- You are here: Home
- Applications
- Neurological Disorder
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- In Vivo Model Service
- Induced Damage Model
- Colchicine Induced Model
Applications
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Colchicine Induced Model
Colchicine can selectively destroy hippocampal pyramidal cells and granulosa cells, resulting in cholinergic system damage and short-term learning and memory impairment. Generally, we can induce dementia by injecting colchicine into the ventricles of rats.
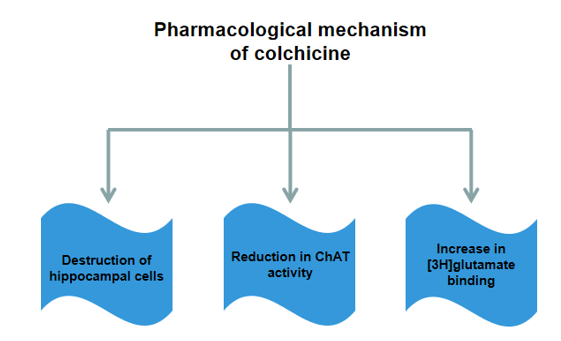 Figure. 1. Pharmacological mechanism of colchicine-induced Alzheimer's disease model
Figure. 1. Pharmacological mechanism of colchicine-induced Alzheimer's disease model
Our capabilities
- We can provide comprehensive behavioral and cognitive testing on AD model and the drug screening.
- We can evaluate anti-oxidative stress in the hippocampus of animals treated with drug candidates.
- We can evaluate various biomarkers through WB, IHC, ELISA, sequencing, etc.
Assays available
- Learning and memory deficits tests
- Oxidative stress
- Neuroinflammation
- Phosphorylated tau
- Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3β)
- Neurofilament Light Chain levels
- Enzyme activity related to cholinergic system
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Brain slice staining and synaptic electrophysiology
With 10 years of hard working and continuous development, as a senior leader specialize in AD research with enormous industrial experience, Creative Bioarray is exceptionally positioned to be your partner. We will make our best efforts to meet your unique requires by providing individually customized service.
Study examples
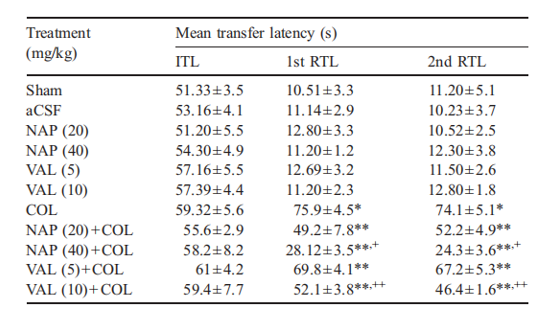 Figure. 2. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on elevated plus maze performance task in colchicines-treated rats
Figure. 2. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on elevated plus maze performance task in colchicines-treated rats
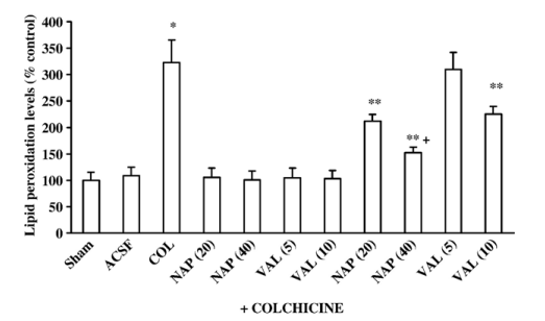 Figure. 3. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain lipid peroxidation levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E.M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)- injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures twoway ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
Figure. 3. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain lipid peroxidation levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E.M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)- injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures twoway ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
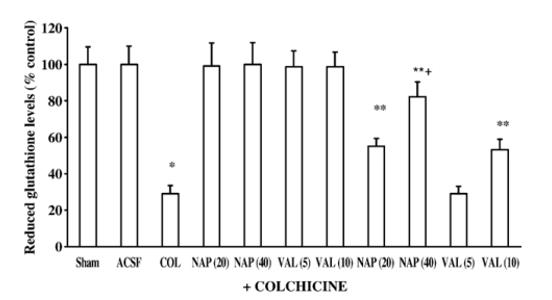 Figure. 4. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain reduced glutathione levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E.M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)- injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures twoway ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
Figure. 4. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain reduced glutathione levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E.M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)- injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures twoway ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
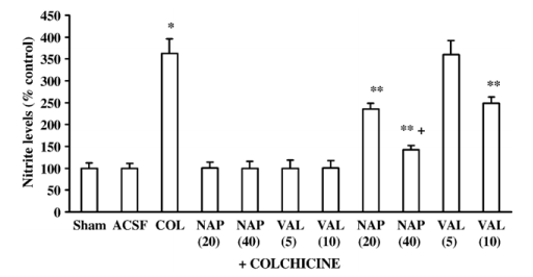 Figure. 5. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain nitrite levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E. M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)-injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
Figure. 5. Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors (naproxen (NAP) 20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o. and valdecoxib (VAL) 5 and 10 mg/kg, p.o.) on brain nitrite levels in intracerebroventricular colchicine (COL)-injected rats. Values are mean ± S.E. M. * P<0.05 as compared to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)-injected group; ** P<0.05 as compared to colchicine-injected group; **+ P<0.05 as compared to NAP (20) +COL group. (Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparisons). Note: aSCF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid, NAP = Naproxan, COL = Colchicine, VAL = Valdecoxib.
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Kumar A et al. Differential effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on intracerebroventricular colchicine-induced dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2006, 551(1-3):58-66.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

