3 (5H6) antibodies, CTB and anti-GM2 (YHD-06) antibodies of lipid extracts from the tissues of patients with several types of cervical carcinoma (Tanaka K, Murakami I, et al., 2023).
Overexpression of RNase1 Promoted HCC Cell Highly Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Treatment
RNases serve as a defense mechanism against pathogens and their high expression in various cancers affects cellular growth and stemness properties. The exact function and control mechanisms of RNases within tumor microenvironments (TMEs) have not yet been fully determined. The analysis of HCC patient samples who received nivolumab treatment showed RNase1 expression levels were higher in non-responders which correlated with decreased survival rates across different cancers. To explore RNase1's impact on anti-PD-1 therapy efficacy, Liu's team used RNase1-negative HCA-1 cells to create stable RNase1-expressing lines (Fig. 3a) and injected them into immunocompetent mice. These mice were treated with anti-PD-1 antibody (αPD-1) (Fig. 4b). Mice with RNase1-expressing tumors (HCA-1/R1) showed higher RNase1 plasma levels (Fig. 3a), similar to HCC patients. αPD-1 was less effective in these mice compared to those with HCA-1/Vec tumors (Fig. 3c), and it didn't improve their survival rate (Fig. 3d). Consistently, RNase1 overexpression in orthotopic models resulted in increased tumor size and poor response to anti-PD-1 after 3 weeks (Fig. 4b–e), confirming RNase1 promotes resistance.
