Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
MFE-296
Cat.No.: CSC-C0459
Species: Human
Source: endometrium adenocarcinoma
Morphology: epithelial-like polymorphic cells growing adherently in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 -, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM -, GFAP -, neurofilament -,
MEF-296 cell line originates from a moderately differentiated (G2 grade) primary tumor of endometrial adenocarcinoma in a 68-year-old Caucasian woman. Endometrial adenocarcinoma represents one of the most prevalent malignancies of the female reproductive system which develops due to abnormal estrogen levels along with obesity and diabetes. MEF-296 cells contain fully active androgen receptors where androgens suppress cell growth and these cells lack estrogen receptors. The cells display expression profiles for vimentin and cytokeratins 7, 8, 18, and 19. MEF-296 cells in nude mice models show tumor-forming capability while maintaining a human diploid karyotype with 20% polyploid cells denoted as 46<2n>XX yet display no consistent chromosomal abnormalities.
The origin of MEF-296 cells from endometrial adenocarcinoma tissue and their tumorigenic properties make them appropriate for research into tumor development and progression mechanisms and tumor cell behavior including invasion and metastasis in endometrial adenocarcinoma. The cell line also serves as a valuable resource for scientists researching androgen receptors to better understand androgens' impact on endometrial adenocarcinoma and to develop targeted receptor therapies.
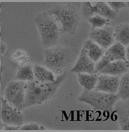 Fig. 1. MEF-296 (Qu W L, Zhao Y L, et al., 2018).
Fig. 1. MEF-296 (Qu W L, Zhao Y L, et al., 2018).
MSM Decreases Viability of EC Cells in A Dose-Dependent Manner
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), a low-toxicity dietary supplement, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties in cancers. So far, the MSM might have a potentially beneficial effect in endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Kowalska et al. assessed MSM's impact on EC cell (ISHIKAWA、MFE-296、MFE-280) viability, finding it reduced viability dose-dependently (Fig. 1a). The ISHIKAWA cell line, representing well-differentiated EC, showed the greatest sensitivity compared to MFE-296 and MFE-280. Viability significantly decreased in ISHIKAWA and MFE-296 at MSM doses below 600 mM. For MFE-280, a significant viability decrease occurred at 300 mM or higher. Therefore, 300 mM and 400 mM MSM concentrations were selected for further testing, with these doses exceeding the