Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
ONCO-DG-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0517
Species: Human
Source: ovary adenocarcinoma
Morphology: epithelial-like adherent cells with large vacuoles growing as monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 +, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endot
The ONCO-DG-1 cell line was developed from the papillary thyroid carcinoma tissue taken from a 49-year-old woman. The thyroid gland resides at the front of the neck where it functions as a vital endocrine gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that control body functions including metabolism and growth. Papillary thyroid carcinoma stands as the most prevalent thyroid cancer type which demonstrates both a high incidence rate and an excellent prognosis. These cells exhibit epithelial-like features including polygonal or cuboidal shapes with large, regular nuclei and rich cytoplasm, and they connect through structures like tight junctions to form an arrangement resembling normal epithelial tissue.
ONCO-DG-1 cell lines serve as widely adopted research tools in cancer science and prove especially useful in papillary thyroid carcinoma studies. Researchers utilize this cell line to study tumor cell migration along with invasion patterns and their reactions to chemotherapy treatments. This cell line also supports anti-cancer drug screening and pharmacological research while enabling gene function studies to understand thyroid cancer-related gene mechanisms. Filter tests results show that ONCO-DG-1 cell line performance indices suggest possible biomedical engineering applications.
Interferometric Measurement of TGF-β Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Tumor Cells
