Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
EGI-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0433
Species: Human
Source: bile duct carcinoma
Morphology: adherent polymorphic (epitheloid or dendritric) cells growing in monolayers with multilayer foci
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vime
The EGI-1 cell line was originally created in 1984. The cell line was originally isolated and grown from the primary tumor of a 52-year-old male with late stage malignant bile duct carcinoma, who hadn't had chemotherapy before cell isolation. This cell line was established by three transfections in female nude mice (nu/nu mice). In microscope view, EGI-1 cells are epithelial in shape, often polygonal, crisscrossed, interlinked between cells, monolayer or multilayer with the appearance of epithelial tissue. These cells are human hypertriploid, 8 per cent polyploid, and have unique chromosomal abnormalities.
In the scientific arena, EGI-1 cell line is used extensively, especially in the case of bile duct carcinoma. For example, in EGI-1 cells, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway (cell proliferation) and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway (cell survival) are both in high activity. These illegitimate signaling pathways are directly implicated in the onset, progression and chemotherapeutic resistance of gallbladder cancer. In addition, EGI-1 cells produce a variety of bioactive compounds such as cytokines, growth factors and certain proteins that are directly related to the formation of tumors and angiogenesis. This means that deep-dive studies of EGI-1 cells can shed light on the mechanism of progression of gallbladder cancer and yield scientific evidence for new treatment options.
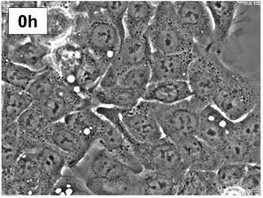 Fig. 1. Image of EGI-1 cells (Malacrida A, Rigolio R, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. Image of EGI-1 cells (Malacrida A, Rigolio R, et al., 2021).
Effect of CX-4945 on CCA Cell Viability, Apoptosis, and Colony Formation Ability
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a particularly lethal liver cancer that occurs in its majority in late-stage stages when it's too late to have any curative surgery. Traditional gemcitabine-and-cisplatin chemotherapy is ineffective. The activity of casein kinase II (CK2) is associated with poorer results in CCA. A selective CK2 inhibitor, CX-4945, has demonstrated antitumor activity against other cancers through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Zakharia et al. investigated the antineoplastic activity of CX-4945 against CCA with PI3K/AKT inhibition. After teasing them with CX-4945 for 24, 48, and 72 hours, they observed the cell viability, apoptosis, and ability to form colonies of CCA cells. These showed that 24 to 72 hours treatment of HuCCT1 cells with CX-4945 resulted in a time-dependent inhibition of cell death. 72 hours later, CX-4945 essentially destroyed the HuCCT1, EGI-1 and Liv27 cells at an IC50 of 7.3, 9.5 and 9.4 M respectively (Fig. 1A). Analysis of the caspase 3/7 activity revealed increased apoptosis, which increased at lower doses after 72 hours (Fig. 1B). Effects were confirmed by DAPI staining. CX-4945 treatment for 10 days reduced colony formation in HuCCT1 and EGI-1 cells with IC50 values of 3.8 and 1.6 μM, respectively, confirming dose-dependent inhibition of CCA cell colony formation (Fig. 1C and D). These results confirm that treatment with CX-4945 inhibits CCA cell colony formation in a dose-dependent manner.
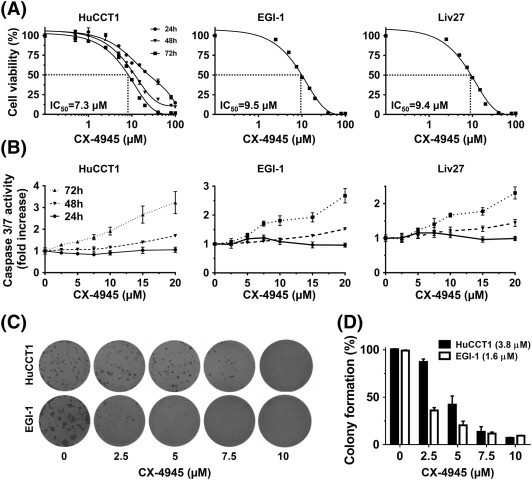 Fig. 1. CX-4945 decreases cell viability of HuCCT1, EGI-1, and Liv27 CCA cell lines in dose-dependent manner (Zakharia K, Miyabe K, et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. CX-4945 decreases cell viability of HuCCT1, EGI-1, and Liv27 CCA cell lines in dose-dependent manner (Zakharia K, Miyabe K, et al., 2019).