IC50 for ISHIKAWA (538.6 mM), MFE-296 (551.1 mM), and MFE-280 (380 mM), as determined by AlamarBlue assay. They re-evaluated EC cell viability by pre-treating with MSM before DOX to assess enhanced toxicity (Fig. 1b). Pre-treatment with MSM significantly reduced viability in ISHIKAWA and MFE-280 cells compared to DOX alone. In MFE-296, 400 mM MSM pre-treatment also significantly decreased viability. While no significant differences were found between MSM alone and MSM plus DOX treatments, cell viability decreased.
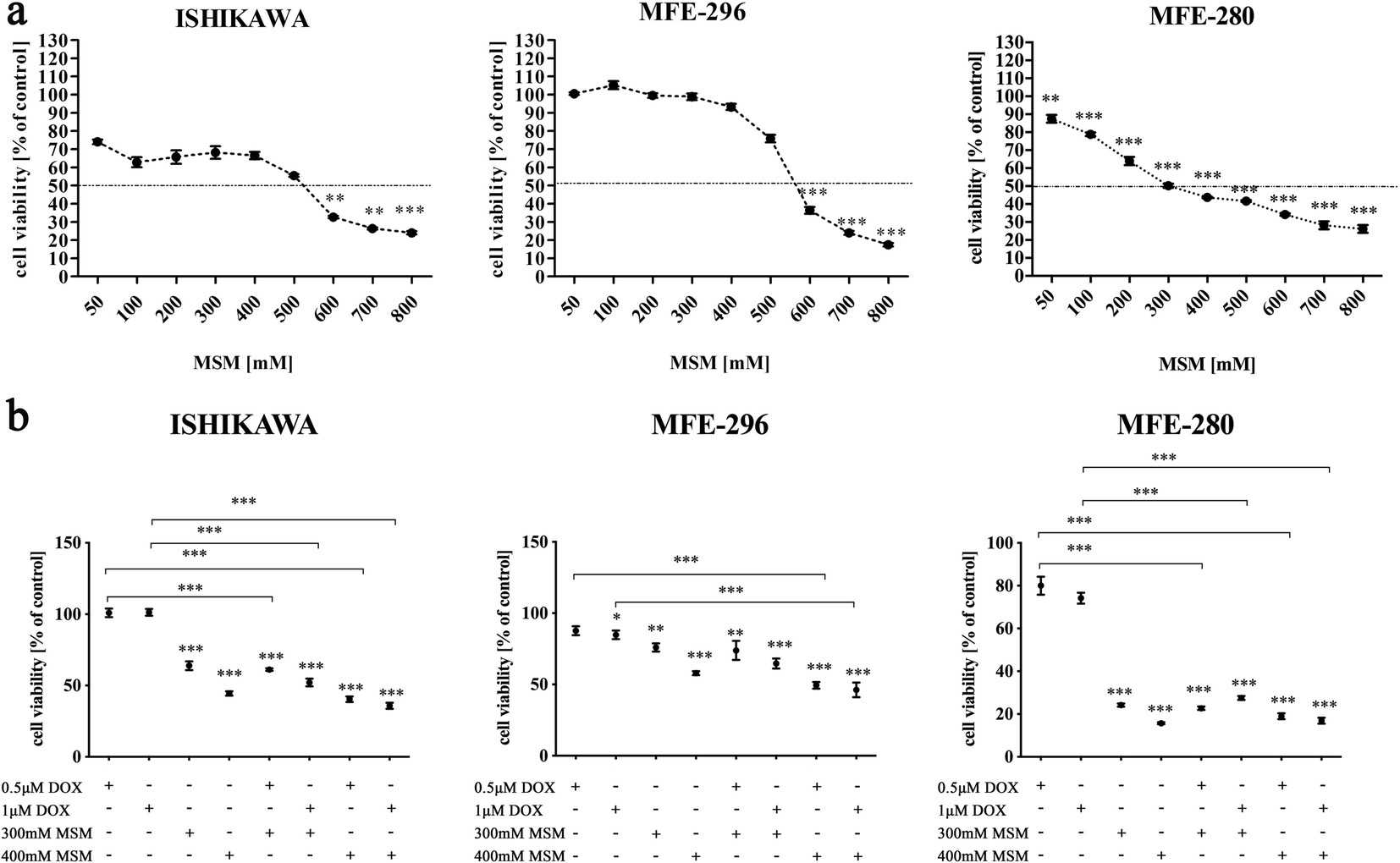 Fig. 1. Methylsulfonylmethane sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to doxorubicin (Kowalska K, Habrowska-Górczyńska D E, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. Methylsulfonylmethane sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to doxorubicin (Kowalska K, Habrowska-Górczyńska D E, et al., 2021).
PMS2L2 Reduced the Viability of EA Cells Under 300 µM Carboplatin Treatment
LncRNA PMS2L2 plays critical protective roles in chondrocytes during lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Zhang's team using deep sequencing revealed the altered expression of PMS2L2 in endometrial adenocarcinoma (EA) during chemotherapy. Then, they aim to investigate PMS2L2's functionality in modulating chemosensitivity and its impact on cell viability. PMS2L2 expression vectors and siRNAs were transfected into MFE-296 and TOV-112D cells. Transfection significantly altered PMS2L2 expression after 24 hours (Fig. 2A, p<0.05), confirming success. Post-transfection, cells were treated with 0 or 300 µM carboplatin for 24 hours, and viability was assessed via MTT assay. Carboplatin at 300 µM significantly reduced cell viability (Fig. 2B, p<0.05). PMS2L2 overexpression decreased EA cell viability, while its siRNA silencing increased viability only at 300 µM carboplatin (Fig. 2B, p<0.05).
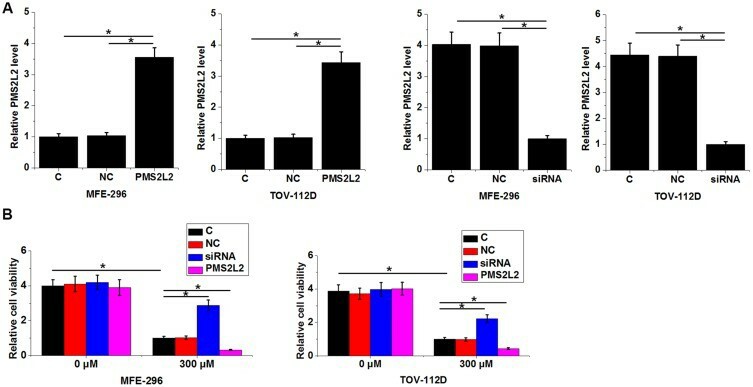 Fig. 2. PMS2L2 improved the viability of EA cells under 300 µM carboplatin treatment (Zhang D, Sun X, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. PMS2L2 improved the viability of EA cells under 300 µM carboplatin treatment (Zhang D, Sun X, et al., 2019).
Changes in the number of CTCs over time can provide valuable information about treatment efficacy and disease progression.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
A superior choice
Consistently high cell viability and purity, combined with unparalleled compatibility, made these cell biology products a superior choice for our research needs.
01 Dec 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need