The visualization of live cells in three-dimensional cultures poses significant challenges due to the scattering nature of cell mediums. Accurate imaging is crucial because these cultures closely mimic natural cellular conditions. Varol et al. propose using a phase-stepping, Mach–Zehnder-based setup combined with high-frequency piezo actuators and CMOS sensors for imaging the EMT process in cell cultures. The methodology improves noise cancellation and offers a real-time monitoring capability without compromising cell viability.
Using a Watershed transform-based segmentation method, they isolated the cell depth map from the background, revealing that modified surface structures enhance CTCs' adherence to flat surfaces while reducing mesenchymal traits. Results clearly demonstrate the epithelial cells' morphological changes during EMT, showing reduced adhesion and transition to spherical shapes, with increased mobility. Holographic imaging provides valuable insights into the behavioral patterns of cancer cells. Depth maps reconstructed at 0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 hours post-TGF-β treatment (Fig. 1) illustrate EMT-induced changes within the first 24 hours, showing less variation in mesenchymal cells than epithelial cells, which become more rounded. Eccentricity, indicating circularity, decreased across cell lines after treatment. Figure 2 compares parameters before and after EMT, highlighting more spherical transformations and reduced adhesion as surface area and eccentricity values drop.
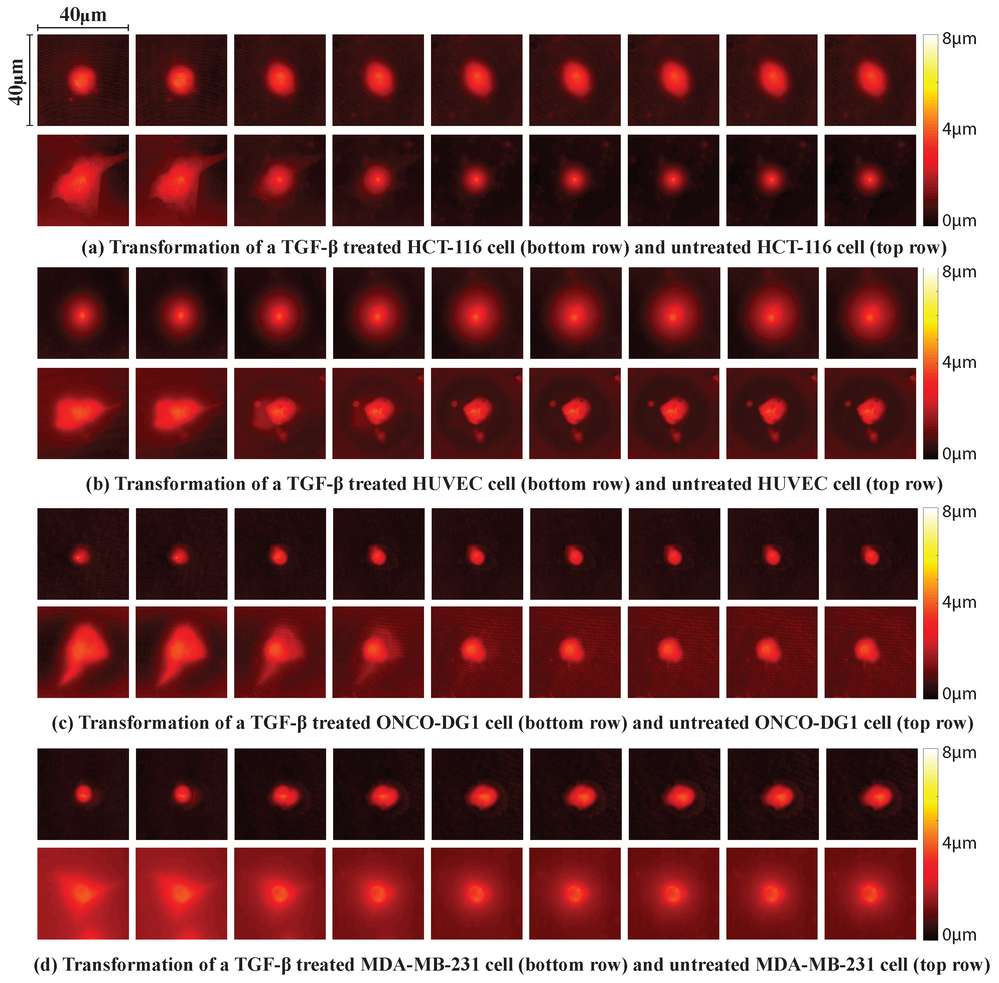 Fig. 1. A reconstruction of the depth maps for each cell line throughout a 48 h period in 6 h intervals (Varol R, Esmer GB, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. A reconstruction of the depth maps for each cell line throughout a 48 h period in 6 h intervals (Varol R, Esmer GB, et al., 2020).
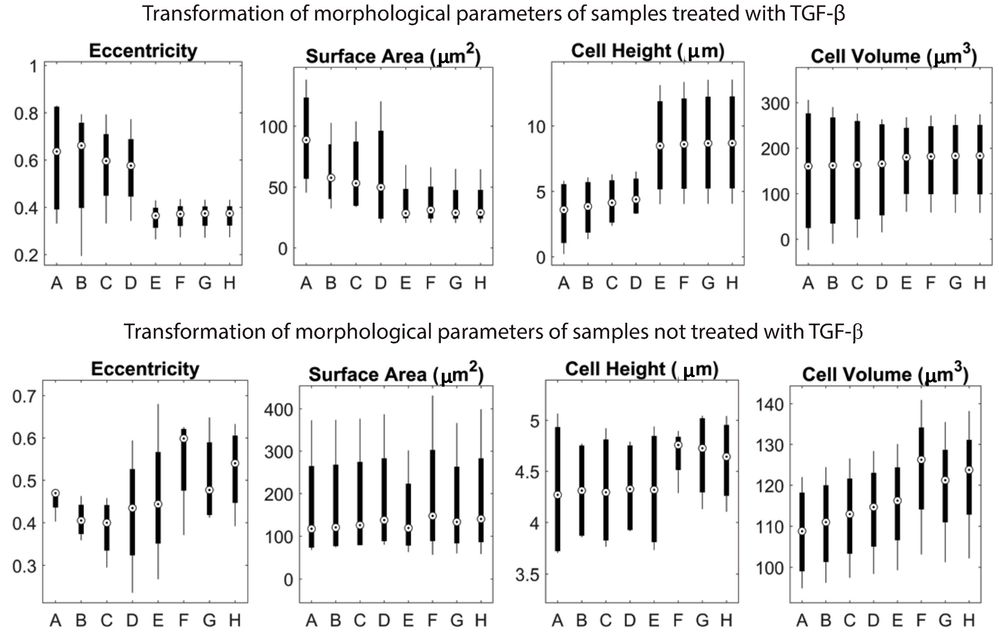 Fig. 2. Eccentricity, surface area, cell height, and cell volume parameters are calculated and summarized in these graphs (Varol R, Esmer GB, et al., 2020).