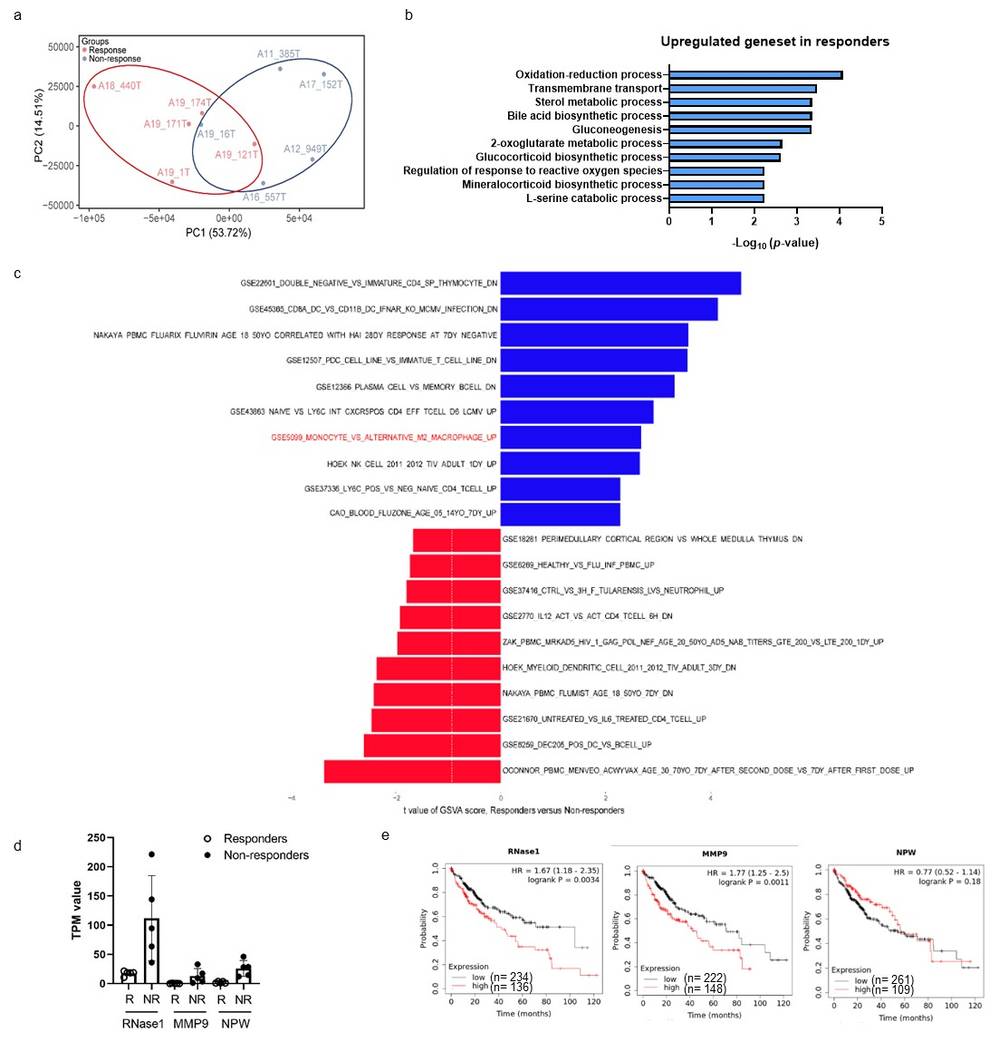 Fig. 3. GO analysis of RNA sequencing data and correlation between RNase1 expression and OS rate for human cancers (Liu C, Zhou C, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. GO analysis of RNA sequencing data and correlation between RNase1 expression and OS rate for human cancers (Liu C, Zhou C, et al., 2024).
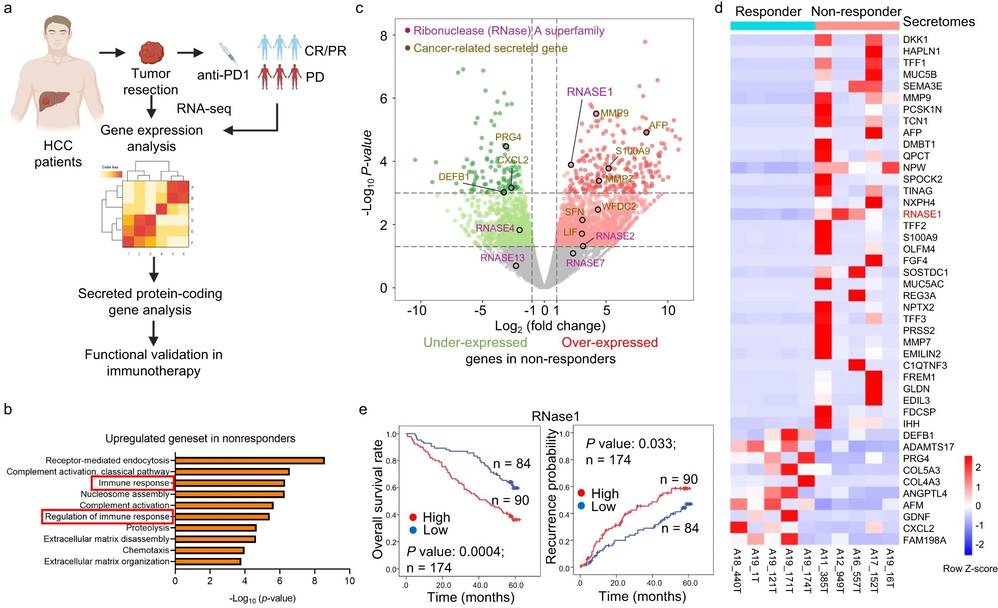 Fig. 4. RNase1 expression is correlated with extensive infiltration of immunosuppressive myeloid cells (Liu C, Zhou C, et al., 2024).
Fig. 4. RNase1 expression is correlated with extensive infiltration of immunosuppressive myeloid cells (Liu C, Zhou C, et al., 2024).
Common types of uterine tumors include endometrial stromal sarcoma, uterine leiomyosarcoma, and endometrial adenocarcinoma. Cervical tumors can include squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and cervical sarcoma.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Satisfied
The cell product surpassed my expectations in terms of cell viability, with consistently high cell survival rates across multiple experiments.
21 Mar 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need