Trametinib Treatment Directly Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
The subtype iCCA, a type of primary liver cancer, has an exceptionally poor 5-year survival of 10%. Though immune checkpoint inhibitors have been effective in many solid cancers, they have had only partial efficacy in iCCA. In contrast, MEK inhibitors such as trametinib have been found to be effective at reducing cell growth and altering the tumor microenvironment in iCCA preclinical models. So, Wabitsch's team evaluated trametinib's in vitro growth inhibition of the 2 available murine iCCA cell lines, SB1 and LD-1, and one human iCCA cell line, EGI-1. The growth inhibition of EGI-1 cells (IC50: 27.89 nmol/L) was particularly strong for trametinib, but less significant and visible for KRAS wild-type murine cell lines SB1 (IC50: 41.50 nmol/L) and LD-1 (IC50: 56.1 nmol/L) (Fig. 2A-C). Further, treatment with 25 nmol/L trametinib inhibited EGI-1, SB1 and LD-1 cell proliferation after 48 hours (Fig. 2D-F). As observed in vitro, trametinib significantly inhibited in vivo tumor formation in SB1 and LD-1 patients, with mice treated with 1 mg/kg trametinib displaying smaller tumors at 15 days compared with controls (Fig. 2G-I). This demonstrated that trametinib also prevented iCCA tumor growth, even in KRAS wild-type cells.
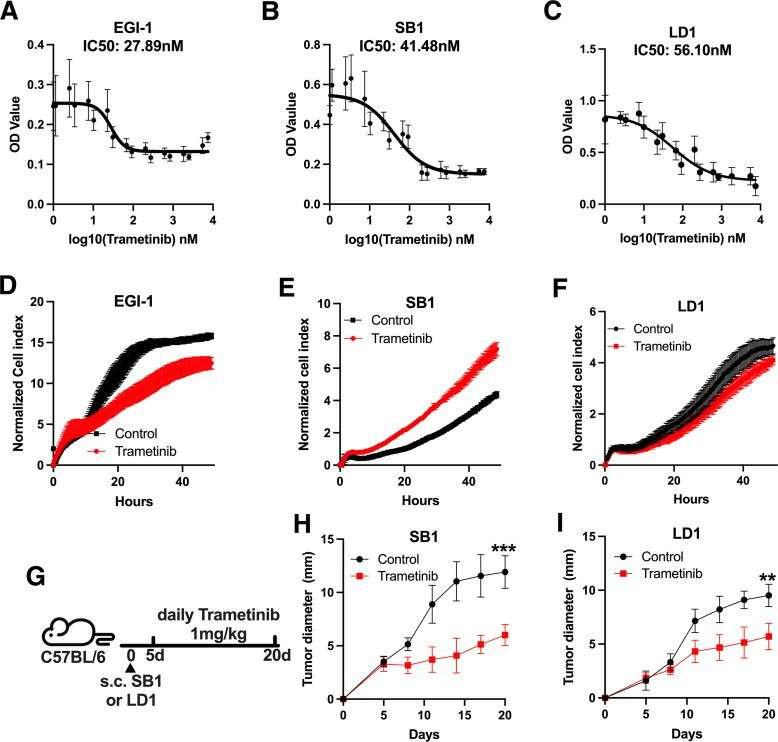 Fig. 2. Trametinib decreases tumor growth in vitro and in vivo (Wabitsch S, Tandon M, et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. Trametinib decreases tumor growth in vitro and in vivo (Wabitsch S, Tandon M, et al., 2021).
EMEM should be stored in a cool, dry place and protected from light. Proper storage conditions help maintain the stability of the medium and its components.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Reliable applications
I've used this cell product for gene expression studies. The cells showed the expected gene signatures, allowing me to analyze molecular pathways accurately.
8 Oct 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review