Fig. 2. Eccentricity, surface area, cell height, and cell volume parameters are calculated and summarized in these graphs (Varol R, Esmer GB, et al., 2020).
Morphological Change of Immpobulized Cancer Cells on a Chip
Cavitation in biomedical applications shows promise due to its ability to alter tissues and cells through the energy released by collapsing bubbles. It has a wide range of uses such as in removing kidney stones or blood-brain barrier opening. Gevari et al. introduced a method using cavitating flows from a micro nozzle on immobilized cancer cells, and investigated hydrodynamic cavitation's impact on cancer cell lines HCT-116, MDA-MB-231, and ONCO-DG-1.
Each cell line was initially cultured on silica/glass surfaces under controlled conditions and returned to their medium post-exposure to maintain morphology. Samples were exposed to cavitation flows for 3 seconds to preserve cancer cells on the surface. PBS was used as the working fluid to assess the impact on cancer and normal cells, maintaining cell viability. Two similar samples were prepared for each cell line to compare pre- and post-exposure conditions. Cavitation was applied for 3 seconds at 1720 kPa and 3450 kPa, with effects observed only above 2070 kPa, where cells began detaching at 3450 kPa. Post-exposure, cells were washed with PBS and prepared for SEM imaging. Figure 3 show SEM images of cancer cells post-cavitation. At 1720 kPa, cavitation impact is minimal, but beyond 2070 kPa, cell damage is evident. At 3450 kPa, the cell membrane and filopodia structure break down. ONCO-DG1 lines show morphological changes between 2070 and 2760 kPa. Other images illustrate effects at 2070 and 2760 kPa. Crater diameters on cells are approximately 4 μm, consistent with previous studies of collapsing bubbles at similar channels, indicating a significant role in disrupting immobilized cancer cells.
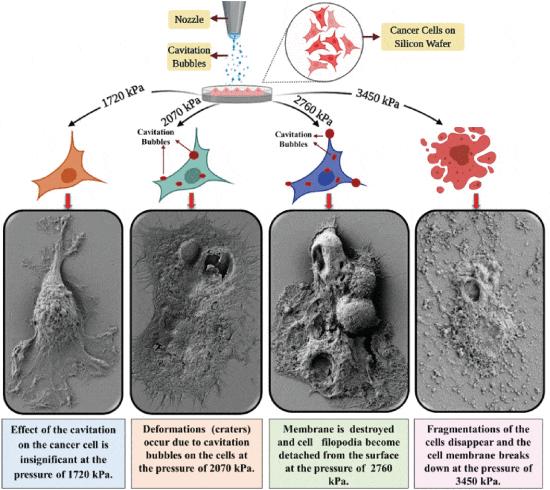 Fig. 3. Morphological deformation modes on the surface of ONCO-DG-1 (Ovarian Adenocarcinoma) cancer cells exposed to cavitation (carpet bombardment) are shown (Gevari M T, Aydemir G, et al., 2021).
Fig. 3. Morphological deformation modes on the surface of ONCO-DG-1 (Ovarian Adenocarcinoma) cancer cells exposed to cavitation (carpet bombardment) are shown (Gevari M T, Aydemir G, et al., 2021).
Thyroid tumor cell lines can be used to investigate the metastatic potential of thyroid cancer by assessing their invasive properties in vitro and their ability to form tumors in animal models. These studies help understand the molecular mechanisms underlying thyroid cancer metastasis and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Exceptional quality
The cells performed as expected, and the customer support provided by the company was outstanding.
13 Feb 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need