Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
CL-40
Cat.No.: CSC-C0543
Species: Human
Source: colon carcinoma
Morphology: adherent epithelial-like cells growing as monolayers and in aggregates
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vimentin -
Viruses: PCR:
The CL-40 cell line is derived from a primary colorectal cancer (CRC) tumor of a woman diagnosed with TNM stage 3. This classification indicates the presence of significant tumor growth with regional lymph node involvement, but no distant metastasis. The origin of the CL-40 cell line from the right colon suggests that it is representative of tumors that may have different biological behavior and molecular characteristics compared to left-sided colon cancers. Understanding the specific attributes of right-sided tumors is crucial as they can exhibit variations in prognosis and response to treatment.
The cells in the CL-40 line were characterized as well-differentiated, which implies that they retain some of the functional and morphological characteristics of normal colorectal epithelial cells. Well-differentiated tumors tend to resemble their tissue of origin more closely than poorly differentiated tumors, often leading to more favorable clinical outcomes. This differentiation status can influence the cell line's behavior in vitro, including growth patterns and responses to therapeutic agents.
In the laboratory, CL-40 has been utilized extensively for research into CRC biology, drug development, and the mechanisms underlying tumor progression and metastasis. Its establishment has provided a valuable tool for studying the biochemical and genetic alterations associated with colorectal carcinogenesis. The insights gained from research involving the CL-40 cell line contribute to a deeper understanding of tumorigenesis in the right colon, potentially guiding the development of targeted therapies tailored to this subtype of CRC.
Test the Susceptibility of Tumour Cell Lines to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Receptor ACE2 and surface proteinase TMPRSS2 have been shown to play a key role in SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry. To shed light on the infectivity and permissiveness of the appointed cell lines in the context of their ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression, cells were subjected to experimental infection with wild-type SARS-CoV-2. the majority of tested cell lines (15 of 29) showed no detectable virus replication despite the presence of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 (Fig. 1A). Further, 11 cell lines showed detectable SARS-CoV-2 infectious titers that did not exceed the amount of the inoculum. Only three cell lines were categorized as highly permissive, amplifying the initial virus inoculum by factors of 2 to 500 between 1 and 4 dpi. These were the colon carcinoma cell lines CL-14 and CL-40, as well as breast carcinoma cell line CAL-51. Infectious titers of SARS-CoV-2 grown on CL-14 and on CAL-51 were concurrent with the widely used CALU-3 (lung carcinoma), CACO-2 (colon carcinoma), VERO-E6 and VERO-B4 (normal African green monkey kidney cells) (Fig. 1B). Whereas CL-14 already has been described to be permissive in a preprint, the breast carcinoma cell line CAL-51 with high levels of NRP1 beside ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and the colon carcinoma cell line CL-40 have not been identified before. Despite comparable peak titers, virus replication kinetics differed largely between cell lines, where CAL-51 and CACO-2 showed an increase in titers throughout day three postinfection while VERO-E6, VERO-B4, and CL-14 produced the highest levels within 24 h, while the viral titer for CL-40 remained close to the level of the initial inoculum of SARS-CoV-2 (Fig. 1, Table 1).
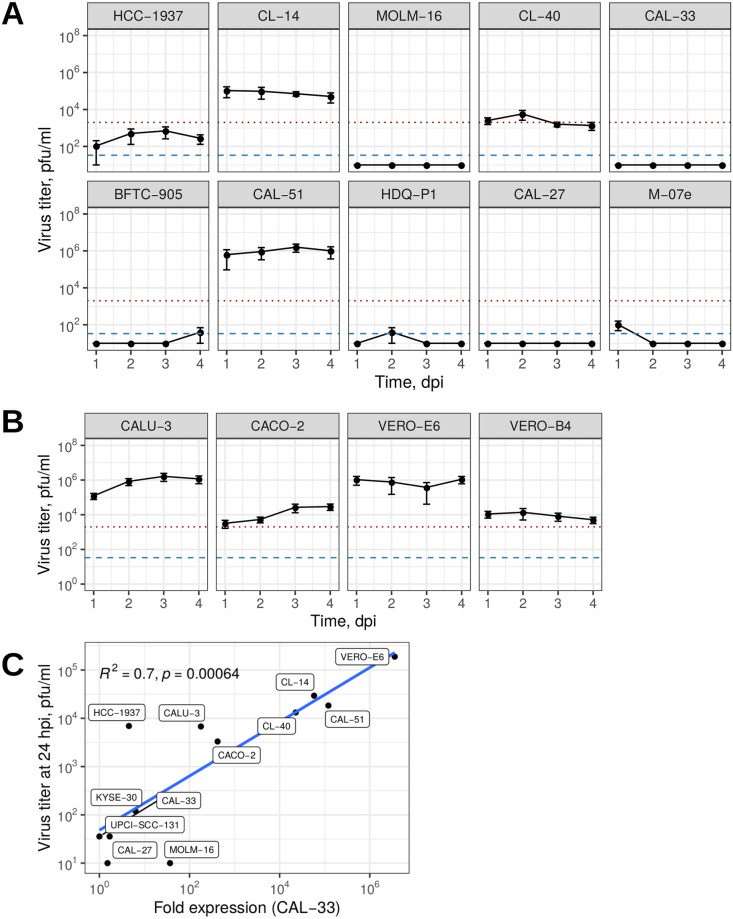 Fig. 1 Susceptibility of tumor cell lines toward SARS-CoV-2 infection. (Pommerenke C, et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Susceptibility of tumor cell lines toward SARS-CoV-2 infection. (Pommerenke C, et al., 2021)
Table 1. Permissive cell line characteristics. (Pommerenke C, et al., 2021)
| Cell line | Species | Sex | Tissue | Peak viral load, dpi | Maximal peak, pfu/ml | Doubling time |
| CL-14 | human | male | colon | 1 | 1.1×105 | ~1 w |
| CL-40 | human | female | colon | 2 | 5.8×105 | ~3-4 d |
| CAL-51 | human | female | breast | 3 | 1.6×106 | ~30 h |
| CALU-3 | human | male | lung | 3 | 1.6×106 | ~84 h |
| CACO-2 | human | male | colon | 4 | 3.0×105 | 80 h |
| VERO-B4 | monkey | female | kidney | 2 | 1.4×105 | ~25 h |
| VERO-E6 | monkey | female | kidney | 4 | 1.1×106 | 22 h |
Tumor cells usually metastasize to a specific destination without affecting other organs, also known as "organ affinity".
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Top-notch products
This product is perfect for my needs and the quality is top-notch!
08 Nov 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need